(Press-News.org) Early diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease requires reliable and cost-effective screening methods. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have now discovered that a type of sugar molecule in blood is associated with the level of tau, a protein that plays a critical role in the development of severe dementia. The study, which is published in Alzheimer's & Dementia, can pave the way for a simple screening procedure able to predict onset ten years in advance.
“The role of glycans, structures made up of sugar molecules, is a relatively unexplored field in dementia research,” says the study’s first author Robin Zhou, medical student and affiliated researcher at the Department of Neurobiology, Care Sciences and Society (NVS), Karolinska Institutet. “We demonstrate in our study that blood levels of glycans are altered early during the development of the disease. This could mean that we’ll be able to predict the risk of Alzheimer’s disease with only a blood test and a memory test.”
In Alzheimer’s disease, the neurons of the brain die, which is thought to be a result of the abnormal accumulation of the proteins amyloid beta and tau. Clinical trials for Alzheimer’s drugs show that treatment should commence early in the pathological process, before too many neurons have died, to reverse the process before it is too late.
More blood biomarkers needed
There is both a practical and a financial need for non-invasive screening methods for Alzheimer’s. Markers in blood are preferable, as taking samples of the cerebrospinal fluid is more difficult and brain imaging is expensive.
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have now shown that the level of a certain glycan structure in blood, denoted bisected N-acetylglucosamine, can be used to predict the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
The research group has previously demonstrated a link between tau protein and glycan levels in people with Alzheimer’s disease, but these analyses were done on cerebrospinal fluid. Glycans are sugar molecules found on the surface of proteins, the building blocks of life, and determine the location and function of these proteins in the body.
By measuring blood glycan levels the researchers found that individuals with matching levels of glycans and tau were over twice as likely to develop Alzheimer’s-type dementia.
“We also show that a simple statistical model that take into account blood glycan and tau levels, the risk gene APOE4 and a memory test, can be used to predict Alzheimer’s disease to a reliability of 80 per cent almost a decade before symptoms such as memory loss appear,” says corresponding author Sophia Schedin Weiss, docent at NVS, Karolinska Institutet.
17-year follow-up
The results are based on 233 participants of the Swedish National Study on Aging and Care in Kungsholmen (SNAC-K). The samples were collected between 2001 and 2004, and the participants were monitored regularly with respect to factors such as memory loss and the presence of dementia. The follow-ups were carried out every three to six years and continued for 17 years.
The researchers will now be analysing blood samples from the remaining participants of the SNAC-K study as well as from participants of other aging studies in and outside Sweden.
“We’re collaborating with researchers in primary care in Sweden to evaluate different biomarkers for dementia at primary health care centres,” says Dr Schedin Weiss. “We hope that glycans in the blood will prove to be a valuable complement to current methods of screening people for Alzheimer’s disease that will enable the disease to be detected early.”
The study was conducted by researchers in Lars Tjernberg’s research group at the Division of Neurogeriatrics at Karolinska Institutet in collaboration with the Aging Research Centre at Karolinska Institutet, the Stockholm Gerontology Research Center and Karolinska University Hospital.
It was financed by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, Stiftelsen Gamla Tjänarinnor, the Gun and Bertil Stohnes Foundation, the Swedish Alzheimer’s Foundation, Stiftelsen Dementia, JPND, Vinnova and Region Stockholm (ALF). The researchers report no conflicts of interest.
Publication: “A glycan epitope correlates with tau in serum and predicts progression to Alzheimer’s disease in combination with APOE4 allele status”. Robin Ziyue Zhou, Davide Liborio Vetrano, Giulia Grande, Frida Duell, Linus Jönsson, Erika J Laukka, Claudia Fredolini, Bengt Winblad, Lars Tjernberg, Sophia Schedin-Weiss. Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, online 12 April 2023.
END
Sugar molecule in blood can predict Alzheimer’s disease
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Starting small and simple - key to success for evolution of mammals
2023-04-12
The ancestors of modern mammals managed to evolve into one of the most successful animal lineages – the key was to start out small and simple, a new study reveals.
In many vertebrate groups, such as fishes and reptiles, the skull and lower jaw of animals with a backbone are composed of numerous bones. This was also the case in the earliest ancestors of modern mammals over 300 million years ago.
However, during evolution the number of skull bones was successively reduced in early mammals around 150 to 100 million years ago.
Publishing their findings today ...
New “AI scientist” combines theory and data to discover scientific equations
2023-04-12
In 1918, the American chemist Irving Langmuir published a paper examining the behavior of gas molecules sticking to a solid surface. Guided by the results of careful experiments, as well as his theory that solids offer discrete sites for the gas molecules to fill, he worked out a series of equations that describe how much gas will stick, given the pressure.
Now, about a hundred years later, an “AI scientist” developed by researchers at IBM Research, Samsung AI, and the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) has reproduced a key part of Langmuir’s Nobel Prize-winning work. The system—artificial intelligence ...
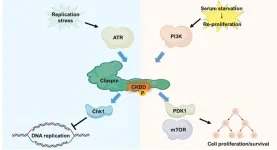
When cells sense the cue for growth
2023-04-12
Researchers of the Genome Dynamics Project team at Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science ·revealed new mechanism controlling cellular proliferation in response to serum, which triggers growth of resting cells.
One of the key pathways for cellular growth is the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) –mTOR (mechanistic/mammalian target of rapamycin) pathway. mTOR regulates the cellular response to nutrient availability. Dysregulation of the mTOR signaling pathway is intimately involved in many human diseases, especially the multitude of different human cancers. This ...
Most plastic eaten by city vultures comes straight from food outlets
2023-04-12
Since the 1950s, humanity has produced an estimated 8.3bn tons of plastic, adding a further 380m tons to this amount each year. Only 9% of this gets recycled. The inevitable result is that plastic is everywhere, from the depths of the oceans to the summit of Everest – and notoriously, inside the tissues of humans and other organisms.
The long-term effects of ingested plastic on people aren’t yet known. But in rodents, ingested microplastics can impair the function of the liver, intestines, and exocrine and reproductive organs.
Especially ...
To more effectively sequester biomass and carbon, just add salt
2023-04-12
Reducing global greenhouse gas emissions is critical to avoiding a climate disaster, but current carbon removal methods are proving to be inadequate and costly. Now researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, have proposed a scalable solution that uses simple, inexpensive technologies to remove carbon from our atmosphere and safely store it for thousands of years.
As reported today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers propose growing biomass crops to capture carbon from the air, then burying the harvested vegetation in engineered dry biolandfills. This ...
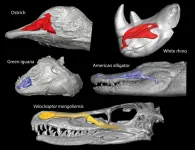
How to cool your brain? These warm-blooded animals use their nose
2023-04-12
A research team led by Seishiro Tada and Takanobu Tsuihiji of the University of Tokyo shows that the living warm-blooded descendants of theropod dinosaurs evolved a better nasal cooling system aided by larger nasal cavities than cold-blooded animals. The study provides clues to the evolution of nasal cooling in warm-blooded animals from their theropod dinosaur ancestors.
Endotherms, or warm-blooded animals, maintain their high body temperature through internal heat sources. Birds, humans, and other mammals are endotherms. But ectotherms, or cold-blooded animals such as reptiles, use external heat sources to keep ...
It’s all in the wrist: energy-efficient robot hand learns how not to drop the ball
2023-04-12
Researchers have designed a low-cost, energy-efficient robotic hand that can grasp a range of objects – and not drop them – using just the movement of its wrist and the feeling in its ‘skin’.
Grasping objects of different sizes, shapes and textures is a problem that is easy for a human, but challenging for a robot. Researchers from the University of Cambridge designed a soft, 3D printed robotic hand that cannot independently move its fingers but can still carry out a range of complex movements.
The robot hand was trained to ...
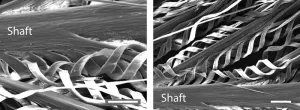
How an African bird might inspire a better water bottle
2023-04-12
An extreme closeup of feathers from a bird with an uncanny ability to hold water while it flies could inspire the next generation of absorbent materials.
With high resolution microscopes and 3D technology, researchers at Johns Hopkins University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology captured an unprecedented view of feathers from the desert-dwelling sandgrouse, showcasing the singular architecture of their feathers and revealing for the first time how they can hold so much water.
“It’s super fascinating to see how nature managed to create structures so perfectly efficient to take ...
Time-restricted fasting could cause fertility problems
2023-04-12
Time-restricted fasting diets could cause fertility problems according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today shows that time-restricted fasting affects reproduction differently in male and female zebrafish.
Importantly, some of the negative effects on eggs and sperm quality can be seen after the fish returned to their normal levels of food consumption.
The research team say that while the study was conducted in fish, their findings highlight the importance of considering not just the effect of fasting on weight and health, but also on fertility.
Prof Alexei Maklakov, from UEA’s School of Biological Sciences, said: “Time-restricted ...
Scientists uncover the amazing way sandgrouse hold water in their feathers
2023-04-12
Many birds’ feathers are remarkably efficient at shedding water — so much so that “like water off a duck’s back” is a common expression. Much more unusual are the belly feathers of the sandgrouse, especially Namaqua sandgrouse, which absorb and retain water so efficiently the male birds can fly more than 20 kilometers from a distant watering hole back to the nest and still retain enough water in their feathers for the chicks to drink and sustain themselves in the searing deserts ...