(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial, postoperative follow-up for patients undergoing breast reconstruction and gynecologic oncology surgery using smartphone app–assisted monitoring led to improved quality of recovery and equal satisfaction with care compared with conventional in-person follow-up.
Authors: Claire Temple-Oberle, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.0616)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamasurgery/fullarticle/10.1001/jamasurg.2023.0616?guestAccessKey=4771574c-5fff-4630-a084-f94730de04cb&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=041223
END
Effect of smartphone app home monitoring after oncologic surgery on quality of recovery
JAMA Surgery
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Taking a placebo improves adherence to treatment for opioid use disorder, study finds
2023-04-12
Substance use disorder affects 20 million Americans, and more than 100,000 people died from a drug overdose in 2021, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. While the medication methadone has the strongest evidence-based effectiveness to prevent relapse, about half of patients drop out of their treatment within one year of initiation. The solution could lie in taking a simple “sugar pill” or placebo along with the methadone, according to a randomized clinical trial led by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
In a randomized ...
New study flips the script on liver cancer
2023-04-12
Liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death and the sixth most common cancer type worldwide. Major risk factors include environmental and metabolic stressors, such as obesity, viral hepatitis and steatohepatitis (fatty and inflamed liver).
These stressors damage the liver by killing hepatocytes, the major cell type in the liver. The cell death then triggers an inflammatory response which signals the liver to generate a new batch of hepatocytes. But this sudden push towards cellular proliferation also increases the risk of tumor formation.
In ...
SWOG S2302 Pragmatica-Lung study opens to enrollment, a model for easier, more representative clinical trials
2023-04-12
A clinical trial that breaks new ground with its dramatically streamlined design and unusually broad eligibility criteria is now opening and available to patients with stage 4 or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer at cancer treatment clinics all across the United States.
The S2302 Pragmatica-Lung trial, developed and led by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), is designed to be easier for institutions to open and run and with few limits on eligibility, making it available to a larger group of patients with advanced non-small cell lung ...
Researchers reveal stability origin of Dion-Jacobson 2D perovskites
2023-04-12
Yin-Yang theory is an ancient Chinese philosophy in which Yin-Yang forces are interdependent and work in opposition to each other to create balance.
Recently, inspired by this ancient theory, a research team led by Prof. GUO Xin and Prof. LI Can from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has revealed the origin of the stability of Dion–Jacobson (DJ) phase two-dimensional (2D) perovskite materials.
Their findings were published in Joule on April 12.
DJ 2D perovskites, a class of organic–inorganic ...
Scientists track evolution of microbes on the skin’s surface
2023-04-12
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Human skin is home to millions of microbes. One of these microbes, Staphylococcus aureus, is an opportunistic pathogen that can invade patches of skin affected by eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis.
In a new study, researchers at MIT and other institutions have discovered that this microbe can rapidly evolve within a single person’s microbiome. They found that in people with eczema, S. aureus tends to evolve to a variant with a mutation in a specific gene that helps it grow faster on the skin.
This study marks ...
NCCN Annual Conference brings up important questions for improving cancer care
2023-04-12
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 12, 2023] — The NCCN 2023 Annual Conference took place in-person in Orlando and virtually, with a particular focus on human connection. That connection was underscored with more than 2,000 registrants from across the continuum of cancer care, including approximately 1,000 who returned in-person for the first time since 2019. Educational sessions highlighted the importance of ensuring care meets the latest standards while also rejecting a one-size-fits-all approach.
“At NCCN, we don’t shy away from difficult discussions; we want our conference attendees to take away the message that ...
Insilico Medicine successfully discovered potent, selective, and orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of CDK8 using generative AI
2023-04-12
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, today announced that it has successfully discovered a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of CDK8 for the treatment of cancer using a structure-based generative chemistry approach enabled by the Chemistry42 multi-modal generative reinforcement learning platform. The research was published in the American Chemical Society’s Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, a leading journal in medicinal chemistry.
As members of the CDK family, CDK8 and its paralog protein CDK19 play critical roles in regulating transcription of ...
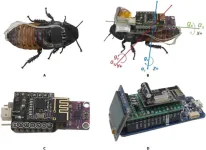
Movement optimization for a cyborg cockroach in a bounded space incorporating machine learning
2023-04-12
Have you ever wondered why some insects like cockroaches prefer to stay or decrease movement in darkness? Some may tell you it’s called photophobia, a habit deeply coded in their genes. A further question would be whether we can correct this habit of cockroaches, that is, moving in the darkness just as they move in bright backgrounds. Scientists from Osaka University may have answered this question with a positive answer. They solved this question by converting a cockroach into a cyborg. They published this research in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems. ...
SwRI joins new NASA institute to qualify, certify additive manufacturing methods
2023-04-12
SAN ANTONIO — April 12, 2023—Southwest Research Institute will contribute to a new NASA institute to improve understanding and enable rapid certification of metal parts created using advanced additive manufacturing (AM) techniques. The Institute for Model-based Qualification & Certification of Additive Manufacturing (IMQCAM) will work to improve computer models of additively manufactured metal parts and expand their utility in spaceflight applications.
Additive manufacturing uses 3D printing or rapid prototyping to build ...
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center experts to present noteworthy research at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) 2023 Annual Meeting
2023-04-12
Physicians and scientists from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) will join oncology experts and members of the global cancer research community to present the latest advances in cancer during the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting on April 14-19 in Orlando, Florida.
MSK experts will present significant research and will be available to comment on topics including cancer disparities, analytical tools for precision medicine, genomic biomarkers, tumor biology, immunology and more.
Deb Schrag, MD, MPH, will offer insights ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
[Press-News.org] Effect of smartphone app home monitoring after oncologic surgery on quality of recoveryJAMA Surgery