(Press-News.org) As the number of children in need of access to timely evaluation and intervention for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) continues to rise, new research is showing how barriers to diagnoses and treatment can be reduced through an innovative training program first developed at the University of Missouri.
ASD can be identified and diagnosed in young children by a well-trained clinician, and early diagnosis is vital to quickly establishing access to evidence-based therapies and interventions. However, long specialty center waitlists, distance, and cost often hinder early diagnosis.
The Extension for Community Healthcare Outcomes (ECHO) Autism STAT model shows promise at eliminating these barriers. The program leverages the existing Project ECHO model to build the capacity of primary care physicians and clinicians to evaluate and diagnose children in local communities. The University of Missouri’s ECHO program uses video-conferencing technology to create learning communities that promote best practices among primary care clinicians through case-based learning and guided practice. The ECHO Autism STAT model builds on the existing ECHO Autism framework by adding more intensive training elements specifically focused on the diagnostic assessment of young children.
“By adding to and using the skills of community-based primary care doctors and advanced practice providers, there exists the potential to drastically increase critical access to diagnostic assessment for ASD among children in underserved areas,” said lead researcher Kristin Sohl, MD, professor, Department of Child Health at the University of Missouri School of Medicine and the founder of ECHO Autism. “This accelerates the process for these children to receive the essential therapies and services, while allowing autism specialty centers to focus on care for those with more complex diagnostic needs.”
Through an evaluation of participants in the program, the researchers found that the ECHO Autism STAT primary care physician diagnoses were congruent with gold-standard evaluations completed at autism specialty centers. Likert scale surveys showed families were overwhelmingly pleased with their experiences and preferred to undergo diagnostic assessments in their local communities with local doctors.
“These results support the ECHO Autism STAT model as an effective means to advance the skills of community doctors and strengthen their confidence to diagnose young children with obvious signs of autism,” said Alexandra James, MD, assistant professor of clinical child health University of Missouri School of Medicine. “Training and supporting primary care clinicians to diagnose ASD builds capacity and expertise in underserved areas, such as rural communities, which in turn decreases wait times at specialty centers and speeds access to care.”
The University of Missouri researchers recently published “ECHO (Extension for Community Healthcare Outcomes) Autism STAT: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study of Community-Based Primary Care Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder” in the Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics.
END
Innovative healthcare extension project enables community-based physicians to diagnose autism in young children
Earlier diagnoses speeds connection to evidence-based therapies for children in underserved communities
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson Research Highlights: AACR 2023 Special Edition
2023-04-12
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
This special edition features presentations by MD Anderson researchers at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023. In addition to these studies, forthcoming press releases will feature groundbreaking research on perioperative immunotherapy for operable lung cancer (Abstract CT005), ...
Scientists sequence genome of little skate, the stingray’s cousin
2023-04-12
Rutgers geneticists, working with an international team of scientists, have conducted the most comprehensive sequencing yet of the complete DNA sequence of the little skate – which, like its better-known cousin, the stingray, has long been viewed as enigmatic because of its shape.
The scientists, writing in Nature, reported that by studying the intricacies of Leucoraja erinacea’s genome, they have gained a far better understanding of how the fish evolved from its ancestor – which possessed a much narrower body – over a period of 300 million years to become a flat, winged bottom-dweller.
“We ...
The brain’s support cells may play a key role in OCD
2023-04-12
A type of cell usually characterized as the brain’s support system appears to play an important role in obsessive-compulsive disorder-related behaviors, according to new UCLA Health research published April 12 in Nature.
The new clue about the brain mechanisms behind OCD, a disorder that is incompletely understood, came as a surprise to researchers. They originally sought to study how neurons interact with star-shaped “helper” cells known as astrocytes, which are known to provide support and protection to neurons.
However, ...
Pragmatica-Lung Study, a streamlined model for future cancer clinical trials, begins enrolling patients
2023-04-12
The National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has helped launch a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (NCT05633602) of a two-drug combination to treat patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Called the Pragmatica-Lung Study (or S2302), this is one of the first NCI-supported clinical trials to use a trial design that removes many of the barriers that prevent people from joining clinical trials. This “pragmatic” approach aims to increase accessibility ...
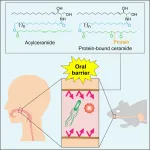
Oral barrier is similar in ceramide composition to skin barrier
2023-04-12
Acylceramides and protein-bound ceramides are vital for the formation of the oral barrier in mice, similar to their role in skin, protecting from infection.
The skin is the body’s first line of defense against the environment, particularly against pathogens, chemicals, and allergens. It is now known that a class of biological molecules called acylceramides and their metabolites, protein-bound ceramides, are essential to the formation of this barrier. The outermost tissues of the mouth are closely related to the skin and have similar functions—an oral barrier. However, little ...
How did Earth get its water?
2023-04-12
Washington, DC—Our planet’s water could have originated from interactions between the hydrogen-rich atmospheres and magma oceans of the planetary embryos that comprised Earth’s formative years, according to new work from Carnegie Science’s Anat Shahar and UCLA’s Edward Young and Hilke Schlichting. Their findings, which could explain the origins of Earth’s signature features, are published in Nature.
For decades, what researchers knew about planet formation was based ...
Effect of smartphone app home monitoring after oncologic surgery on quality of recovery
2023-04-12
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial, postoperative follow-up for patients undergoing breast reconstruction and gynecologic oncology surgery using smartphone app–assisted monitoring led to improved quality of recovery and equal satisfaction with care compared with conventional in-person follow-up.
Authors: Claire Temple-Oberle, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.0616)
Editor’s ...
Taking a placebo improves adherence to treatment for opioid use disorder, study finds
2023-04-12
Substance use disorder affects 20 million Americans, and more than 100,000 people died from a drug overdose in 2021, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. While the medication methadone has the strongest evidence-based effectiveness to prevent relapse, about half of patients drop out of their treatment within one year of initiation. The solution could lie in taking a simple “sugar pill” or placebo along with the methadone, according to a randomized clinical trial led by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
In a randomized ...
New study flips the script on liver cancer
2023-04-12
Liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death and the sixth most common cancer type worldwide. Major risk factors include environmental and metabolic stressors, such as obesity, viral hepatitis and steatohepatitis (fatty and inflamed liver).
These stressors damage the liver by killing hepatocytes, the major cell type in the liver. The cell death then triggers an inflammatory response which signals the liver to generate a new batch of hepatocytes. But this sudden push towards cellular proliferation also increases the risk of tumor formation.
In ...
SWOG S2302 Pragmatica-Lung study opens to enrollment, a model for easier, more representative clinical trials
2023-04-12
A clinical trial that breaks new ground with its dramatically streamlined design and unusually broad eligibility criteria is now opening and available to patients with stage 4 or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer at cancer treatment clinics all across the United States.
The S2302 Pragmatica-Lung trial, developed and led by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), is designed to be easier for institutions to open and run and with few limits on eligibility, making it available to a larger group of patients with advanced non-small cell lung ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
[Press-News.org] Innovative healthcare extension project enables community-based physicians to diagnose autism in young childrenEarlier diagnoses speeds connection to evidence-based therapies for children in underserved communities