(Press-News.org) Washington, DC—Our planet’s water could have originated from interactions between the hydrogen-rich atmospheres and magma oceans of the planetary embryos that comprised Earth’s formative years, according to new work from Carnegie Science’s Anat Shahar and UCLA’s Edward Young and Hilke Schlichting. Their findings, which could explain the origins of Earth’s signature features, are published in Nature.
For decades, what researchers knew about planet formation was based primarily on our own Solar System. Although there are some active debates about the formation of gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn, it is widely agreed upon that Earth and the other rocky planets accreted from the disk of dust and gas that surrounded our Sun in its youth.
As increasingly larger objects crashed into each other, the baby planetesimals that eventually formed Earth grew both larger and hotter, melting into a vast magma ocean due to the heat of collisions and radioactive elements. Over time, as the planet cooled, the densest material sank inward, separating Earth into three distinct layers—the metallic core, and the rocky, silicate mantle and crust.
However, the explosion of exoplanet research over the past decade informed a new approach to modeling the Earth’s embryonic state.
“Exoplanet discoveries have given us a much greater appreciation of how common it is for just-formed planets to be surrounded by atmospheres that are rich in molecular hydrogen, H2, during their first several million years of growth,” Shahar explained. “Eventually these hydrogen envelopes dissipate, but they leave their fingerprints on the young planet’s composition.”
Using this information, the researchers developed new models for Earth’s formation and evolution to see if our home planet’s distinct chemical traits could be replicated.
Using a newly developed model, the Carnegie and UCLA researchers were able to demonstrate that early in Earth’s existence, interactions between the magma ocean and a molecular hydrogen proto-atmosphere could have given rise to some of Earth’s signature features, such as its abundance of water and its overall oxidized state.
The researchers used mathematical modeling to explore the exchange of materials between molecular hydrogen atmospheres and magma oceans by looking at 25 different compounds and 18 different types of reactions—complex enough to yield valuable data about Earth’s possible formative history, but simple enough to interpret fully.
Interactions between the magma ocean and the atmosphere in their simulated baby Earth resulted in the movement of large masses of hydrogen into the metallic core, the oxidation of the mantle, and the production of large quantities of water.
Even if all of the rocky material that collided to form the growing planet was completely dry, these interactions between the molecular hydrogen atmosphere and the magma ocean would generate copious amounts of water, the researchers revealed. Other water sources are possible, they say, but not necessary to explain Earth’s current state.
“This is just one possible explanation for our planet’s evolution, but one that would establish an important link between Earth’s formation history and the most common exoplanets that have been discovered orbiting distant stars, which are called Super-Earths and sub-Neptunes,” Shahar concluded.
This project was part of the interdisciplinary, multi-institution AEThER project, initiated and led by Shahar, which seeks to reveal the chemical makeup of the Milky Way galaxy’s most common planets—Super-Earths and sub-Neptunes—and to develop a framework for detecting signatures of life on distant worlds. Funded by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, this effort was developed to understand how the formation and evolution of these planets shape their atmospheres. This could—in turn—enable scientists to differentiate true biosignatures, which could only be produced by the presence of life, from atmospheric molecules of non-biological origin.
“Increasingly powerful telescopes are enabling astronomers to understand the compositions of exoplanet atmospheres in never-before-seen detail,” Shahar said. “AEThER’s work will inform their observations with experimental and modeling data that, we hope, will lead to a foolproof method for detecting signs of life on other worlds.”
__________________
This work is funded, in part, by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.
The Carnegie Institution for Science (carnegiescience.edu) is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with three research divisions on both coasts. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in the life and environmental sciences, Earth and planetary science, and astronomy and astrophysics.
END
How did Earth get its water?
Exoplanet discoveries inform new model that could explain the origin of some of Earth’s signature features, such as its abundance of water
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Effect of smartphone app home monitoring after oncologic surgery on quality of recovery
2023-04-12
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial, postoperative follow-up for patients undergoing breast reconstruction and gynecologic oncology surgery using smartphone app–assisted monitoring led to improved quality of recovery and equal satisfaction with care compared with conventional in-person follow-up.
Authors: Claire Temple-Oberle, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.0616)
Editor’s ...
Taking a placebo improves adherence to treatment for opioid use disorder, study finds
2023-04-12
Substance use disorder affects 20 million Americans, and more than 100,000 people died from a drug overdose in 2021, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. While the medication methadone has the strongest evidence-based effectiveness to prevent relapse, about half of patients drop out of their treatment within one year of initiation. The solution could lie in taking a simple “sugar pill” or placebo along with the methadone, according to a randomized clinical trial led by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
In a randomized ...
New study flips the script on liver cancer
2023-04-12
Liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death and the sixth most common cancer type worldwide. Major risk factors include environmental and metabolic stressors, such as obesity, viral hepatitis and steatohepatitis (fatty and inflamed liver).
These stressors damage the liver by killing hepatocytes, the major cell type in the liver. The cell death then triggers an inflammatory response which signals the liver to generate a new batch of hepatocytes. But this sudden push towards cellular proliferation also increases the risk of tumor formation.
In ...
SWOG S2302 Pragmatica-Lung study opens to enrollment, a model for easier, more representative clinical trials
2023-04-12
A clinical trial that breaks new ground with its dramatically streamlined design and unusually broad eligibility criteria is now opening and available to patients with stage 4 or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer at cancer treatment clinics all across the United States.
The S2302 Pragmatica-Lung trial, developed and led by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), is designed to be easier for institutions to open and run and with few limits on eligibility, making it available to a larger group of patients with advanced non-small cell lung ...
Researchers reveal stability origin of Dion-Jacobson 2D perovskites
2023-04-12
Yin-Yang theory is an ancient Chinese philosophy in which Yin-Yang forces are interdependent and work in opposition to each other to create balance.
Recently, inspired by this ancient theory, a research team led by Prof. GUO Xin and Prof. LI Can from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has revealed the origin of the stability of Dion–Jacobson (DJ) phase two-dimensional (2D) perovskite materials.
Their findings were published in Joule on April 12.
DJ 2D perovskites, a class of organic–inorganic ...
Scientists track evolution of microbes on the skin’s surface
2023-04-12
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Human skin is home to millions of microbes. One of these microbes, Staphylococcus aureus, is an opportunistic pathogen that can invade patches of skin affected by eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis.
In a new study, researchers at MIT and other institutions have discovered that this microbe can rapidly evolve within a single person’s microbiome. They found that in people with eczema, S. aureus tends to evolve to a variant with a mutation in a specific gene that helps it grow faster on the skin.
This study marks ...
NCCN Annual Conference brings up important questions for improving cancer care
2023-04-12
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 12, 2023] — The NCCN 2023 Annual Conference took place in-person in Orlando and virtually, with a particular focus on human connection. That connection was underscored with more than 2,000 registrants from across the continuum of cancer care, including approximately 1,000 who returned in-person for the first time since 2019. Educational sessions highlighted the importance of ensuring care meets the latest standards while also rejecting a one-size-fits-all approach.
“At NCCN, we don’t shy away from difficult discussions; we want our conference attendees to take away the message that ...
Insilico Medicine successfully discovered potent, selective, and orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of CDK8 using generative AI
2023-04-12
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, today announced that it has successfully discovered a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of CDK8 for the treatment of cancer using a structure-based generative chemistry approach enabled by the Chemistry42 multi-modal generative reinforcement learning platform. The research was published in the American Chemical Society’s Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, a leading journal in medicinal chemistry.
As members of the CDK family, CDK8 and its paralog protein CDK19 play critical roles in regulating transcription of ...
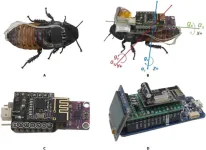
Movement optimization for a cyborg cockroach in a bounded space incorporating machine learning
2023-04-12
Have you ever wondered why some insects like cockroaches prefer to stay or decrease movement in darkness? Some may tell you it’s called photophobia, a habit deeply coded in their genes. A further question would be whether we can correct this habit of cockroaches, that is, moving in the darkness just as they move in bright backgrounds. Scientists from Osaka University may have answered this question with a positive answer. They solved this question by converting a cockroach into a cyborg. They published this research in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems. ...
SwRI joins new NASA institute to qualify, certify additive manufacturing methods
2023-04-12
SAN ANTONIO — April 12, 2023—Southwest Research Institute will contribute to a new NASA institute to improve understanding and enable rapid certification of metal parts created using advanced additive manufacturing (AM) techniques. The Institute for Model-based Qualification & Certification of Additive Manufacturing (IMQCAM) will work to improve computer models of additively manufactured metal parts and expand their utility in spaceflight applications.
Additive manufacturing uses 3D printing or rapid prototyping to build ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] How did Earth get its water?Exoplanet discoveries inform new model that could explain the origin of some of Earth’s signature features, such as its abundance of water