(Press-News.org) Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283465
Article Title: Impact assessment of immunization and the COVID-19 pandemic on varicella across Europe using digital epidemiology methods: A descriptive study
Author Countries: Sweden, Lithuania, Ireland, USA, Spain
Funding: Funding for this research was provided by Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (MSD). We confirm that the funder provided support in the form of salaries for Ugne Sabale, Ligita Jarmale, Janice Murtagh, Manjiri Pawaskar, and Goran Bencina, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
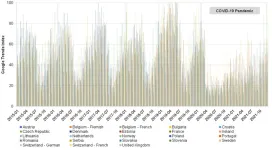
Google Trends reveal how the spread of chickenpox may have been suppressed during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
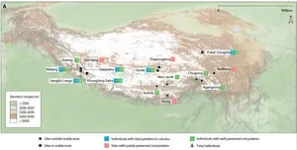
Got milk? The ancient Tibetans did, according to study
2023-04-12
New research into ancient populations that resided on the Tibetan Plateau has found that dairy pastoralism was being practiced far earlier than previously thought and may have been key to long-term settlement of the region’s extreme environment.
Professor Michael Petraglia, Director of Griffith’s Australian Research Centre for Human Evolution, was part of the international research team that set out to understand how prehistoric populations adapted to the vast, agriculturally poor highlands of the Tibetan Plateau.
The research, ...
From tragedy, a new potential cancer treatment
2023-04-12
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a lethal pediatric brain cancer that often kills within a year of diagnosis. Surgery is almost impossible because of the tumors’ location. Chemotherapy has debilitating side effects. New treatment options are desperately needed.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Adrian Krainer is best known for his groundbreaking research on antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)—molecules that can control protein levels in cells. His efforts led to Spinraza®, ...
Dairy foods helped ancient Tibetans thrive in one of Earth’s most inhospitable environments
2023-04-12
The Tibetan Plateau, known as the “third pole”, or “roof of the world”, is one of the most inhospitable environments on Earth. While positive natural selection at several genomic loci enabled early Tibetans to better adapt to high elevations, obtaining sufficient food from the resource-poor highlands would have remained a challenge.
Now, a new study in the journal Science Advances reveals that dairy was a key component of early human diets on the Tibetan Plateau. The study reports ancient ...
Multifunctional patch offers early detection of plant diseases, other crop threats
2023-04-12
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed an electronic patch that can be applied to the leaves of plants to monitor crops for different pathogens – such as viral and fungal infections – and stresses such as drought or salinity. In testing, the researchers found the patch was able to detect a viral infection in tomatoes more than a week before growers would be able to detect any visible symptoms of disease.
“This is important because the earlier growers can identify plant diseases or fungal infections, the ...
Predictive power of climate models may be masked by volcanoes
2023-04-12
Simulated volcanic eruptions may be blowing up our ability to predict near-term climate, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
The research, led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), finds that the way volcanic eruptions are represented in climate models may be masking the models’ ability to accurately predict variations in sea surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific that unfold over multiple years to a decade.
These decadal variations in sea surface ...
Industry veteran Pablo Velez, RN, Ph.D., named CEO of El Centro Regional Medical Center
2023-04-12
In coordination with the El Centro Regional Medical Center (ECRMC) Board of Trustees, UC San Diego Health today announced that Pablo Velez, RN, PhD, has been appointed by UC San Diego Health as ECRMC’s chief executive officer effective April 17. Reporting to UC San Diego Health CEO Patty Maysent, Velez will oversee day-to-day operational, clinical and financial management of ECRMC, leading UC San Diego Health’s overall efforts to support the strategic and operational plan that was announced ...
Genes are read faster and more sloppily in old age
2023-04-12
In a large joint project, a total of six research groups from the University of Cologne Cluster of Excellence on Cellular Stress Responses in Age-Associated Diseases (CECAD), the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Aging (MPI) in Cologne and the University of Göttingen have demonstrated the following findings which apply across the animal kingdom: with increasing age, the transcriptional elongation speed of genes increases, whereby the quality of the gene products suffers. With dietary restrictions, ...
Rates of food insecurity in US may be significantly higher than surveys suggest
2023-04-12
Key Points
Many federal and local government agencies send out a United States Department of Agriculture survey once a year or less to determine whether households experienced food insecurity in the last 12 months.
In a new study, USC researchers found that households are more likely to accurately report food insecurity when surveyed more often and asked about their recent experiences. They also found that the USDA measure may be underreporting the true rate by as much as one-third.
Without ...
Humans need Earth-like ecosystem for deep-space living
2023-04-12
ITHACA, N.Y. – Can humans endure long-term living in deep space? The answer is a lukewarm maybe, according to a new theory describing the complexity of maintaining gravity and oxygen, obtaining water, developing agriculture and handling waste far from Earth.
Dubbed the Pancosmorio theory – a word coined to mean “all world limit” – it was described in a paper published in Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences.
“For humans to sustain themselves and all of their technology, infrastructure and society in space, they need a ...
Nobel Prize-winning immuno-oncology expert receives Block Memorial Lectureship
2023-04-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – James P. Allison, PhD, is the recipient of the 25th Herbert and Maxine Block Memorial Lectureship Award for Distinguished Achievement in Cancer. A 2018 Nobel Prize co-recipient in physiology/medicine, Allison serves as the chair of immunology and executive director of the Immunotherapy Platform at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
He is a renowned immunologist whose research led to the discovery of the immune system’s T-cell receptor structure and later a molecule ...