(Press-News.org) Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed an electronic patch that can be applied to the leaves of plants to monitor crops for different pathogens – such as viral and fungal infections – and stresses such as drought or salinity. In testing, the researchers found the patch was able to detect a viral infection in tomatoes more than a week before growers would be able to detect any visible symptoms of disease.
“This is important because the earlier growers can identify plant diseases or fungal infections, the better able they will be to limit the spread of the disease and preserve their crop,” says Qingshan Wei, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State.
“In addition, the more quickly growers can identify abiotic stresses, such as irrigation water contaminated by saltwater intrusion, the better able they will be to address relevant challenges and improve crop yield.”
The technology builds on a previous prototype patch, which detected plant disease by monitoring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by plants. Plants emit different combinations of VOCs under different circumstances. By targeting VOCs that are relevant to specific diseases or plant stress, the sensors can alert users to specific problems.
“The new patches incorporate additional sensors, allowing them to monitor temperature, environmental humidity, and the amount of moisture being ‘exhaled’ by the plants via their leaves,” says Yong Zhu, co-corresponding author of the paper and Andrew A. Adams Distinguished Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at NC State.
The patches themselves are small – only 30 millimeters long – and consist of a flexible material containing sensors and silver nanowire-based electrodes. The patches are placed on the underside of leaves, which have a higher density of stomata – the pores that allow the plant to “breathe” by exchanging gases with the environment.
The researchers tested the new patches on tomato plants in greenhouses, and experimented with patches that incorporated different combinations of sensors. The tomato plants were infected with three different pathogens: tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV); early blight, which is a fungal infection; and late blight, which is a type of pathogen called an oomycete. The plants were also exposed to a variety of abiotic stresses, such as overwatering, drought conditions, lack of light, and high salt concentrations in the water.
The researchers took data from these experiments and plugged them into an artificial intelligence program to determine which combinations of sensors worked most effectively to identify both disease and abiotic stress.
“Our results for detecting all of these challenges were promising across the board,” Wei says. “For example, we found that using a combination of three sensors on a patch, we were able to detect TSWV four days after the plants were first infected. This is a significant advantage, since tomatoes don’t normally begin to show any physical symptoms of TSWV for 10-14 days.”
The researchers say they are two steps away from having a patch that growers can use. First, they need to make the patches wireless – a relatively simple challenge. Second, they need to test the patches in the field, outside of greenhouses, to ensure the patches will work under real-world conditions.
“We’re currently looking for industry and agriculture partners to help us move forward with developing and testing this technology,” Zhu says. “This could be a significant advance to help growers prevent small problems from becoming big ones, and help us address food security challenges in a meaningful way.”
The paper, “Abaxial leaf surface-mounted multimodal wearable sensor for continuous plant physiology monitoring,” will be published April 12 in the open-access journal Science Advances. First author of the paper is Giwon Lee, a former postdoctoral researcher at NC State, now on faculty at Kwangwoon University in South Korea. The paper was co-authored by Tatsiana Shymanovich, a postdoctoral researcher at NC State; Oindrila Hossain, Sina Jamalzadegan, Yuxuan Liu and Hongyu Wang, who are Ph.D. students at NC State; Amanda Saville, a research technician at NC State; Rajesh Paul, a former Ph.D. student at NC State; Dorith Rotenberg and Anna Whitfield, who are both professors of entomology and plant pathology at NC State; and Jean Ristaino, William Neal Reynolds Distinguished Professor of Entomology and Plant Pathology at NC State.
The work stems from the Emerging Plant Disease and Global Food Security research cluster at NC State. This interdisciplinary program is focused on developing new knowledge and tools to better understand and counter emerging infectious plant diseases.
The work was done with support from the U.S. Department of Agriculture under grant number 2019-67030-29311 and USDA APHIS Farm Bill grant number 3.0096; and from the National Science Foundation, under grant numbers 1728370 and 2134664.
END
Multifunctional patch offers early detection of plant diseases, other crop threats
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Predictive power of climate models may be masked by volcanoes
2023-04-12
Simulated volcanic eruptions may be blowing up our ability to predict near-term climate, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
The research, led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), finds that the way volcanic eruptions are represented in climate models may be masking the models’ ability to accurately predict variations in sea surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific that unfold over multiple years to a decade.
These decadal variations in sea surface ...
Industry veteran Pablo Velez, RN, Ph.D., named CEO of El Centro Regional Medical Center
2023-04-12
In coordination with the El Centro Regional Medical Center (ECRMC) Board of Trustees, UC San Diego Health today announced that Pablo Velez, RN, PhD, has been appointed by UC San Diego Health as ECRMC’s chief executive officer effective April 17. Reporting to UC San Diego Health CEO Patty Maysent, Velez will oversee day-to-day operational, clinical and financial management of ECRMC, leading UC San Diego Health’s overall efforts to support the strategic and operational plan that was announced ...
Genes are read faster and more sloppily in old age
2023-04-12
In a large joint project, a total of six research groups from the University of Cologne Cluster of Excellence on Cellular Stress Responses in Age-Associated Diseases (CECAD), the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Aging (MPI) in Cologne and the University of Göttingen have demonstrated the following findings which apply across the animal kingdom: with increasing age, the transcriptional elongation speed of genes increases, whereby the quality of the gene products suffers. With dietary restrictions, ...
Rates of food insecurity in US may be significantly higher than surveys suggest
2023-04-12
Key Points
Many federal and local government agencies send out a United States Department of Agriculture survey once a year or less to determine whether households experienced food insecurity in the last 12 months.
In a new study, USC researchers found that households are more likely to accurately report food insecurity when surveyed more often and asked about their recent experiences. They also found that the USDA measure may be underreporting the true rate by as much as one-third.
Without ...
Humans need Earth-like ecosystem for deep-space living
2023-04-12
ITHACA, N.Y. – Can humans endure long-term living in deep space? The answer is a lukewarm maybe, according to a new theory describing the complexity of maintaining gravity and oxygen, obtaining water, developing agriculture and handling waste far from Earth.
Dubbed the Pancosmorio theory – a word coined to mean “all world limit” – it was described in a paper published in Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences.
“For humans to sustain themselves and all of their technology, infrastructure and society in space, they need a ...
Nobel Prize-winning immuno-oncology expert receives Block Memorial Lectureship
2023-04-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – James P. Allison, PhD, is the recipient of the 25th Herbert and Maxine Block Memorial Lectureship Award for Distinguished Achievement in Cancer. A 2018 Nobel Prize co-recipient in physiology/medicine, Allison serves as the chair of immunology and executive director of the Immunotherapy Platform at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
He is a renowned immunologist whose research led to the discovery of the immune system’s T-cell receptor structure and later a molecule ...
UIUC researchers image magnetic behavior at the smallest scales to date
2023-04-12
Permanent magnets, the kind found on refrigerators everywhere, exist because their constituent atoms behave as miniature magnets. They align and combine to form the larger magnet in a phenomenon called ferromagnetism. There are some materials where the atomic magnets instead form an alternating pattern, so the material has no net magnetization. Such antiferromagnets have attracted attention for their potential to create faster and more compact magnetic memory devices for computing.
Realizing the full potential of antiferromagnetic devices will require sensing their atom-to-atom magnetic patterns, ...
Henry Ford Health cardiologists first in US to successfully implant novel tricuspid LuX valve
2023-04-12
DETROIT (April 12, 2023) – Henry Ford Hospital structural heart interventional cardiologists Pedro Villablanca, M.D., and Brian O’Neill, M.D., are the first in the U.S. to successfully implant the new transcatheter tricuspid valve replacement device LuX-Valve Plus™ for the treatment of patients with symptomatic tricuspid valve disease for whom traditional open-heart surgery is too high of a risk.
“These are patients with severe tricuspid regurgitation who have no other options available to them in the U.S., based on the anatomy of their native valve and medical complexities,” ...
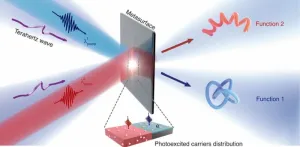
Optically controlled metasurfaces for dynamic dual-mode modulation
2023-04-12
Dynamic control of terahertz (THz) waves at-will with an ultracompact device is important for THz technologies in biomedical imaging, telecommunications, detection, and beyond. However, tunable THz devices made of conventional materials are usually bulky, and they tend to have limited modulation depths and functionalities, due to weak interactions between naturally existing materials and THz waves. Metasurfaces – functional materials endowed with unparalleled flexibility to manipulate light at the deep-subwavelength scale – provide ...
Whether physical exertion feels ‘easy’ or ‘hard’ may be due to dopamine levels, study suggests
2023-04-12
Dopamine, a brain chemical long associated with pleasure, motivation and reward-seeking, also appears to play an important role in why exercise and other physical efforts feel “easy” to some people and exhausting to others, according to results of a study of people with Parkinson’s disease led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers. Parkinson’s disease is marked by a loss of dopamine-producing cells in the brain over time.
The findings, published online April 1 in NPG Parkinson’s Disease, could, the researchers say, eventually lead to more effective ways to help people establish and stick with exercise ...