(Press-News.org) In a large joint project, a total of six research groups from the University of Cologne Cluster of Excellence on Cellular Stress Responses in Age-Associated Diseases (CECAD), the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Aging (MPI) in Cologne and the University of Göttingen have demonstrated the following findings which apply across the animal kingdom: with increasing age, the transcriptional elongation speed of genes increases, whereby the quality of the gene products suffers. With dietary restrictions, these processes could be reversed / Publication in ‘Nature’.
Fast but sloppy, that's how the transcription of genes changes with age. Six research groups from the University of Cologne Cluster of Excellence on Cellular Stress Responses in Age-Associated Diseases (CECAD), the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Aging (MPI) in Cologne and the University of Göttingen discovered a new molecular mechanism that contributes to ageing by studying the transcription process in five different model organisms and in a wide variety of tissues.
Ageing impairs a wide range of cellular processes, many of which affect the quality and concentration of proteins. Among these processes, the reading of genes known as transcription is particularly important, because it is a main regulator of protein levels. Although experts knew that gene expression, i.e. the conversion of genetic information into proteins, changes with age, and also that the control of gene expression may be impaired, it was unclear whether the accuracy of the transcription process itself changes with age and whether such a change would have relevant consequences for organisms.
This is exactly what the researchers have now been able to demonstrate, which makes Andreas Beyer, CECAD working group leader and professor at the Institute for Genetics of the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences at the University of Cologne, extremely happy: “This was a large, collaborative project lasting several years involving multiple teams from the CECAD cluster and other scientific institutions. Data from five species had to be generated and analysed. Only by combining our expertise was it possible to study so many species and types of data.”
In fact, the 26 scientists investigated genome-wide, age-related changes in transcription processes in nematodes, fruit flies, mice, rats and humans, including diverse tissues. And they discovered that the average speed at which the transcript grows through the attachment of RNA building blocks, the nucleotides, increased with age in all five species. Together with the higher speed of this elongation speed (Pol II speed), the researchers also observed changes in the so-called splicing, a further work step within the transcription process from the gene to the finished protein, in which the transcription product is once again shortened and cut to size.
However, the accuracy of the entire transcription process could also be controlled and reversed, for example by dietary restriction or intervention in insulin signaling - both measures that contribute to the extension of lifespan, as has been known for many years. Similarly, the lifespan of flies and the division potential of human cells lengthened when the researchers used interventions to reduce the reading speed.
Professor Beyer says: “Our results uncover fundamental molecular mechanisms underlying animal ageing and interventions to extend lifespan, providing clues as to how we might contribute to healthy ageing in the future. The fact that interventions, such as a reduced calorie intake, also have a positive effect on a healthy ageing process on the molecular level via improving the quality of gene transcription is something which we have now been able to prove quite clearly with our study.”
The study was carried out by the University of Cologne Cluster of Excellence on Cellular Stress Responses in Age-Associated Diseases (CECAD), The Max Planck Institute for Biology of Aging (MPI) in Cologne and the University of Göttingen
Media Contact:
Professor Dr. Andreas Beyer
CECAD Group Leader
+49 221 478 84429
andreas.beyer@uni-koeln.de
Press and Communications Team:
Susanne Kutter
CECAD Press Spokesperson
+49 221 478 84043
+49 160 8879816
susanne.kutter@uni-koeln.de
Authors:
Cédric Debès, Antonios Papadakis, Sebastian Grönke, Özlem Karalay, Luke Tain, Athanasia Mizi, Shuhei Nakamura, Oliver Hahn, Carina Weigelt, Natasa Josipovic, Anne Zirkel, Isabell Brusius, Konstantinos Sofiadis, Mantha Lamprousi, Yu-Xuan Lu, Wenming Huang, Reza Esmaillie, Torsten Kubacki, Martin R. Späth, Bernhard Schermer, Thomas Benzing, Roman-Ulrich Müller, Adam Antebi, Linda Partridge, Argyris Papantonis, Andreas Beyer
Aging-associated changes in transcriptional elongation influence metazoan longevity, Nature, 12. April 2023
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-05922-y
Verantwortlich: Dr. Elisabeth Hoffmann – e.hoffmann@verw.uni-koeln.de
END
Key Points
Many federal and local government agencies send out a United States Department of Agriculture survey once a year or less to determine whether households experienced food insecurity in the last 12 months.
In a new study, USC researchers found that households are more likely to accurately report food insecurity when surveyed more often and asked about their recent experiences. They also found that the USDA measure may be underreporting the true rate by as much as one-third.
Without ...
ITHACA, N.Y. – Can humans endure long-term living in deep space? The answer is a lukewarm maybe, according to a new theory describing the complexity of maintaining gravity and oxygen, obtaining water, developing agriculture and handling waste far from Earth.
Dubbed the Pancosmorio theory – a word coined to mean “all world limit” – it was described in a paper published in Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences.
“For humans to sustain themselves and all of their technology, infrastructure and society in space, they need a ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – James P. Allison, PhD, is the recipient of the 25th Herbert and Maxine Block Memorial Lectureship Award for Distinguished Achievement in Cancer. A 2018 Nobel Prize co-recipient in physiology/medicine, Allison serves as the chair of immunology and executive director of the Immunotherapy Platform at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
He is a renowned immunologist whose research led to the discovery of the immune system’s T-cell receptor structure and later a molecule ...
Permanent magnets, the kind found on refrigerators everywhere, exist because their constituent atoms behave as miniature magnets. They align and combine to form the larger magnet in a phenomenon called ferromagnetism. There are some materials where the atomic magnets instead form an alternating pattern, so the material has no net magnetization. Such antiferromagnets have attracted attention for their potential to create faster and more compact magnetic memory devices for computing.
Realizing the full potential of antiferromagnetic devices will require sensing their atom-to-atom magnetic patterns, ...
DETROIT (April 12, 2023) – Henry Ford Hospital structural heart interventional cardiologists Pedro Villablanca, M.D., and Brian O’Neill, M.D., are the first in the U.S. to successfully implant the new transcatheter tricuspid valve replacement device LuX-Valve Plus™ for the treatment of patients with symptomatic tricuspid valve disease for whom traditional open-heart surgery is too high of a risk.
“These are patients with severe tricuspid regurgitation who have no other options available to them in the U.S., based on the anatomy of their native valve and medical complexities,” ...
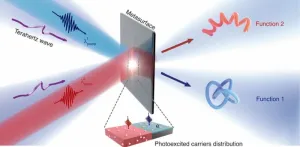
Dynamic control of terahertz (THz) waves at-will with an ultracompact device is important for THz technologies in biomedical imaging, telecommunications, detection, and beyond. However, tunable THz devices made of conventional materials are usually bulky, and they tend to have limited modulation depths and functionalities, due to weak interactions between naturally existing materials and THz waves. Metasurfaces – functional materials endowed with unparalleled flexibility to manipulate light at the deep-subwavelength scale – provide ...
Dopamine, a brain chemical long associated with pleasure, motivation and reward-seeking, also appears to play an important role in why exercise and other physical efforts feel “easy” to some people and exhausting to others, according to results of a study of people with Parkinson’s disease led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers. Parkinson’s disease is marked by a loss of dopamine-producing cells in the brain over time.
The findings, published online April 1 in NPG Parkinson’s Disease, could, the researchers say, eventually lead to more effective ways to help people establish and stick with exercise ...
BOSTON – There were more than 100,000 reported deaths from opioid overdoses in 2021, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Methadone treatment remains one of the most reliable means of treating opioid use disorder, with success rates reportedly ranging from 60 to 90 percent for patients who stick with the long-term regimen. Adherence, though, remains a challenge.
In a novel randomized clinical trial published in JAMA Network Open, senior author Ted J. Kaptchuk at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center ...
ORLANDO, April 12, 2023 – A University of Central Florida researcher will be using the newly constructed Two-meter Twin Telescope (TTT) in the Canary Islands, Spain, to study metal-rich M-type asteroids.
The work can inform the study of asteroids like 16 Psyche, an M-type, or metal, asteroid NASA is launching a mission in October 2023 to visit.
The M-type asteroids offer both high concentrations of metals that could be harnessed to make structures in space as well as clues to the formation of ...
As the number of children in need of access to timely evaluation and intervention for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) continues to rise, new research is showing how barriers to diagnoses and treatment can be reduced through an innovative training program first developed at the University of Missouri.
ASD can be identified and diagnosed in young children by a well-trained clinician, and early diagnosis is vital to quickly establishing access to evidence-based therapies and interventions. However, long specialty center waitlists, distance, and ...