(Press-News.org) Women working in healthcare who are regularly exposed to radiation from x-rays and other imaging procedures need better ionising radiation protection to help minimise their risk of developing breast cancer, argue doctors in The BMJ today.
Ionising radiation is a known human carcinogen and breast tissue is highly radiation sensitive. As such, there are concerns that regular exposure to ionising radiation during image guided procedures may be linked to a higher risk of breast cancer in female healthcare workers.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as lead gowns are used to shield the body from harmful radiation during these procedures. But studies have shown that current radiation PPE provides inadequate protection to breast tissue as it leaves the area close to the armpit (known as the upper outer quadrant and axilla - the most common site of breast cancer) exposed.
“Providing adequate breast covering PPE could therefore reduce radiation exposure and potentially help prevent breast cancer in female healthcare workers,” write Isobel Pilkington and colleagues.
They acknowledge that measuring the risk of occupational radiation induced breast cancer in women working in healthcare is challenging, but as the number of female trainees entering these specialties increases, they say “it is essential that the available evidence is considered and equipment provision improved to minimise this risk.”
They point to observational evidence suggesting an increase in breast cancer risk among female US orthopaedic surgeons compared with an age matched female population, and to a small Finnish study showing breast cancer at 1.7 times the expected rate in radiologists, surgeons, and cardiologists compared with female physicians not working with radiation.
In a study using artificial female torsos to measure radiation exposure, researchers found inadequate upper outer quadrant protection and no statistically significant reduction in dose when standard PPE was compared with a torso without PPE.
Occupational radiation exposure has not been identified as a risk factor for male breast cancer. However, the Ionising Radiation Regulations 2017 state that the radiation dose delivered to all workers should be As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA). The most effective way to achieve this, say the authors, is by reducing the duration of exposure, increasing the distance from the source, and shielding all workers with effective PPE.
They point to additional protection, such as capped sleeves and axillary wings, that can be worn under standard gowns to protect the upper outer quadrant of the breast, and say the European Society for Vascular Surgery 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines on Radiation Safety have already recommended female operators consider adopting this extra protection.
“Providing appropriate protection is a legal requirement of an employer, who has a duty of care to all workers exposed to radiation,” they write. “The female breast appears to be particularly vulnerable and it is therefore important employers invest in protective equipment that enhances the safety of all their staff.”
[Ends]
END
Female healthworkers need better radiation protection to minimise breast cancer risk
Standard PPE does not fully protect breast tissue; Employers should invest in equipment that ensures the safety of all their staff
2023-04-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Higher dose corticosteroids associated with a 60% increased risk of death in hypoxic COVID-19 patients requiring only non-invasive oxygen therapy (The Lancet / RECOVERY trial)
2023-04-13
*Note: this is a joint press release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) and The Lancet. Please credit both the congress and the journal in your stories*
A new study to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen 15-18 April), and published in The Lancet, shows that, compared with standard care that included low dose corticosteroid use, treating hypoxic COVID-19 patients needing ...
Assisted reproduction kids grow up just fine – but it may be better to tell them early about biological origins, twenty-year study suggests
2023-04-13
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1y9GfgYkRdUtwyq6nBhySePTUHZYP6iAj?usp=share_link
Landmark study finds no difference in psychological wellbeing or quality of family relationships between children born by assisted reproduction (egg or sperm donation or surrogacy) and those born naturally at age 20.
However, findings suggest that telling children about their biological origins early – before they start school – can be advantageous for family relationships and healthy adjustment.
The study, by University of Cambridge researchers, is the first to examine the long-term ...
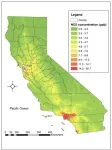
The hidden culprit behind nitrogen dioxide emissions
2023-04-13
Nitrogen dioxide is one of the criteria air pollutants that plays an important role as a precursor gas of fine particulate matter and ozone. NO2 emissions are known to be primarily generated by industrial facilities or vehicle exhausts. Recently, a research team from POSTECH analyzed satellite remote sensing data from the European Space Agency (ESA) and released results showing that food processing facilities and high-rise apartments that are 10 stories or higher are significant sources of NO2 emissions. Their findings have drawn attention from NASA.
A ...
Notable birth cohort effects on the incidence trend of renal replacement therapy in Japan
2023-04-13
Niigata, Japan - A new Japanese study reveals significant birth cohort effects on the incidence trend of ESKD requiring RRT.
“Different birth cohorts may have different levels of exposure to a particular risk factor, which may produce a change in disease incidence for individuals born at a particular time, i.e. a cohort effect,” said Dr. Wakasugi, the corresponding author of the study. “Age-Period-Cohort (APC) analysis, a statistical method to distinguish between age, period, and ...
Time out: We all need a three-day weekend
2023-04-13
As a four-day work week is trialled in countries across the globe, health researchers at the University of South Australia say they’re ‘all in’ when it comes to a long weekend, especially as new empirical research shows that the extra time off is good for our health.
Assessing changes in daily movements before, during and after holidays, researchers found that people displayed more active, healthy behaviours when they were on holiday, even when they only had a three-day break.
Across the 13-month study period, people generally took an average two to three holidays, each being around 12 days. The most common holiday type was ‘outdoor ...
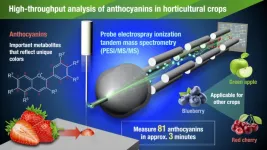
Using a new technique, PESI/MS/MS, to analyze the nutritional compounds in crops
2023-04-13
Anthocyanins are compounds related to the color of plants. They also have beneficial effects on human health and are used as a supplement. Various species of anthocyanins, divided by their molecular shape, are present in plants. Therefore, simple, and rapid, analytical techniques that can distinguish among these species in crops are necessary for breeding and quality assessment. A team of Nagoya University researchers in Japan has used a technique called probe electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (PESI/MS/MS) to analyze anthocyanins in crops. ...
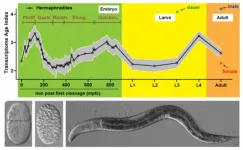
HKU biologists determine the evolutionary age of individual cell types providing critical insights for animal development
2023-04-13
A research team led by Dr Chaogu ZHENG from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently made a significant discovery about the evolutionary age of different type of cells in a small animal called Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). By using single-cell transcriptomic data and refined phylostratigraphy, the team determines the transcriptomic age of individual cells, which means they are able to estimate the evolutionary origin of different cells based on the age of the genes expressed in the ...
Coral-eating fish poo may act as ‘probiotics’ for reefs
2023-04-13
Until recently, fish that eat coral — corallivores — were thought to weaken reef structures, while fish that consume algae and detritus — grazers — were thought to keep reefs healthy. But scientists have discovered that feces from grazers leave large lesions on coral, possibly because they contain coral pathogens. By contrast, feces from corallivores may provide a source of beneficial microbes that help coral thrive.
“Corallivorous fish are generally regarded as harmful because they bite the corals,” said Dr Carsten Grupstra of Rice University, ...
New study demonstrates hospital safety climate and organizational characteristics predict healthcare-associated infections and occupational health outcomes
2023-04-13
Arlington, Va., April 13, 2023 – New data published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) provide the first published evidence that a positive safety climate and adherence to standard precautions predict key healthcare-associated infection (HAI) and occupational health outcomes among patients and health care workers, respectively. The findings highlight features within hospitals’ organizations and safety climates that could be modified to improve these outcomes.
“Despite the infection prevention and safety benefits associated with standard precautions, generating consistent adherence in the healthcare setting has been ...
Selenium as a predictor of metabolic syndrome in middle age women
2023-04-12
“Recently, optimizing selenium intake in the population to prevent diseases [...] has been an important issue in modern health care worldwide.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Selenium as a predictor of metabolic syndrome in middle age women.”
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a widespread clinical entity that has become almost a global epidemic. Selenium plays an important role in metabolic homeostasis. It has been suggested that it ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Female healthworkers need better radiation protection to minimise breast cancer riskStandard PPE does not fully protect breast tissue; Employers should invest in equipment that ensures the safety of all their staff