(Press-News.org) A new paper in Molecular Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, provides interesting new evidence about the evolution of North American wolves, which has been a subject of debate among conservationists and taxonomists.
Southeastern Canada is home to populations of wolves and coyotes whose origins and genetic relationships have long puzzled scientists. In particular, eastern wolves have been the subject of great dispute, and it remains unknown whether these canids represent a distinct species or if they are the result of recent hybridization between coyotes and grey wolves. The Canidae animal family includes coyotes, foxes, jackals, wolves, and domestic dogs.
In Canada, the eastern wolf (also known as the eastern timber wolf or the Algonquin wolf) has been recognized by some as a distinct species based on genetic and behavioral studies. Eastern wolves are listed as “Special Concern” in Canada under the federal Species at Risk Act and “Threatened” in Ontario under the provincial Endangered Species Act. But whereas previous studies have noted the distinctiveness of eastern wolves from coyotes and grey wolves in Canada, the provincial government currently manages them as a single species across their primary range in central Ontario. This pooling of these three taxonomic entities for management is considered necessary because it is so difficult for humans to visually distinguish between wild canids and their hybrids in central Ontario. This leads to frustration among some hunters, trappers, and farmers, and challenges in enforcing hunting and trapping regulations.
To test hypotheses related to these competing findings for eastern wolves, researchers sequenced whole genomes of 25 animals of known origin and levels of contemporary hybridization, representative of all Canadian wolf-like canid types. The analysis shows that eastern wolves that inhabit the Great Lakes region in southeastern Canada are genetically distinct from other canids in the region. Based on the findings it appears that eastern wolves evolved separately from grey wolves about 67,000 years ago. The scientists here believe that eastern wolves bred with coyotes about 37,000 years ago and continue to mix with both coyotes and grey wolves.
“This manuscript addresses key evolutionary questions among North American wolf-like canids, but also provides data of direct and applied relevance,” said the paper’s lead author, Christopher Kyle. “This work represents a strong international collaboration that culminates from complementary expertise between wolf experts from the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry and scholars from the University of Ferrara in Italy, and Trent University in Ontario, Canada, with a long-standing interest in North American Canis ancestry and genetics.”
The paper, “Tracing eastern wolf origins from whole-genome data in context of extensive hybridization,” is available (at midnight on April 13th ) at: https://academic.oup.com/mbe/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/molbev/msad055.
Direct correspondence to:
Christopher J. Kyle
Professor of Forensic Science
Trent University
1600 West Bank Drive
Peterborough, ON K9L 0G2 CANADA
christopherkyle@trentu.ca
To request a copy of the study, please contact:
Daniel Luzer
daniel.luzer@oup.com
END
Eastern wolves evolved separately from grey wolves
2023-04-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Visualizing differences in nuclear structure
2023-04-13
Helium usually has two protons and two neutrons strongly bound to each other, often forming a substructure within the nucleus. A nucleus composed of several such substructures is called a cluster structure. In the standard picture, nuclei are difficult to understand in terms of so-called shell structure; because there was no way to clearly distinguish whether each nucleus has a cluster or a shell structure.
Associate Professor Wataru Horiuchi and Professor Naoyuki Itagaki from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science, have developed an ...
The Lancet Neurology: Identifying ‘hallmark’ Parkinson’s disease protein build-up could aid early detection and pave way for improved diagnosis and treatment
2023-04-13
Cross-sectional study of 1,123 participants confirms α-synuclein seed amplification assay (αSyn-SAA) technique is highly accurate at identifying people with Parkinson’s disease.
The technique detects at-risk individuals and those with early, non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease prior to diagnosis, suggesting that a positive result on αSyn-SAA may be an early indicator of disease onset.
Differences in the frequency of a positive αSyn-SAA result were detected based on age and sex, and if people ...
Free trade deal is a major threat to UK public health, warn experts
2023-04-13
The UK’s decision to join one of the world’s largest free trade agreements, known as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement on Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), poses a major threat to UK public health, warn experts in The BMJ today.
In acceding to the CPTPP, the government hopes to boost trade, improve economic growth, and strengthen the UK’s strategic position as a global rule setter.
But Courtney McNamara and colleagues argue that free trade deals have serious and wide ranging implications for public health and ...
Female healthworkers need better radiation protection to minimise breast cancer risk
2023-04-13
Women working in healthcare who are regularly exposed to radiation from x-rays and other imaging procedures need better ionising radiation protection to help minimise their risk of developing breast cancer, argue doctors in The BMJ today.
Ionising radiation is a known human carcinogen and breast tissue is highly radiation sensitive. As such, there are concerns that regular exposure to ionising radiation during image guided procedures may be linked to a higher risk of breast cancer in female healthcare workers.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as lead gowns are used to shield the body from harmful radiation during these ...
Higher dose corticosteroids associated with a 60% increased risk of death in hypoxic COVID-19 patients requiring only non-invasive oxygen therapy (The Lancet / RECOVERY trial)
2023-04-13
*Note: this is a joint press release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) and The Lancet. Please credit both the congress and the journal in your stories*
A new study to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen 15-18 April), and published in The Lancet, shows that, compared with standard care that included low dose corticosteroid use, treating hypoxic COVID-19 patients needing ...
Assisted reproduction kids grow up just fine – but it may be better to tell them early about biological origins, twenty-year study suggests
2023-04-13
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1y9GfgYkRdUtwyq6nBhySePTUHZYP6iAj?usp=share_link
Landmark study finds no difference in psychological wellbeing or quality of family relationships between children born by assisted reproduction (egg or sperm donation or surrogacy) and those born naturally at age 20.
However, findings suggest that telling children about their biological origins early – before they start school – can be advantageous for family relationships and healthy adjustment.
The study, by University of Cambridge researchers, is the first to examine the long-term ...
The hidden culprit behind nitrogen dioxide emissions
2023-04-13
Nitrogen dioxide is one of the criteria air pollutants that plays an important role as a precursor gas of fine particulate matter and ozone. NO2 emissions are known to be primarily generated by industrial facilities or vehicle exhausts. Recently, a research team from POSTECH analyzed satellite remote sensing data from the European Space Agency (ESA) and released results showing that food processing facilities and high-rise apartments that are 10 stories or higher are significant sources of NO2 emissions. Their findings have drawn attention from NASA.
A ...
Notable birth cohort effects on the incidence trend of renal replacement therapy in Japan
2023-04-13
Niigata, Japan - A new Japanese study reveals significant birth cohort effects on the incidence trend of ESKD requiring RRT.
“Different birth cohorts may have different levels of exposure to a particular risk factor, which may produce a change in disease incidence for individuals born at a particular time, i.e. a cohort effect,” said Dr. Wakasugi, the corresponding author of the study. “Age-Period-Cohort (APC) analysis, a statistical method to distinguish between age, period, and ...
Time out: We all need a three-day weekend
2023-04-13
As a four-day work week is trialled in countries across the globe, health researchers at the University of South Australia say they’re ‘all in’ when it comes to a long weekend, especially as new empirical research shows that the extra time off is good for our health.
Assessing changes in daily movements before, during and after holidays, researchers found that people displayed more active, healthy behaviours when they were on holiday, even when they only had a three-day break.
Across the 13-month study period, people generally took an average two to three holidays, each being around 12 days. The most common holiday type was ‘outdoor ...
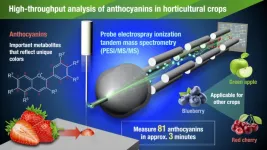
Using a new technique, PESI/MS/MS, to analyze the nutritional compounds in crops
2023-04-13
Anthocyanins are compounds related to the color of plants. They also have beneficial effects on human health and are used as a supplement. Various species of anthocyanins, divided by their molecular shape, are present in plants. Therefore, simple, and rapid, analytical techniques that can distinguish among these species in crops are necessary for breeding and quality assessment. A team of Nagoya University researchers in Japan has used a technique called probe electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (PESI/MS/MS) to analyze anthocyanins in crops. ...