(Press-News.org)
EMBARGOED UNTIL 17-APR-2023 11:00 ET
Basel, April 17, 2023 Using a new approach for studying live embryonic mouse brains at single-cell resolution, researchers have identified an active multi-layer circuit that forms in the cortex during an unexpectedly early stage of development. Perturbing the circuit genetically led to changes similar to those seen in the brains of people with autism. The findings are reported today in Cell by a team based at the Institute of Molecular and Clinical Ophthalmology Basel.
“Understanding the detailed development of cell types and circuits in the cortex can provide important insights into autism and other neurodevelopmental diseases,” says Botond Roska, Director at IOB and the paper’s corresponding author. “This is what our findings confirm.”
Autism has long been associated with faulty circuits in the cortex, which is the part of the brain that governs sensory perception, cognition, and other high-order functions. Most of the cortex is composed of excitatory cells called pyramidal neurons. The IOB team wanted to study when and how these neurons assemble into the first active circuits in the cortex, but that posed a difficult challenge. Pyramidal neurons measure only a tenth of the width of a human hair, and any movement during experimental procedures might lead to inaccurate recordings of activity. To keep the neurons stable for research, the team devised a surgical solution: Embryos were secured inside of agar-filled 3D holding devices within the mother’s abdominal cavity, so that normal embryonic blood flow and temperature could be maintained.
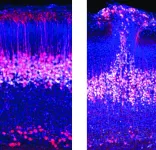
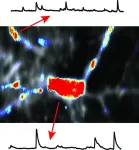
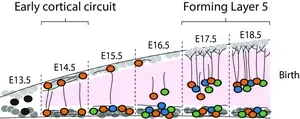
The prevailing view is that the cortex develops in an “inside out fashion”, with the deepest of its six layers appearing first. Seen this way, pyramidal neurons were thought to slowly become active as they migrate to their final locations in the cortex and form connections with each other. But during the research, "we actually detected a very different activity pattern,” says Arjun Bharioke, a systems neuroscientist in IOB’s Central Visual Circuits Group, and one of the paper’s two lead authors. Focusing specifically on pyramidal neurons that develop into layer 5 of the cortex, the team discovered a very early transient circuit that was already highly active and correlated even before the six-layer cortex had formed. This indicates that the neurons were already connected prior to their migration to form layer 5. The transient circuit initially had 2 layers: a deep layer and a superficial layer. Later, the superficial layer became silent and vanished, while the classical layer-by-layer cortical development resumed, with a third intermediate layer forming layer 5.
"We also wanted to understand how this circuit changes in an autism model," says Martin Munz, an IOB developmental biologist in the Central Visual Circuits Group and the paper's other lead author. Working with knock-out mouse lines missing one or both alleles of two autism-associated genes--Chd8 and Grin2b--the team made a key finding. The absence of these genes is known to cause significant autism in children. And in homozygous and heterozygous knockout mice, the superficial layer remained active as a developmental remnant. "Throughout embryonic development, it never disappeared," Munz says. Moreover, the knockout mouse brains contained patchy areas of cortical disorganization similar to those seen in people with autism.
The findings suggest that the spatial organization of pyramidal neurons is regulated by the newly-found circuit, and that "changes to embryonic circuits play a role in dysfunctions associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorder," Bharioke says.
In future research, IOB researchers will "carefully look at the superficial and deep layers of this early circuitry and independently manipulate them," Roska says. "This will be instructive for learning about the etiology of neurodevelopmental diseases."
Original Publication:
Pyramidal neurons form active, transient, multilayered circuits perturbed by autism-associated mutations at the inception of neocortex
Martin Munz, Arjun Bharioke, Georg Kosche, Verónica Moreno-Juan, Alexandra Brignall, Tiago M. Rodrigues, Alexandra Graff-Meyer, Talia Ulmer, Stephanie Haeuselmann, Dinko Pavlinic, Nicole Ledergeber, Brigitte Gross-Scherf, Balázs Rózsa, Jacek Krol, Simone Picelli, Cameron S. Cowan, Botond Roska
2023, Cell 186
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.025
About IOB
At the Institute of Molecular and Clinical Ophthalmology Basel (IOB), basic researchers and clinicians work hand in hand to advance the understanding of vision and its diseases, and to develop new therapies for vision loss. IOB started its operations in 2018. The institute is constituted as a foundation, granting academic freedom to its scientists. Founding partners are the University Hospital Basel, the University of Basel and Novartis. The Canton of Basel-Stadt has granted the institute substantial financial support.
www.iob.ch
Follow us on Social Media
Twitter @IOB_ch
YouTube IOB Basel Switzerland
IOB Media Contact:
clara.vuille-dit-bille@iob.ch
END
Researchers discover a new embryonic brain circuit
The findings may provide new insights into circuit abnormalities in autism
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study links poor diet to 14 million cases of type 2 diabetes globally
2023-04-17
A research model of dietary intake in 184 countries, developed by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, estimates that poor diet contributed to over 14.1 million cases of type 2 diabetes in 2018, representing over 70% of new diagnoses globally. The analysis, which looked at data from 1990 and 2018, provides valuable insight into which dietary factors are driving type 2 diabetes burden by world region. The study was published April 17 in the journal Nature Medicine.
Of the 11 dietary factors considered, three had an outsized contribution to the rising global incidence of type 2 diabetes: ...
SpyLigation uses light to switch on proteins
2023-04-17
Scientists can now use light to activate protein functions both inside and outside of living cells. The new method, called light-activated SpyLigation, can turn on proteins that are normally off to allow researchers to study and control them in more detail. This technology has potential uses in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and understanding how the body works.
Proteins perform nearly every important task in biology, including processing DNA, metabolizing nutrients, and fighting off infections. When, where, and how proteins become active is important for a variety of biological processes. Increasingly, ...
Dexamethasone for inpatients with COVID-19 in a national cohort
2023-04-17
About The Study: In this national multicenter cohort study of inpatients with COVID-19, early administration of dexamethasone was associated with significantly reduced odds of mortality or discharge to hospice in those requiring supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation and/or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation but not in those requiring no supplemental oxygen or noninvasive positive pressure ventilation. These results support the continued use of systemic dexamethasone in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Authors: Laine ...
Investigational drug may improve stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients
2023-04-17
The standard treatment for patients with multiple myeloma often includes stem cell transplantation in which the patient’s own stem cells are harvested and stored while the patient receives intensive chemotherapy to kill the cancer. Then, the patient’s stem cells are returned to the patient to help with recovery. But for a significant proportion of patients, the number of stem cells that can be harvested is not optimal for transplant and negatively affects patient outcomes.
However, an international phase 3 clinical trial led by physicians at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has shown that the investigational ...
University of Rochester researchers discover how to steer army of immune cells toward cancer
2023-04-17
Immunotherapy, particularly CAR T-Cell treatment for cancer, is extending the lives of many patients. But sometimes the therapy randomly migrates to places it shouldn’t go, tucking into the lungs or other noncancerous tissue and causing toxic side effects. A University of Rochester/Wilmot Cancer Institute team discovered the molecule responsible for guiding T cells toward tumors, setting the stage for scientists to improve upon the groundbreaking treatment.
The next step is to find a drug that can manipulate the ...
Poverty is the fourth greatest cause of U.S. deaths, analysis published in JAMA finds.
2023-04-17
Poverty has long been linked to shorter lives. But just how many deaths in the United States are associated with poverty? The number has been elusive – until now.
UC Riverside paper published Monday in the Journal of the American Medical Association associated poverty with an estimated 183,000 deaths in the United States in 2019 among people 15 years and older.
This estimate is considered conservative because the data is from the year just prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused spikes in deaths worldwide and continues to take its toll.
The analysis found that only heart disease, ...
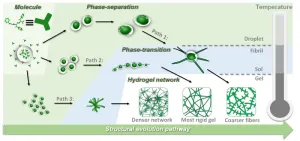
Steering phase-separated droplets to control mechanical properties of supramolecular peptide hydrogels
2023-04-17
Self-assembled peptide supramolecular hydrogels have shown great application prospects in various areas, including tissue engineering, drug delivery, and biosensing.
Precisely and flexibly controlling the mechanical properties of peptide hydrogels to match the targeted applications is important. The common methods to regulate the mechanical properties of supramolecular hydrogels generally include: changing the formula (different peptide sequences, adding cross-linking agents) or changing the environmental conditions (concentration, temperature, pH and ions), both of which inevitably change the chemical composition of the ...
Facile synthesis of high-performance perovskite oxides for acid–base catalysis
2023-04-17
Bifunctional acid−base catalysts are highly desirable for industrially relevant chemical processes. Owing to their ability to activate electrophiles and nucleophiles simultaneously, they allow the catalysis to proceed synergistically and cooperatively. Solid acid−base catalysts are particularly advantageous since they are reusable and result in no waste products. However, controlling the structure of such catalysts for cooperatively workable active sites is challenging. Simple and effective methods that enable the synthesis of high-performance solid acid−base ...
Quantum light source goes fully on-chip, bringing scalability to the quantum cloud
2023-04-17
An international team of researchers from Leibniz University Hannover (Germany), the University of Twente (Netherlands), and the start-up company QuiX Quantum has presented an entangled quantum light source fully integrated for the first time on a chip. “Our breakthrough allowed us to shrink the source size by a factor of more than 1000, allowing reproducibility, stability over a longer time, scaling, and potentially mass-production. All these characteristics are required for real-world applications such as quantum processors,” says Prof. Dr. Michael Kues, head of the Institute ...
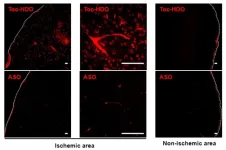
Lipid molecules help to get stroke therapies into the brain
2023-04-17
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that, when a stroke therapy is linked to a specific kind of lipid and injected into the blood, it is taken up preferentially in the stroke-lesioned brain
Tokyo, Japan – To get therapies into the brain after a stroke, researchers are increasingly making use of the blood–brain barrier, which allows only certain molecules to pass from the blood into the brain. In a study published earlier this year in Molecular Therapy, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
[Press-News.org] Researchers discover a new embryonic brain circuitThe findings may provide new insights into circuit abnormalities in autism