(Press-News.org) Marm Dixit, a Weinberg Distinguished Staff Fellow at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was nominated for his work on imaging techniques for solid-state batteries.
Marm Dixit, a Weinberg Distinguished Staff Fellow at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was named the 2023 recipient of the Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award.
Since 2004, this biannual award has been given by the Advanced Photon Source (APS) user organization. It recognizes important scientific or technical accomplishments at (or beneficial to) the APS by a young investigator, typically a senior graduate student or early career researcher. The APS is a DOE Office of Science user facility located at DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory.
The award is named for Rosalind Franklin, a chemist who played a critical, but largely unacknowledged role in the discovery of the structure of DNA.
“I am thrilled, ecstatic, and deeply humbled in equal measures on receiving the Rosalind Franklin Award from the APS. Every day I spent on the floor at APS, I learned something I had never known before, and I can’t wait to be back for more.” — Marm Dixit, Weinberg Distinguished Staff Fellow at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Dixit was a visiting student with the Material Physics and Engineering group at the APS in June 2020. He worked closely with beamline scientists on developing and implementing advanced diffraction-based imaging methods for solid-state batteries. These types of batteries use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones. His research dove into the characterization challenges unique to these batteries. It helped provide influential contributions and foundational knowledge in the field.
“I am thrilled, ecstatic and deeply humbled in equal measures on receiving the Rosalind Franklin Award from the APS,” said Dixit. “My sincerest thanks to everyone involved in all my beamtimes that helped to make this happen. Every day I spent on the floor at APS, I learned something I had never known before, and I can’t wait to be back for more.”
Over the course of his early career, Dixit already has 22 first-author publications (45 total), four book chapter publications, 10 patents (either granted or filed) and has received several fellowships and awards. His work has been integral in a range of fields. This includes batteries, energy conversion, water desalination, synchrotron science and manufacturing. In addition, Dixit has made exceptional scientific contributions in the field of in situ and operando X-ray characterization of materials.
Those who nominated Dixit applauded his scientific contributions, forward-looking approach and collaborative demeanor. His ability to conceive new ways to address technologically relevant problems using advanced synchrotron techniques will undoubtedly inspire others to take similar roads, his nominators concluded.
His ability to push the boundaries of cutting-edge synchrotron techniques and investigate solid-state batteries in new ways also impressed his nominators.
Dixit received his Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from Vanderbilt University and his Bachelor of Technology degree from Charotar University of Science and Technology.
About the Advanced Photon Source
The U. S. Department of Energy Office of Science’s Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the world’s most productive X-ray light source facilities. The APS provides high-brightness X-ray beams to a diverse community of researchers in materials science, chemistry, condensed matter physics, the life and environmental sciences, and applied research. These X-rays are ideally suited for explorations of materials and biological structures; elemental distribution; chemical, magnetic, electronic states; and a wide range of technologically important engineering systems from batteries to fuel injector sprays, all of which are the foundations of our nation’s economic, technological, and physical well-being. Each year, more than 5,000 researchers use the APS to produce over 2,000 publications detailing impactful discoveries, and solve more vital biological protein structures than users of any other X-ray light source research facility. APS scientists and engineers innovate technology that is at the heart of advancing accelerator and light-source operations. This includes the insertion devices that produce extreme-brightness X-rays prized by researchers, lenses that focus the X-rays down to a few nanometers, instrumentation that maximizes the way the X-rays interact with samples being studied, and software that gathers and manages the massive quantity of data resulting from discovery research at the APS.
This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation’s first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America’s scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.
END
Dixit receives 2023 Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medical dramas influence thoughts on dangers from vaping, new Twitter analysis reveals
2023-04-17
After three popular primetime medical dramas included storylines about health harms from using e-cigarettes, hundreds of people took to Twitter to comment – including some who said they planned to quit vaping because of what they saw on the shows. A new analysis led by University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health scientists and published in the Journal of Health Communication examines the tweets for insights into the use of television shows to share public health messaging.
Following the January 2020 episodes of New Amsterdam, Chicago Med and Grey’s Anatomy that each included plots involving adolescents with vaping-associated lung-injury, ...
The Green Mediterranean / high polyphenols diet promotes dramatic proximal aortic de-stiffening, twice as much as the healthy Mediterranean diet
2023-04-17
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, April 17, 2023 – The green Mediterranean – high polyphenols diet substantially regresses proximal aortic stiffness (PAS), a marker of vascular aging and increased cardiovascular risk. The green Mediterranean diet was pitted against the healthy Mediterranean diet and a healthy guideline-recommended control diet in the DIRECT PLUS, a large-scale clinical intervention trial. Researchers found that the green Mediterranean diet regressed proximal aortic stiffness by 15%, the Mediterranean diet by 7.3%, and ...
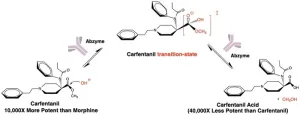
Therapeutic can seek and destroy potent opioid to treat overdoses
2023-04-17
LA JOLLA, CA—A new therapeutic designed by Scripps Research chemists can alter the molecular structure of the potent opioid carfentanil, inactivating the opioid and reversing a carfentanil overdose. The compound, which is described in an ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science paper published on April 17, 2023, and hasn’t yet been studied in humans, works in a fundamentally different way than existing treatments for opioid overdose.
Carfentanil is up to 10,000 times more potent than morphine and 100 times stronger than fentanyl, making it one of the deadliest opioids. It is typically only used as a tranquilizer ...
No magic number for time it takes to form habits
2023-04-17
Putting on your workout clothes and getting to the gym can feel like a slog at first. Eventually, you might get in the habit of going to the gym and readily pop over to your Zumba class or for a run on the treadmill. A new study from social scientists at Caltech now shows how long it takes to form the gym habit: an average of about six months.
The same study also looked at how long it takes health care workers to get in the habit of washing their hands: an average of a few weeks.
“There is no magic number for habit formation,” says Anastasia Buyalskaya (PhD ’21), now an assistant professor of marketing at HEC Paris. Other authors ...
Cai wins 2023 Gopal K. Shenoy Excellence in Beamline Science Award
2023-04-17
Cai from Argonne’s X-ray Science division recognized for his commitment and advances in beamline science, most notably X-ray diffraction.
Physicist Zhonghou Cai is the 2023 recipient of the Gopal K. Shenoy Excellence in Beamline Science Award. He is a beamline scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory.
The annual award recognizes active beamline scientists at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science user facility, for significant contributions to research or instrumentation and support of the beamline user community. The APS Users Office, which grants the award, renamed it ...
AACR: Mutations in three key genes associated with poor outcomes in lung cancer patients treated with KRAS G12C inhibitors
2023-04-17
ABSTRACT: 3431
ORLANDO, Fla. ― A new study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center discovered that co-occurring mutations in three tumor suppressor genes – KEAP1, SMARCA4 and CDKN2A – are linked with poor clinical outcomes in patients with KRAS G12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with the KRAS G12C inhibitors adagrasib or sotorasib.
The findings were presented today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023 and published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the AACR. This study, which encompasses the largest cohort to date of patients with KRAS G12C-mutant NSCLC treated with ...
Scientists create powerful, most-accurate tools to research deadliest blood cancer, study says
2023-04-17
New York, NY (April 17, 2023) — Tisch Cancer Center scientists have developed unique models of the deadliest blood cancer, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), creating a transformative resource to study this cancer and eventually its drug response and drug resistance. The models were described in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research and simultaneously published in Blood Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
These are the first powerful models that are ...
EMBARGOED: Two brain networks are activated while reading, study finds
2023-04-17
When a person reads a sentence, two distinct networks in the brain are activated, working together to integrate the meanings of the individual words to obtain more complex, higher-order meaning, according to a study at UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by Oscar Woolnough, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, and Nitin Tandon, MD, professor and chair ad interim of the department in the medical school, was published ...
The surprising science behind long-distance bird migration
2023-04-17
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of scientists led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has recently made a surprising discovery, with the help of a wind tunnel and a flock of birds. Songbirds, many of which make twice-yearly, non-stop flights of more than 1,000 miles to get from breeding range to wintering range, fuel themselves by burning lots of fat and a surprising amount of the protein making up lean body mass, including muscle, early in the flight. This flips the conventional wisdom ...
Fossils reveal the long-term relationship between feathered dinosaurs and feather-feeding beetles
2023-04-17
New fossils in amber have revealed that beetles fed on the feathers of dinosaurs about 105 million years ago, showing a symbiotic relationship of one-sided or mutual benefit, according to an article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America today*.
The main amber fragments studied, from the Spanish locality of San Just (Teruel), contain larval moults of small beetle larvae tightly surrounded by portions of downy feathers. The feathers belonged to an unknown theropod dinosaur, either avian (a term referring ...