(Press-News.org) Berkeley — Rates of school discipline fluctuate widely and predictably throughout a school year and increase significantly faster for Black students than for their white counterparts, University of California, Berkeley, researchers have found.
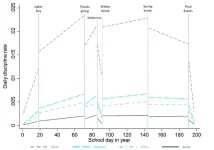
A new study published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences documents for the first time the “dynamic” nature of student discipline during an academic year. Daily rates of punishment across all schools in the study ratchet up in the weeks before Thanksgiving break, decline immediately before major vacations and increase rapidly again when classes resume.
Schools with a high degree of racial disparity regarding discipline referrals or suspensions early in the year see discipline rates for Black students increase even faster as the semester continues, researchers found. By November, the Black student discipline rate is 10 times higher than at the beginning of the year. Compared to white students, it’s 50 times higher.
“This work is a game-changer,” said Jason Okonofua, assistant professor of psychology at UC Berkeley, and the study’s principal investigator. “We can predict year-long suspension rates in just the first 21 days of school. That's information that we needed to know. And now we do.”
Okonofua and his colleagues used improved daily discipline-tracking technology to study the snapshots of middle school punishments. Going forward, the granular information they gleaned can help educators keep tabs on escalating school tension. It can even help teachers and school officials ward off potential discipline-causing incidents, much like they modify a lesson plan to overcome a learning gap in the classroom.
“The more information you have, the better decisions you can make,” Okonofua said. “If principals or teachers know by Halloween in any given year these students are facing this very heightened risk of being kicked out of school, or in which schools these students face the highest risk, we can get in there and do something about it, as opposed to letting it fester.
“Because the data shows, it would.”
Long the focus of federal inquiries, policy debate and scholarly interest, school discipline disparities have been well-documented nationwide. Recent research has shown that high school students who are suspended are more than twice as likely to be charged or convicted of a crime and incarcerated as young adults. Brief online coursework for teachers can even increase empathy and reduce suspensions. Yet, the debate is increasing about whether school officials should be quicker to kick students out of class.
While cycles of school tension might seem intuitive, the focus historically has not been on measuring punishment rates in real-time or introducing interventions before incidents occur.
Instead, districts collect data on student discipline and produce year-end reports for state and federal regulators to examine how discipline varies among schools, which ones are more punitive and where to target interventions. While that “static” data provides a summary of what’s gone on throughout the year, it fails to capture the day-to-day realities at school.
To understand this more “dynamic nature” of student discipline, Okonofua and his colleagues assembled four years of data about the daily disciplinary experiences of 46,964 students across 61 middle schools in one of the 10 largest school districts in the country. The district was located in a southern U.S. state and, like an increasing number of organizations, it had implemented a more sophisticated discipline data tracking system.
The results — especially the disparities — were immediately startling.
“It is incredibly important, useful and valuable to know we should do a specific type of intervention at a specific point in the year based on the real-time data. That's where we're going to get the biggest bang for our buck,” Okonofua said. “If we can be more cost-efficient, everybody wins.”
Okonofua’s co-authors — Sean Darling-Hammond of UCLA, Michael Ruiz of UC Berkeley and Jennifer L. Eberhardt of Stanford University — also published a short video that uses beeping tones to illustrate discipline disparities between Black and white students. The anxiety-inducing tones are meant to simulate how stressful school can be when students are witnessing increasing discipline.
Okonofua likened school discipline tracking tools to an athlete’s heart rate monitor at the gym. Rather than simply estimating how hard a workout was, real-time data can be more useful.
“The more data we have, the more we know,” Okonofua said. “And the more we know, the more we can do.”
The study shows how important it is for districts to create systems for teachers to regularly monitor school discipline, he said. Policy leaders should likewise take note as they write policies and dedicate funding meant to curb discipline, alleviate disparities and minimize disruption.
“It's important to think about each data point. That's a whole story,” said Okonofua, reflecting on discipline's lasting effects on both the student in trouble and classmates witnessing the punishment. “I hope we can do as much as possible going forward to just keep in mind that each one of these data points is a whole life.”
END
School discipline can be predicted, new research says. Is it preventable?
2023-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How electricity can heal wounds three times as fast
2023-04-18
Chronic wounds are a major health problem for diabetic patients and the elderly – in extreme cases they can even lead to amputation. Using electric stimulation, researchers in a project at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, and the University of Freiburg, Germany, have developed a method that speeds up the healing process, making wounds heal three times faster.
There is an old Swedish saying that one should never neglect a small wound or a friend in need. For most people, a small wound does not lead to any serious complications, but many common diagnoses ...
Orb weaver spider glue properties evolve faster than their glue genes, scientists find
2023-04-18
Spiders that don’t weave good silk don’t get to eat. The silk spiders produce which creates their webs is key to their survival – but spiders live in many different places which require webs fine-tuned for local success. Scientists studied the glue that makes orb weaver spiders’ webs sticky to understand how its material properties vary in different conditions.
“Discovering the sticky protein components of biological glues opens the doors to determining how material properties evolve,” said Dr Nadia Ayoub of Washington and Lee University, co-corresponding author of the study ...
Machine learning can help to flag risky messages on Instagram while preserving users’ privacy
2023-04-17
As regulators and providers grapple with the dual challenges of protecting younger social media users from harassment and bullying, while also taking steps to safeguard their privacy, a team of researchers from four leading universities has proposed a way to use machine learning technology to flag risky conversations on Instagram without having to eavesdrop on them. The discovery could open opportunities for platforms and parents to protect vulnerable, younger users, while preserving their privacy.
The team, led by researchers from Drexel University, Boston University, Georgia Institute of Technology ...
TOP advisory board welcomes new chair and members
2023-04-17
Charlottesville, VA – The Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines Advisory Board welcomes its new chair, Sean Grant, and board members to support its mission to promote transparency across the research lifecycle.
Grant is a Research Associate Professor at the HEDCO Institute for Evidence-Based Educational Practice at the University of Oregon with extensive experience researching TOP as Co-Principal Investigator for Transparency of Research Underpinning Social Intervention ...
UC Irvine physicists discover first transformable nano-scale electronic devices
2023-04-17
Irvine, Calif., April 17, 2023 — The nano-scale electronic parts in devices like smartphones are solid, static objects that once designed and built cannot transform into anything else. But University of California, Irvine physicists have reported the discovery of nano-scale devices that can transform into many different shapes and sizes even though they exist in solid states.
It’s a finding that could fundamentally change the nature of electronic devices, as well as the way scientists research atomic-scale quantum materials. The study is published ...
Dixit receives 2023 Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award
2023-04-17
Marm Dixit, a Weinberg Distinguished Staff Fellow at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was nominated for his work on imaging techniques for solid-state batteries.
Marm Dixit, a Weinberg Distinguished Staff Fellow at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was named the 2023 recipient of the Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award.
Since 2004, this biannual award has been given by the Advanced Photon Source (APS) user organization. It recognizes important scientific or technical accomplishments at (or beneficial to) the APS by a young investigator, typically a senior graduate student or early career researcher. The APS is a DOE Office ...
Medical dramas influence thoughts on dangers from vaping, new Twitter analysis reveals
2023-04-17
After three popular primetime medical dramas included storylines about health harms from using e-cigarettes, hundreds of people took to Twitter to comment – including some who said they planned to quit vaping because of what they saw on the shows. A new analysis led by University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health scientists and published in the Journal of Health Communication examines the tweets for insights into the use of television shows to share public health messaging.
Following the January 2020 episodes of New Amsterdam, Chicago Med and Grey’s Anatomy that each included plots involving adolescents with vaping-associated lung-injury, ...
The Green Mediterranean / high polyphenols diet promotes dramatic proximal aortic de-stiffening, twice as much as the healthy Mediterranean diet
2023-04-17
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, April 17, 2023 – The green Mediterranean – high polyphenols diet substantially regresses proximal aortic stiffness (PAS), a marker of vascular aging and increased cardiovascular risk. The green Mediterranean diet was pitted against the healthy Mediterranean diet and a healthy guideline-recommended control diet in the DIRECT PLUS, a large-scale clinical intervention trial. Researchers found that the green Mediterranean diet regressed proximal aortic stiffness by 15%, the Mediterranean diet by 7.3%, and ...
Therapeutic can seek and destroy potent opioid to treat overdoses
2023-04-17
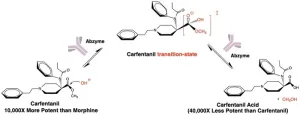
LA JOLLA, CA—A new therapeutic designed by Scripps Research chemists can alter the molecular structure of the potent opioid carfentanil, inactivating the opioid and reversing a carfentanil overdose. The compound, which is described in an ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science paper published on April 17, 2023, and hasn’t yet been studied in humans, works in a fundamentally different way than existing treatments for opioid overdose.
Carfentanil is up to 10,000 times more potent than morphine and 100 times stronger than fentanyl, making it one of the deadliest opioids. It is typically only used as a tranquilizer ...
No magic number for time it takes to form habits
2023-04-17
Putting on your workout clothes and getting to the gym can feel like a slog at first. Eventually, you might get in the habit of going to the gym and readily pop over to your Zumba class or for a run on the treadmill. A new study from social scientists at Caltech now shows how long it takes to form the gym habit: an average of about six months.
The same study also looked at how long it takes health care workers to get in the habit of washing their hands: an average of a few weeks.
“There is no magic number for habit formation,” says Anastasia Buyalskaya (PhD ’21), now an assistant professor of marketing at HEC Paris. Other authors ...