(Press-News.org)
The University of Virginia School of Medicine has launched a new Center for Health Equity and Precision Public Health to improve the health and well-being of rural residents, the economically challenged and minority groups across Virginia and beyond.
The center will bring to bear expertise from across UVA to tackle many of today’s greatest public health issues. The goal: reduce health disparities and promote health equity to help people live longer, healthier lives.
“The pandemic has really taught us that, one, our public health infrastructure is not nearly as strong as it should be. And, two, we can't think of healthcare and public health in this one-size-fits-all type of mentality,” said Keith L. Keene, PhD, the center’s founding director.
Keene has been recruited from East Carolina University, where he was the director of its Center for Health Disparities, for his far-reaching expertise in the subject. At UVA, he is taking a big-picture approach to complicated problems that he hopes will yield practical benefits for both society at large and individual patients.
In his new role, Keene is not only part of UVA’s Department of Public Health Sciences, but, as a researcher investigating the genetic risk factors for complex disease, he works closely with UVA’s Center for Public Health Genomics. Genomics is the study of an organism’s complete set of genetic material and the factors that affect gene function. One of Keene’s objectives is to connect that type of important but complex research directly with patient outcomes.
“Our goal here is to build a new center – an interdisciplinary center – that's really devoted to integrating precision medicine,” he said. “So we’ll use the genomics work that we do here in the Center for Public Health Genomics along with public health and health informatics approaches to think about how we can improve the health and well-being of rural, economically challenged and racial/ethnic minority populations.”
At first blush, it may seem contradictory to take such a macro approach when targeting individual outcomes. But capitalizing on vast amounts of data is one of the great opportunities of modern medical research. “We want to really factor in things such as the social determinants of health – how the conditions in which someone lives influences biology, or human diseases in our case,” Keene explained. “We can then see how the biology and environment interplay to create the overall health profile of individuals. Then we can take it a step further and think about how we can bring in data such as anonymized electronic health records to really give us a full picture of why certain individuals are more likely to have a particular disease or respond to a particular treatment.”
The result, he hopes, will be a new way of thinking about the holistic picture of human health. This, he says, will help us reduce health disparities, ensure health equity and move toward a society where every person can “attain his or her full health potential,” regardless of race, location or economic background.
“Being able to incorporate all of those types of data can really help us think about the overall picture of health and healthcare,” Keene said. “We see how desperately it is needed – across the state there is just an increasing lack of specialists and an increasing lack of access. We want to do something about that, and to ensure people have good options.”
Those goals align closely with UVA Health’s first-ever 10-year strategic plan, which aims to cultivate healthy communities, enable discoveries that benefit human health and ensure no Virginian needs to leave the state to receive even the most complex care.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog at http://makingofmedicine.virginia.edu.
END
Scientists in Melbourne have designed a new type of oral capsule that could mean pain-free delivery of insulin and other protein drugs.
Co-lead researcher Professor Charlotte Conn, a biophysical chemist from RMIT University, said protein drugs had proven challenging to deliver orally as the drugs degrade very quickly in the stomach – until now.
“These types of drugs are typically administered with an injection – thousands of diabetics in Australia need insulin injections up to several times a day, which can be unpleasant for the patient and results in high healthcare costs,” said Conn, from RMIT’s School of Science.
She said the new technology could also be ...
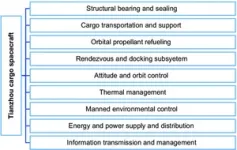
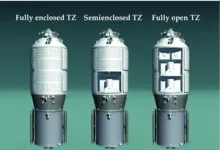
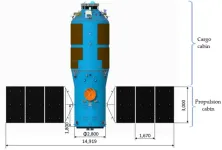
Cargo spacecraft is robotic spacecraft designed to support space station operation by transporting food, propellant and other supplies. Tianzhou cargo spacecraft (The abbreviation is TZ) is a Chinese automated cargo spacecraft developed by the China Academy of Space Technology, as part of China's manned space Station program. The China Academy of Space Technology began to design TZ in 2010. Its main tasks are transporting and storing supplies for the space station, storing and descending waste materials for the space ...
SAN ANTONIO – 4.19.23 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) will host the inaugural Global Decarbonized Mobility Summit (GDMS) on Nov. 13-17. The multi-day summit will bring together key stakeholders in the transportation industry to discuss technology challenges associated with sustainable decarbonized mobility solutions for on-and-off-road applications.
The GDMS will assemble industry members from SwRI’s many automotive-related consortia and joint industry projects at its San Antonio headquarters. Throughout the summit, SwRI staff experts will hold sessions on the latest research and development advancements, pathways ...
Researchers are beginning to better understand the toll of polarized politics on mental and physical health, and a new study suggests that Americans’ political anxiety crescendos before a major election.
Led by University of Nebraska–Lincoln political scientist Kevin Smith, with Aaron Weinschenk of the University of Wisconsin–Green Bay and Costas Panagopoulos of Northeastern University, the study is the first to examine anxiety tethered to a specific political event — the 2020 presidential election, touted by both sides as the ...
A recent study using mice has revealed a way to turn back the clock after heart attack. The researchers behind the work used RNAs to instruct cells in an injured heart to eliminate scar tissue and recreate cardiac muscle, allowing the heart to function like new again.
Cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, is the leading cause of death worldwide.
“Adult human hearts are not very good at repairing themselves,” said Conrad Hodgkinson, an associate professor of medicine and pathology at Duke University School of Medicine who oversaw the study. “Once they have a heart attack or any type of damage, ...
Does a commitment to one’s God facilitate altruistic behavior that benefits only members of the same religious group? Or does it extend to helping members of a different religion?
University of Illinois Chicago social psychologist Michael Pasek and colleagues examined this question through field and online experiments involving more than 4,700 people from diverse ethnoreligious populations in three political and cultural contexts.
Christians, Muslims, Hindus and Jews in the Middle East, Fiji and the United ...
Researchers from Johns Hopkins University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines how receiving negative medical results might affect how people choose between generic and brand name drugs.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Does Bad Medical News Reduce Preferences for Generic Drugs?” and is authored by Manuel Hermosilla and Andrew T. Ching.
At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, Manuel Hermosilla received a call from a family friend in Chile who had been recently diagnosed with cancer. The friend needed help tracking down Hydroxychloroquine to treat ...
The Japanese island Okinawa is known for its high number of centenarians, healthy diet and lifestyle. Due to this it is one of the few areas in the world that is called “blue zone”. During May 12-13, leading international scientists and inspiring speakers will meet on Okinawa for two full days of talks about the latest research on longevity and healthy ageing – and what we can learn from so called “blue zones”.
“It is a perfect place to interact, update and develop the research ...
Plants that glow under ultraviolet (UV) light aren’t only a figment of science fiction TV and movies. Roots of a traditional medicine plant called the orange climber, or Toddalia asiatica, can fluoresce an ethereal blue hue. And now, researchers in ACS Central Science have identified two coumarin molecules that could be responsible. These natural coumarins have unique fluorescent properties, and one of the compounds could someday be used for medical imaging.
Fluorescent substances take in UV light that’s directed ...
In a project commissioned by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have developed poly(styrenesulfonic acid)-based PEMs with a high density of sulfonic acid groups.
One of the key components of environmentally friendly polymer electrolyte fuel cells is a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM). It generates electrical energy through a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen gases. Examples of practical fuel cells include fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) and fuel cell combined heat and power (CHP) systems.
The best-known PEM is a membrane based on a ...