(Press-News.org) During pregnancy, women are more susceptible to severe respiratory infections from multiple viruses, including influenza A virus (IAV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Additionally, pregnant women are disproportionately affected by influenza, resulting in a more than 10-fold increase in hospitalization risk.
A new study led by Dr. Natalie Johnson, associate professor in the Texas A&M University School of Public Health’s Department of Environmental and Occupational Health, shows that exposure to ultrafine particles (UFPs) during pregnancy enhances respiratory viral infection risk. The results of the study were published recently in Particle and Fibre Toxicology.
“We know that air pollution affects the pulmonary immune system, making individuals more susceptible to viral infections,” Johnson said. “We also know pregnant women are already at increased risk for severe flu. Surprisingly, studies have not interrogated the combined effects of pregnancy, air pollution and influenza. Our findings demonstrate the need to further study these interactions in order to prevent short and perhaps long-term impacts on maternal health.”
In the study, Johnson and her co-authors point out that there are several physiological characteristics that explain maternal susceptibility to viral infection. Among those are increased cardiac output and decreased tidal volume — the amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs with each respiratory cycle — as well as immunological changes such as selective modulation of immune cell subsets to protect the developing fetus.
The research team also highlights that vaccination compliance during pregnancy is generally below 50 percent, despite vaccination against influenza being safe and effective, leading to increased risk for developing respiratory infection.
As a result, air pollution, which is a worldwide environmental health issue, is responsible for one in nine deaths with an annual premature mortality of more than 7 million. A mixture of gases and tiny airborne particulate matter, which is categorized as UFPs, are critical to recognize and identify, especially to protect vulnerable populations.
The research team says these findings support future clinical and regulatory interventions for protecting pregnant women and controlling UFPs. According to the researchers, it is imperative that pregnant women in urban cities, where influenza and UFPs are more prevalent, are provided vaccinations and preventive measures limiting UFP exposure to protect maternal health.
“Air pollution is a pervasive environmental health issue,” Johnson said. “Strategies to protect the most vulnerable, like pregnant women, are of high priority to decrease adverse health effects.”
Additional authors include Nicholas L. Drury, Texas A&M Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Texas A&M Department of Nutrition; Toriq Mustapha, Texas A&M Department of Environmental and Occupational Health; Ross A. Shore, Texas A&M Department of Environmental and Occupational Health, Jiayun Zhao, Texas A&M Department of Chemistry; Gus A. Wright, Texas A&M Department of Veterinary Pathobiology; Aline Rodrigues Hoffmann, University of Florida Department of Comparative, Diagnostic, and Population Medicine; Susanne U. Talcott, Texas A&M Department of Nutrition; Annette Regan, University of San Francisco School of Nursing and Health Professions; Robert M. Tighe, Duke University Department of Medicine; and Renyi Zhang, Texas A&M Department of Chemistry and Texas A&M Department of Atmospheric Sciences.
By Tim Schnettler, Texas A&M University School of Public Health
END
Exposure to air pollution during pregnancy increases risk for flu
A School of Public Health study shows exposure to ultrafine particles during pregnancy enhances the risk for respiratory viral infection.
2023-04-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Trim the sugar: New HIV vaccine design improves immune response
2023-04-20
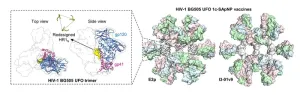
LA JOLLA, CA— A new HIV vaccine from Scripps Research has shown a significantly improved ability to neutralize the virus in preclinical tests, and it will soon be studied in healthy people who volunteer to participate in clinical trials.
The new and unique vaccine design, described in a paper in Nature Communications on April 9, 2023, uses tiny protein “nanoparticles” to display multiple copies of HIV’s surface protein Env, thus presenting itself to the immune system much as real HIV particles would ...
Immediate carbon cuts, common marine heatwave terminology urged
2023-04-20
Over the past two hundred years, the ocean and atmosphere have been accumulating massive amounts of carbon dioxide as factories, automobiles, airplanes, and more churn out the powerful greenhouse gas. Two articles published recently in Nature by University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa oceanographers provide a reality check on the limitations of carbon dioxide removal and a warning that marine heatwaves need clear definitions so communities can adapt.
Carbon dioxide removal is not the golden ticket
In all the scenarios assessed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, nations around the world must dramatically and rapidly reduce their dependence ...
Paul Hessburg receives Distinguished Landscape Ecologist Award
2023-04-20
Paul Hessburg received the International Association for Landscape Ecology-North America Chapter’s 2023 Distinguished Landscape Ecologist Award. The annual award recognizes major scientific contributions to landscape ecology, honors scientists who have played a pivotal role in shaping the field, and is the organization’s highest honor.
Hessburg is a senior research ecologist with the USDA Forest Service's Pacific Northwest Research Station based at the Wenatchee Forestry Sciences Laboratory. He was honored for a highly diverse career that has "greatly enhanced the capacity of landscape practitioners to develop strategies and ...
Cut council tax for green gardeners to help cities tackle climate change
2023-04-20
Homeowners should be rewarded to garden sustainably, new research by Professor of Environmental Horticulture at University of Sheffield, recommends
Rewards for sustainable gardening could include reductions to council tax, water bills or assistance with resources
Ensuring urban gardeners have the ability to have planted gardens will have numerous benefits for the environment and communities
Banning environmentally damaging materials, such as pesticides; or practices such as installing astroturf, could also benefit the environment
Research shows that some cities may have lost as much as 50 per cent of their green garden space over the last ...
Online tool found to be effective at assessing dementia risk
2023-04-20
Researchers at UNSW Sydney and Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA) have developed and evaluated a tool for assessing dementia risk, with promising initial results.
Currently, over 55 million people are living with dementia around the world, with that number set to increase to 78 million by 2030, and the focus on dementia research increasingly shifting towards prevention.
The online tool takes approximately 20 minutes to complete and provides a personalised dementia risk report that patients can discuss with their doctor.
Since developing the risk tool – known as CogDRisk – in 2022, the team has been evaluating the success of the tool, by trialling it on four existing datasets, ...
A myth no more: Cranberry products can prevent urinary tract infections for women
2023-04-20
Drinking cranberry juice has long been a mythical prevention strategy for women who develop a urinary tract infection – and new medical evidence shows consuming cranberry products is an effective way to prevent a UTI before it gets started.
A global study looking at the benefits of cranberry products published in Cochrane Reviews has determined cranberry juice, and its supplements, reduce the risk of repeat symptomatic UTIs in women by more than a quarter, in children by more than half, and in people susceptible to UTI following medical interventions by about ...
Recycling lake sediments for crop production: A sustainable solution for closing the phosphorus cycle
2023-04-20
A four-year field experiment conducted on the shores of restored Lake Mustijärv in Viljandi, Estonia, has revealed that recycling phosphorus-rich lake sediments back to agriculture could have positive impacts on crop production.
The study was conducted by doctoral researcher Mina Kiani and the AgriChar research group, and it is globally the first of its kind to cover the environmental aspects of recycling lake sediments to agriculture over several years. Kiani defends her thesis on 21 April at the University of Helsinki Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry.
The study aimed to find a sustainable solution for closing the leaking agricultural phosphorus (P) cycle by recycling P-rich ...
Chicken breeding in Japan dates back to fourth century BCE
2023-04-20
Conclusive evidence of chicken breeding in the Yayoi period of Japan has been discovered from the Karako-Kagi site.
The chicken is one of the most common domesticated animals, with a current estimated population of over 33 billion individuals. They are reared for their meat and eggs, and may be kept as pets.
The chicken is believed to have been domesticated in Southeast Asia about 3500 years ago, following which they were carried to all corners of the world. The exact date of introduction of chicken breeding to Japan is under debate, as there are no historical records and archeological evidence ...
Protecting the vision of premature babies
2023-04-20
AUGUSTA, Ga. (April 20, 2023) – In the spiraling cycle that can lead to vision loss in premature newborns, Medical College of Georgia scientists have found a new target and drug that together appear to stop the destruction in its tracks.
In babies, the development of the blood vessels of the retina should be complete by birth. But with preterm birth, the still-immature retina can develop a potentially blinding eye disorder known as retinopathy of prematurity.
When premature babies transition from inside the womb, where ...
African penguins: climate refugees from a distant past?
2023-04-20
Imagine the view from the western coastline of southern Africa during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) over twenty thousand years ago: in the distance you would see at least fifteen large islands – the largest 300 square kilometres in area – swarming with hundreds of millions of marine birds and penguin colonies.
Now imagine sea levels rising up to a hundred metres between fifteen to seven thousand years ago, gradually covering these large islands until only small hill tops and outcrops remained above water. Over the past 22 000 years this resulted in a tenfold ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] Exposure to air pollution during pregnancy increases risk for fluA School of Public Health study shows exposure to ultrafine particles during pregnancy enhances the risk for respiratory viral infection.