Highly sensitive and self-healing conductive hydrogels fabricated from cationic cellulose nanofiber-dispersed liquid metal for strain sensors
2023-04-21
(Press-News.org)
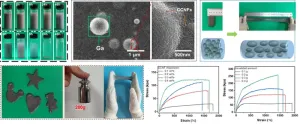
This study is led by Dr. Wenxia Liu (State Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials and Green Papermaking, Qilu University of Technology, Shandong Academy of Science). To uniformly disperse LM into hydrogel, she conceived and designed using CCNFs rich in quaternary ammonium groups to encapsulate LM droplets through an approach of Pickering emulsion. “The strong electrostatic attraction and ion-dipole interaction between the quaternary ammonium groups of CCNFs and the hydroxyl groups on LM droplet surfaces were expected to prevent the LM droplets from aggregation and coalescence. The incorporation of CCNFs into hydrogel with the LM droplets was also expected to improve the mechanical properties of hydrogel by forming a reversible hard polymer network. “Using CCNFs to prevent LM droplets from coalescence is a strategy of more with less” Liu says.
Master degree candidate Mr. Shihao Wu further designed the polymer matrix for the conductive hydrogel. “By inducing acrylic acid (AA) polymerization and crosslinking of poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) in the presence of a CCNF-stabilized LM emulsion, a conductive hydrogel was expected to be prepared with the formation of reversible hydrogen bonds, ionic coordination, electrostatic attraction and ion-dipole interaction among CCNFs, LM droplets, and PAA” Wu says.
Wu and another master degree candidate Miss Bingyan Wang performed the experiments in Liu’s Laboratory of Qilu University of Technology. The team collected and figured the related data. Liu and Wu analyzed the morphology and properties of the as-prepared LM emulsion and hydrogel.
The team found that bulk Ga could be broken into droplets in the presence of CCNFs under sonification. The formed Ga droplets possess a regular spherical shape with CCNFs covering their surfaces, where the CCNFs form mechanical barriers to prevent the Ga droplets from coalesce and aggregation, confirming the excellent stabilization effect of CCNFs on Ga droplets. In the presence of CCNF-encapsulated Ga droplets, a hydrogel could be formed at room temperature owing to the in situ polymerization of AA and ionic crosslinking of PAA promoted by Ga droplets and Ga3+ formed by reaction of Ga with AA, respectively. The ionically crosslinked PAA contributes a soft network while the reversibly crosslinked CCNFs by hydrogen, electrostatic attraction and ion-dipole interaction contribute a hard polymeric network for the hydrogel. The occurrence of double network and Ga/Ga3+ as well as the reversible crosslinking enables the hydrogel to possess good conductivity, excellent stretchability and tensile strength, good adhesiveness, quick self-healing capacity (see below).
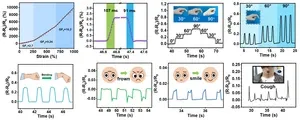
The researchers also explored the sensing performance and application of the hydrogels as a strain sensing material. They found that the hydrogel exhibited a very high sensing sensitivity (GF = 16.2), a low strain detection limit (less than 1%), a short response/recovery time (107/91 ms), and good repeatability and durability. When directly attached to human body via its adhesiveness, the hydrogel-based strain sensor could repeatedly monitor various human activities (see below). “The excellent sensing performance, self-adhesiveness and self-healing capacity enable the hydrogel-based strain sensor to be a good candidate for wearable electronics.” Wu and Liu say.
The good stability of LM emulsion and the compatibility of LM droplets with polymeric matrix are critical for uniformly dispersing LM droplets in hydrogel and fabrication of conductive hydrogels with high sensing preformation. The CCNFs provide good mechanical barriers for Ga droplets and improve the compatibility of Ga with PAA, enabling Ga droplets uniformly dispersing in PAA hydrogel. The combination of Ga, CCNFs and PAA allows the hydrogel to possess multifunctional properties and high sensing performance.
See the article:
Highly sensitive and self-healing conductive hydrogels fabricated from cationic cellulose nanofiber-dispersed liquid metal for strain sensors
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-022-2328-8
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-21
Recently-published research from an international team of physicists reveals how the three-dimensional shape of rigid microscopic filaments determines their dynamics when suspended in water, and how control of that shape can be used to engineer solid-like behavior even when the suspension is more than 99% water.
The paper, “Bonded straight and helical flagellar filaments form ultra-low-density glasses,” was co-authored by Georgetown physics professors Peter Olmsted and Jeffrey Urbach and graduate student Matthew ...
2023-04-21
The alga Melosira arctica, which grows under Arctic sea ice, contains ten times as many microplastic particles as the surrounding seawater. This concentration at the base of the food web poses a threat to creatures that feed on the algae at the sea surface. Clumps of dead algae also transport the plastic with its pollutants particularly quickly into the deep sea - and can thus explain the high microplastic concentrations in the sediment there. Researchers led by the Alfred Wegener Institute have now reported this in the journal Environmental Science and Technology.
It is a food lift for bottom-dwelling animals in the deep sea: the alga Melosira arctica grows ...
2023-04-21
The genomes of two hornet species, the European hornet and the Asian hornet (or yellow-legged hornet) have been sequenced for the first time by a team led by UCL (University College London) scientists.
By comparing these decoded genomes with that of the giant northern hornet, which has recently been sequenced by another team, the researchers have revealed clues suggesting why hornets have been so successful as invasive species across the globe.
Hornets are the largest of the social wasps; they play important ...
2023-04-21
Running is one of the most accessible forms of exercise with an array of proven cardiovascular and musculoskeletal benefits, and an added bonus of increased mental health. Good quality running gear, such as the right pair of shoes, is vital to improve running performance and reduce injury risk. For women particularly, a well-designed sports bra protects from exercise-induced breast pain, which can be a significant barrier to practicing sports. Up to 72% of women experience breast pain while running.
Previous research has shown that the increased ...
2023-04-21
SAN ANTONIO – 4.20.23 -Scientists from Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) led a team in the unique Citizen Continental-America Telescopic Eclipse (CATE) experiment to image the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona, during a short solar eclipse on the opposite side of the Earth. Using four platforms in the northwest corner of Australia, the team successfully observed the million-degree solar corona at the April 20 eclipse viewed from the Exmouth peninsula. The Australian eclipse serves both as a unique scientific opportunity and a training exercise for the program’s leadership in preparation ...
2023-04-21
Staff in public and private hospitals in Mexico City are likely to follow well-established and reinforced earthquake early warning (EEW) protocols for evacuation, according to an ongoing study.
Overall, staff are likely to follow the protocols especially when they are “reinforced with drills that help practice the correct protective action,” said Sandra Vaiciulyte of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. She discussed her research at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)’s 2023 Annual Meeting.
In the study, there have been “no accounts of injuries of patients and staff because of the particular reaction by staff,” ...
2023-04-21
Concern about the mental health of hospital professionals has been increasing in recent years, and when, in early 2020, the Covid-19 pandemic was declared and rapidly spread, there was a large increase in the overload of workers in Intensive Care Units (ICUs). Given this, researchers from the D’Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) and other national institutions assessed the prevalence and extent of psychological disorders such as burnout, anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder ...
2023-04-21
Faults in the Ridgecrest, California area were very sensitive to solid earth tidal stresses in the year and a half before the July 2019 Ridgecrest earthquake sequence, researchers reported at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)’s 2023 Annual Meeting.
“The signal of tidal modulation becomes extremely strong” after 2018, said Eric Beauce of Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, who noted that the signal was identified with seismicity that occurred around the faults that broke in the 2019 magnitude 7.1 earthquake.
The link ...
2023-04-21
A new study published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD])finds that individuals who experienced childhood adversity are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes (T2D) in early adulthood.
The research was conducted by Assistant Professor Leonie K. Elsenburg and colleagues at the Section of Epidemiology, Department of Public Health, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark and aimed to determine whether there was a link between childhood adversity and the development ...
2023-04-21
Nurses exposed to 40 minutes of bright light before their night shifts feel less fatigued and make fewer errors at work, according to a study led by McGill University. The nurses also slept better after their shifts.
“Healthcare workers are experiencing high levels of fatigue due to staffing shortages, difficult schedules, and heavy workloads. Further, the cost of medical errors has been estimated at tens of billions of dollars per year in North America,” says Jay Olson, the senior author of the recent study in Sleep Health, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Highly sensitive and self-healing conductive hydrogels fabricated from cationic cellulose nanofiber-dispersed liquid metal for strain sensors