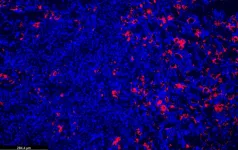
(Press-News.org) Despite the promise of new medications that promote cancer cell death in people with acute myeloid leukemia, leukemic cells often adopt features that let them evade the drugs’ effects within a year.
Now, new research using human tissue samples and mouse models has found that resistance of leukemia cells to a widely prescribed drug called venetoclax occurs because of a rapid increase in the breakdown and turnover of mitochondria, structures inside the cell that help power its functions. In addition to their role in producing energy, mitochondria also tell cells to die under certain adverse conditions.
This process of “programmed cell death” often goes wrong in cancer. Damaged mitochondria can also undergo a form of “self-eating” termed mitophagy that prevents them from sending “death signals.”
Led by scientists at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, the study showed that mitophagy helps leukemia cells to evade the killing effects of venetoclax, a drug in a class of medications known as BH3 mimetics.
Publishing in the journal Cancer Discovery online April 24, researchers found that the levels of several genes associated with mitophagy were increased in 20 leukemia patient samples compared with normal controls. The level of these genes was even higher in samples from leukemia patients with drug resistance than in those leukemic patients who were not. Particularly notable was the increased expression of the gene for Mitofusin-2 (MFN2), which codes for a key protein in the outer mitochondrial membrane.
Further experiments using mice into which bone marrow from acute myeloid leukemia patients was transplanted showed that the drug chloroquine, a known mitophagy inhibitor, restored the ability of venetoclax to kill the cancer cells.
“Overcoming resistance to BH3 mimetic drugs like venetoclax is of unique clinical significance because these medications are often used for treating people with acute myeloid leukemia,” said study co-lead investigator Christina Glytsou, PhD, a former postdoctoral researcher at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and now an assistant professor at Rutgers University.
“Acute myeloid leukemia is notoriously difficult to treat, with fewer than a third of those affected living longer than five years after their diagnosis, so it is important to maximize the impact of existing therapies,” said study co-lead investigator Xufeng Chen, PhD, an instructor in the Department of Pathology at NYU Grossman.
“Our preclinical findings suggest that combining BH3 mimetics like venetoclax with either MFN2 or general mitophagy inhibitors could possibly serve as a future therapy for acute myeloid leukemia, as current drug treatments are stalled due to drug resistance,” said study senior investigator Iannis Aifantis, PhD.
Aifantis, the Hermann M. Biggs Professor and chair of the Department of Pathology at NYU Grossman and Perlmutter, says the research team plans to design a clinical trial to test whether chloroquine, when used in combination with venetoclax, prevents drug resistance in people with acute myeloid leukemia.
Speaking about other study results, the researchers say they not only found that MFN2 was overly active in people with drug-resistant disease, but also that cancer cells exposed to similar cell-death-inducing compounds demonstrated a doubling in mitophagy rates.
Additional testing in cancer cells engineered to lack MFN2 showed increased sensitivity to drugs similar to venetoclax compared with cells that had functional MFN2. The new study and previous research by the team showing misshapen mitochondria in drug-resistant leukemic cells confirmed that increased mitophagy was the source of the problem.
Acute myeloid leukemia, the most common form of adult leukemia, originates in the bone marrow cells and involves the rapid buildup of abnormal blood cells. The blood cancer results in the deaths of more than 11,500 Americans annually. Current treatments include chemotherapy and a limited number of targeted drug therapies. Bone marrow transplantation has also been used when other options fail.
Funding support for the study was provided by National Institutes of Health grants P30CA016087, P30CA013330, R01CA178394, R01CA173636, R01CA228135, R01CA229086, R01CA242020, and K99CA252602. Additional funding support was provided by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society and by AstraZeneca, which provided several of the BH3 mimetic drugs used in these experiments.
Aifantis has received additional research funding from AstraZeneca. This arrangement is being managed in accordance with the policies and practices of NYU Langone Health.
Besides Glytsou, Chen, and Aifantis, other NYU Langone study investigators are Wafa Al-Santli, Hua Zhou, Bettina Nadorp, Soobeom Lee, Audrey Lasry, Zhengxi Sun, Dimitrios Papaioannou, Michael Cammer, Kun Wang, and Aristotelis Tsirigos. Other study co-investigators are Emmanouil Zacharioudakis and Evripidis Gavathiotis, at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York, who have filed a patent on mitofusin inhibition based on this research; Tomasz Zal, Malgorzata Anna Zal, Bing Carter, Jo Ishizawa, and Michael Andreeff, at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston; and Raoul Tibes, at AstraZeneca in Cambridge, the United Kingdom.
Media Inquiries
David March
212-404-3528
david.march@nyulangone.org
STUDY LINK (WILL BECOME ACTIVE AFTER EMBARGO LIFTS)
https://aacrjournals.org/cancerdiscovery/article/doi/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0601
END
Drug combination restores ability of leading treatment to signal for death of blood cancer cells
Future clinical trials to determine if combination chloroquine and venetoclax addresses disease comeback
2023-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Increased risk of testicular cancer in people with neurodevelopmental disorders
2023-04-24
A new study by researchers at Uppsala University and Uppsala University Hospital shows that men who have a neurodevelopmental disorder, such as autism and ADHD, also have a slightly increased risk of testicular cancer, or seminoma. This is the first study to show such a link, with the results to be published in the British Journal of Cancer.
Testicular cancer is the most common form of cancer in young men, and its underlying causes are still largely unknown.
“As testicular cancer can be surgically removed, thus curing the disease, it is important to seek care in time if you feel a lump in your testicle,” notes Ingrid ...
Single CT scan in kids low risk for cancers, but 4 or more CTs increases risk
2023-04-24
For children under age 18 years, a single computed tomography (CT) scan is not associated with an increased risk of brain tumours, leukemia or lymphoma, but exposure to 4 or more scans before adulthood more than doubles the risk, according to new research https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221303 in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Computed tomography in children has increased worldwide in recent decades, but there is conflicting evidence about the risks of cancer from these ...
New programmable smart fabric responds to temperature and electricity
2023-04-24
A new smart material developed by researchers at the University of Waterloo is activated by both heat and electricity, making it the first ever to respond to two different stimuli.
The unique design paves the way for a wide variety of potential applications, including clothing that warms up while you walk from the car to the office in winter and vehicle bumpers that return to their original shape after a collision.
Inexpensively made with polymer nano-composite fibres from recycled plastic, the programmable fabric can change its colour and shape when stimuli are applied.
“As a wearable material alone, it has almost infinite potential ...
International study recommends replacing skull section after treatment for a brain bleed
2023-04-23
A major international trial has concluded that, where possible, surgeons should replace the removed section of the skull following surgery to treat a form of brain haemorrhage. This approach will save patients from having to undergo skull reconstruction further down the line.
The RESCUE-ASDH trial, funded by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), involved 40 centres in 11 countries and involved 450 patients. The results of the trial are published today in the New England Journal of Medicine and are announced at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological ...
Achieving prevention and health, rather than more healthcare
2023-04-23
If more people have access to health insurance, we have to be sure the death rates of those with certain chronic conditions are decreasing.
This is one of the statements Gregory Peck, an acute care surgeon and associate professor at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, will be researching on behalf of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) at the National Institutes of Health.
Funded by NIH grants totaling more than $1 million through a recent two-year award from the New Jersey Alliance for Clinical and Translational Science (NJ ACTS), a Rutgers hub of the National Center for Advancing ...
Inflammation ‘brake’ gene may help reveal outcomes of kidney disease
2023-04-23
A discovery about gene variants of an inflammation ‘brake’ brings scientists a step closer to personalised treatment for patients at risk of kidney disease and kidney failure.
Researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, University of New South Wales, Sydney and Westmead Hospital, found that common genetic variants of TNFAIP3, which increase inflammation in the body, can paradoxically protect the kidneys from damage in the short term.
“We wanted to investigate whether inherited differences in how people regulate inflammation could lead to better or worse kidney health outcomes,” says Professor Shane ...
Too much insulin can be as dangerous as too little
2023-04-22
Just over a century has passed since the discovery of insulin, a time period during which the therapeutic powers of the hormone have broadened and refined. Insulin is an essential treatment for type 1 diabetes and often for type 2 diabetes, as well. Roughly 8.4 million Americans use insulin, according to the American Diabetes Association.
One hundred years of research have greatly advanced medical and biochemical understanding of how insulin works and what happens when it is lacking, but the reverse, how potentially fatal insulin hyper-responsiveness is prevented, has remained a persistent mystery.
In a new study, published in the April 20, 2023 online edition ...
From sheets to stacks, new nanostructures promise leap for advanced electronics
2023-04-22
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have successfully engineered multi-layered nanostructures of transition metal dichalcogenides which meet in-plane to form junctions. They grew out layers of multi-layered structures of molybdenum disulfide from the edge of niobium doped molybdenum disulfide shards, creating a thick, bonded, planar heterostructure. They demonstrated that these may be used to make new tunnel field-effect transistors (TFET), components in integrated circuits with ultra-low power consumption.
Field-effect transistors ...
How alcohol consumption contributes to chronic pain
2023-04-21
LA JOLLA, CA—Chronic alcohol consumption may make people more sensitive to pain through two different molecular mechanisms—one driven by alcohol intake and one by alcohol withdrawal. That is one new conclusion by scientists at Scripps Research on the complex links between alcohol and pain.
The research, published in the British Journal of Pharmacology on April 12, 2023, also suggests potential new drug targets for treating alcohol-associated chronic pain and hypersensitivity.
“There is an urgent need to better ...
Want to make better materials? Read between the lines. Or the “grain boundaries,” as they’re known in materials science.
2023-04-21
The orientations of these infinitesimally small separations between individual “grains” of a polycrystalline material have big effects. In a material such as aluminum, these collections of grains (called microstructures) determine properties such as hardness.
New research is helping scientists better understand how microstructures change, or undergo “grain growth,” at high temperatures.
A team of materials scientists and applied mathematicians developed a mathematical model that more accurately describes such microstructures by integrating data that can be identified from highly magnified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Drug combination restores ability of leading treatment to signal for death of blood cancer cellsFuture clinical trials to determine if combination chloroquine and venetoclax addresses disease comeback