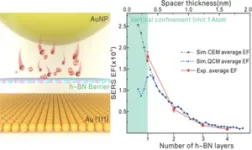
(Press-News.org) A research team led by Prof. YANG Liangbao from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences found that hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) could effectively block electron tunneling and extend the ultimate plasmonic enhancement limits in a single-atom-layer gap, providing deep insights into quantum mechanical effects in plasmonic systems and enabling potential novel applications based on quantum plasmonics.
The results were published in Nano Letters.
The team have been working on developing surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection methods for years and found that the near-field intensity distribution in the nanometer scale is uneven. To achieve greater electromagnetic enhancement, they used adjacent metal nano-gaps but noticed that reducing their size leads to the emergence of quantum tunneling effect, making it disadvantageous for SERS detection.
To overcome this, the team introduced a high tunneling barrier formed by monolayer h-BN, actively blocking the electron tunneling effect. They quantitatively detected the final near-field enhancement limit in the classical framework by detecting the intrinsic SERS intensity of h-BN in a single particle cavity.
The study proved that monolayer h-BN blocks the electron tunneling using hot electron tunneling quantum computation and layer-dependent scattering spectrum experiments. By comparing the experimental results with the calculated results of the classical electromagnetic model and the quantum correction model, the team realized the final near-field enhancement limit detection within the classical framework.
This work provides important guidance for quantum plasmology and nano-gap photodynamics, helping to further analyze quantum mechanical effects in plasma enhancement. These findings are published in the top international journal Nano Letters and selected as the cover of the current issue.
END
Monolayer hexagonal boron nitride can extend plasmonic enhancement limit
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
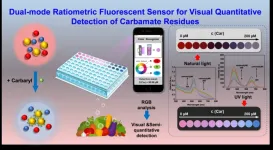
New dual mode ratio fluorescence sensing system enables rapid in situ detection of carbaryl residues
2023-04-25
A team of researchers led by Prof. JIANG Changlong from Institute of Solid State Physics (ISSP), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a new sensing system for detecting carbaryl residues.
The research findings have been published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Carbaryl is a widely used insecticide that can easily enter the body through respiratory intake and dermal contact, resulting in serious health hazards, including carcinogenicity and reproductive abnormalities. Therefore, it is crucial to detect carbaryl residues in environmental and food samples. However, ...
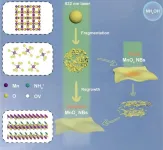
Defect-rich MnOx nanobelts prepared for glutathione detection in recent study
2023-04-25
A recent study published in Sensors and Actuators: B. Chemical highlights the development of highly active oxidase mimics using MnOx nanobelts (NBs) generated through laser irradiation in liquid (LIL) techniques by researchers from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institute of Physical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Although nanozymes with oxidase mimic activity have shown promise for biomarker sensing, their lower activity compared to natural enzymes has constrained their wider application.
In this research, the team identified that MnOx NBs with an ultrathin layered structure ...
Novel treatment regimen appears well tolerated, beneficial to children with relapsed brain tumors
2023-04-25
AUGUSTA, Ga. (April 25, 2023) – The first in-human-study of a new immunotherapy that blocks a natural enzyme tumors commandeer for their protection was well tolerated by children with relapsed brain tumors and enabled many to have unexpected months of a more normal life, researchers say.
“Our kids were by and large out of the hospital and going about their daily activities. They were in school, we had young adults who were in college living in a dorm on their own, taking their medicine on their own and coming to see us once a month,” says Theodore S. Johnson, MD/PhD, pediatric hematologist/oncologist ...
Signs you could be suffering from racial trauma – and tools for healing, according to therapists
2023-04-25
In the United States, depression and anxiety are on the rise in African Americans and the evidence suggests that racism is a contributing factor, creating a ripple effect on mental health.
Janeé M. Steele Ph.D. and Charmeka S. Newton, Ph.D. are licensed mental health professionals and scholars who specialize in culturally responsive therapy. They say: “In the Black community there can be a real resistance to our own trauma – for example, if I wasn’t exposed to physical abuse, is it really that bad?
“But this kind of systemic, permeating racism that exists all ...
Researchers reveal an ancient mechanism for wound repair
2023-04-24
It’s a dangerous world out there. From bacteria and viruses to accidents and injuries, threats surround us all the time. And nothing protects us more steadfastly than our skin. The barrier between inside and out, the body’s largest organ is also its most seamless defense.
And yet the skin is not invincible. It suffers daily the slings and arrows of outrageous fortune, and it tries to keep us safe by sensing and responding to these harms. A primary method is the detection of a pathogen, which kicks the immune system into action. But new research from the lab of Rockefeller’s Elaine Fuchs, published in Cell, reveals an alternative protective ...
Using superconductors to move people, cargo and energy through one combined system
2023-04-24
The promise of superconductivity for electrical power transmission and transportation has long been held back by high costs. Now researchers from the University of Houston and Germany have demonstrated a way to cut the cost and upend both the transit and energy transport sectors by using superconductors to move people, cargo and energy along existing highway infrastructure.
The combined system would not only lower the cost of operating each system but would also provide a way to store and transport liquified hydrogen, an important ...
Brian Clark selected to speak, presented discoveries at NIH workshop and in Journal of Gerontology
2023-04-24
Ohio University Professor of Physiology and Executive Director of the Ohio Musculoskeletal and Neurological Institute (OMNI) Brian Clark Ph.D. was one of 40 expert leaders in the field of aging from around the world chosen to present at a workshop hosted by the National Institute of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Aging (NIA) on the development of function promoting therapies for age-related weakness. Clark was also asked by the NIH to publish a comprehensive review of his research over the past decade in the Journal of Gerontology.
The workshop covered ...
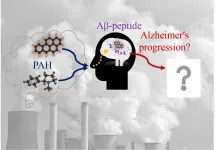
Increased risk of Alzheimer's disease due to exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
2023-04-24
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are typical organic compounds found in cigarette smoke and vehicle exhaust. In addition, PAHs are produced from incomplete combustion of organic material and cooking. The highest concentrations of PM-bound PAHs ranged from 550 ng/m3 to 39000 ng/m3, were observed in Chinese kitchens, fire stations, and ships. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons may combine with ultrafine particles (UFPs) in the air to form particle-bound PAHs. PM0.1 may adsorb large amounts of toxic organic compounds, and long-term exposure to indoor UFPs from cooking resulted in ...
This gel stops brain tumors in mice. Could it offer hope for humans?
2023-04-24
Medication delivered by a novel gel cured 100% of mice with an aggressive brain cancer, a striking result that offers new hope for patients diagnosed with glioblastoma, one of the deadliest and most common brain tumors in humans.
“Despite recent technological advancements, there is a dire need for new treatment strategies,” said Honggang Cui, a Johns Hopkins University chemical and biomolecular engineer who led the research. “We think this hydrogel will be the future and will supplement current treatments for brain cancer.”
Cui’s team combined an anticancer drug and ...
New tools capture economic benefit of restoring urban streams
2023-04-24
An interdisciplinary team of researchers has developed a suite of tools to estimate the total economic value of improving water quality in urban streams. The work can assist federal and state agencies charged with developing environmental regulations affecting urban ecosystems across the Piedmont Region of the United States, which stretches from Maryland to Alabama.
“Urban streams are ubiquitous and face a number of stressors from rapid economic development,” says Roger von Haefen, professor of agricultural and resource economics at North Carolina State University and corresponding ...