(Press-News.org) Researchers have a new scientific tool called Polybot, combining the power of artificial intelligence with robotics. Potential applications include speeding up the discovery of wearable biomedical devices, materials for better batteries and more.
Today’s wearable technologies like smart glasses and watches are just the start. The next generation of flexible electronics will be more efficient and sustainable, better able to monitor our health and treat certain diseases, and much more. They will be composed of electronic polymer materials — a soft pliable substance that can conduct electricity.
“Just imagine the next generation of polymer electronics,” said Jie Xu, assistant chemist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory with a joint appointment in the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago. “They are not going to be rigid anymore.”
To hasten the discovery time, researchers at Argonne have a new tool, a self-driving laboratory called Polybot that automates aspects of electronic polymer research and frees scientists’ time to work on tasks only humans can accomplish. This tool combines the computational power of artificial intelligence (AI) with the automation possible with robotics. It is housed in the Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM), a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne.
“We have plans in place to expand the capabilities of our self-driving lab to take advantage of other Argonne scientific facilities.” — Henry Chan, assistant scientist in the Center for Nanoscale Materials at Argonne.
Polybot is one of several autonomous discovery labs starting up at Argonne and other research organizations. While still in their infancy, their main purpose is to harness the power of AI and robotics to streamline experimental processes, save resources and accelerate the pace of discovery.
The potential applications of Polybot extend far beyond biomedical devices, Xu said. They include materials for computing devices with brain-like features and new sensors for monitoring climate change. They also include new solid electrolytes that would eliminate the current liquid electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries, making them less likely to catch fire.
Using Polybot, the CNM team is focusing on polymer electronics for energy-saving and medical purposes. These include devices that are recyclable or decompose after use.
Scientists usually prepare polymers for electronics by synthesizing polymer molecules with desired chemical structures, creating a solution with a mixture of many components. They then convert the solution into a thin layer of solid material. Layers of different compositions printed together serve as the basis for making different types of devices.
To achieve targeted performance, the number of potential tweaks is overwhelming. They run from spiking the fabrication recipe with different formulations to varying the processing conditions. By conventional experimental means, such development can take years of intense labor. Polybot can greatly reduce the development time and cost.
A typical experiment with Polybot begins by using AI and robots for different tasks. The automated system chooses a promising recipe for a polymer solution, prepares it and prints it as a very thin film at a selected speed and temperature. The system then hardens this film for an optimal length of time and measures key features, such as thickness and uniformity, as a quality check. Next, it assembles multiple layers together and adds electrodes to form a device.
After that, Polybot measures the device’s electrical performance. All the relevant data are automatically recorded and analyzed with machine learning and passed to the AI component. The AI then direct what experiments to do next. Polybot can also respond to feedback provided by users and data from the scientific literature.
“This is all done with minimal human intervention,” Xu said.
“We have plans in place to expand the capabilities of our self-driving lab to take advantage of other Argonne scientific facilities,” said Henry Chan, a CNM assistant scientist.
Already, the properties of electronic devices fabricated in Polybot have been analyzed with a powerful X-ray beam. This was done by using an instrument with a robotic sample handler at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne. And that connection could be strengthened to take full advantage of the APS after its upgrade is complete in 2024.
“X-ray scattering analysis expands the Polybot’s characterization down to the molecular level, revealing information about the orientation and packing of the molecules that can help speed up the search for the best materials with optimal performance,” said Joseph Strzalka, a physicist in Argonne’s X-ray Science division. “We are working on bringing the Polybot’s capabilities to an APS beamline so we can generate the large numbers of materials the APS upgrade will be capable of studying.”
“We are excited at the prospect of leveraging the supercomputing capabilities at Argonne to enhance Polybot,” Chan explained. “The goal is to conduct physics-based simulations prior to, during and after an actual experiment to gain deeper insights into a material or device and provide better feedback to the AI.” The team plans to utilize the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility, a DOE Office of Science user facility, to perform the simulations. This will streamline the discovery process even further.
With these capabilities and more, self-driving labs like Polybot have the potential to accelerate the discovery process from years to months. They also could reduce the cost of complex projects from millions to thousands of dollars.
In an article published as the cover story in Chemistry of Materials, Xu and Chan along with Aikaterini Vriza shared their vision on using self-driving laboratories for different types of materials research. This research was supported by the DOE Office of Basic Energy Sciences and Laboratory Directed Research and Development funding from Argonne.
About Argonne’s Center for Nanoscale Materials
The Center for Nanoscale Materials is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers, premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE’s Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge, Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit https://science.osti.gov/User-Facilities/User-Facilities-at-a-Glance.
The Argonne Leadership Computing Facility provides supercomputing capabilities to the scientific and engineering community to advance fundamental discovery and understanding in a broad range of disciplines. Supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Office of Science, Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR) program, the ALCF is one of two DOE Leadership Computing Facilities in the nation dedicated to open science.
About the Advanced Photon Source
The U. S. Department of Energy Office of Science’s Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the world’s most productive X-ray light source facilities. The APS provides high-brightness X-ray beams to a diverse community of researchers in materials science, chemistry, condensed matter physics, the life and environmental sciences, and applied research. These X-rays are ideally suited for explorations of materials and biological structures; elemental distribution; chemical, magnetic, electronic states; and a wide range of technologically important engineering systems from batteries to fuel injector sprays, all of which are the foundations of our nation’s economic, technological, and physical well-being. Each year, more than 5,000 researchers use the APS to produce over 2,000 publications detailing impactful discoveries, and solve more vital biological protein structures than users of any other X-ray light source research facility. APS scientists and engineers innovate technology that is at the heart of advancing accelerator and light-source operations. This includes the insertion devices that produce extreme-brightness X-rays prized by researchers, lenses that focus the X-rays down to a few nanometers, instrumentation that maximizes the way the X-rays interact with samples being studied, and software that gathers and manages the massive quantity of data resulting from discovery research at the APS.
This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation’s first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America’s scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.
END
Argonne’s self-driving lab accelerates the discovery process for materials with multiple applications
Autonomous discovery lab leading the way in transforming scientific research on sustainable and bio-inspired microelectronics
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Champion for improved perioperative care for older adults: Shelley R. McDonald, DO, PhD, MCG honored as AGS Clinician of the Year
2023-04-25
New York (April 25, 2022) — The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) today announced Shelley R. McDonald, DO, PhD, MCG, as 2023 Clinician of the Year. Dr. McDonald, who is an Associate Professor of Internal Medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, will be honored at the 2023 AGS Annual Scientific Meeting (#AGS23) being held in Long Beach, CA, from May 4-6 (preconference day is May 3).
“Our 2023 Clinician of the year, Dr. Shelley McDonald, is a national champion for improved perioperative care of older adults undergoing surgery,” said ...
RCT-DUPLICATE findings demonstrate capability of real-world evidence studies to reach conclusions similar to randomized clinical trials
2023-04-25
NEW YORK, April 25, 2023 ‒ Aetion®, the global leader in real-world evidence (RWE) technology and analytics, is pleased to announce the culmination of the RCT-DUPLICATE demonstration project, with complete findings published today in The Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). This three-year initiative tested whether researchers asking clinical questions in real-world data (RWD) — data from patients’ day-to-day interactions with the healthcare system — would obtain similar results to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs). In cases where clinical trial designs aligned with real patient care processes, the RWE studies and RCTs came ...
Exposure to cannabinoids in pregnancy increases newborn mortality and respiratory problems
2023-04-25
Consumption of cannabis (marijuana) or derivatives during pregnancy can cause respiratory problems for the baby, such as impaired control of breathing and diminished sensitivity to carbon dioxide, both of which favor sudden infant death syndrome. These are the main findings of a study conducted in Brazil and reported in an article published in the British Journal of Pharmacology.
The authors are researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) and the University of São Paulo (USP). They gave pregnant rats a synthetic compound (WIN 55) that acts on the brain in a similar manner to natural cannabinoids. Harmful effects occurred mainly in male pups.
“Cannabis ...
Matching form and function of brain cell types
2023-04-25
Investigators at Cedars-Sinai have created computer-generated models to bridge the gap between “test tube” data about neurons and the function of those cells in the living brain. Their study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications, could help in the development of treatments for neurological diseases and disorders that target specific neuron types based on their roles.
“This work allows us to start looking at the brain like the complex machine that it is, rather than ...
Small steps can yield big energy savings and cut emissions from MRIs
2023-04-25
Medical centers around the world could significantly reduce their carbon footprint and expenses by turning off MRIs and putting them in the lowest power mode instead of idling them when not in use, a new study in Radiology found.
Health care is responsible for up to 4.4% of global carbon emissions, and imaging contributes an outsized share due to its energy-intensive devices, especially MRI. A 2020 study found that three CTs and four MRIs used the same amount of energy per year as a town of 852 people, for example.
Though turning a machine off is better than idling, a substantial amount of MRI energy consumption occurs in “off” ...
Study links nutrients, brain structure, cognition in healthy aging
2023-04-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, scientists explored the links between three measures known to independently predict healthy aging: nutrient intake, brain structure and cognitive function. Their analysis adds to the evidence that these factors jointly contribute to brain health in older adults.
Reported in the Journal of Nutrition, the study found that blood markers of two saturated fatty acids, along with certain omega-6, -7 and -9 fatty acids, correlated with better scores on tests of memory and with larger brain structures in the frontal, ...
UNC Charlotte faculty member receives NASA Exobiology grant
2023-04-25
For the first time in the University of North Carolina at Charlotte’s nearly 80-year history, a faculty member has won a NASA Exobiology grant. Assistant Professor of Bioinformatics and Genomics Richard Allen White III will use the ultra-competitive grant in his research on microbialites, a kind of “living rock” that could hold the key to how life formed on Earth.
Microbialites form when microbial mats, living colonies of mostly bacteria, transform into stronger hard structures. White explores how viruses may have helped to kickstart the transformation (i.e., lithification) of modern microbialites, which ...
Study: Treatment for opioid addiction lags despite policies designed to increase it
2023-04-25
Treating opioid addiction should be much easier now than it was a few years ago, thanks to pandemic-era rule changes that aim to improve access to buprenorphine, a medicine proven to help in recovery.
But a new study shows the rate of people starting on buprenorphine remained flat from 2019 through 2022, while the percentage of patients who stayed on buprenorphine for at least six months hovered at just over 20% from 2016 through 2022.
Until more health care providers start offering buprenorphine treatment -- and to take advantage of opportunities like emergency visits and hospitalizations ...
Creating a tsunami early warning system using artificial intelligence
2023-04-25
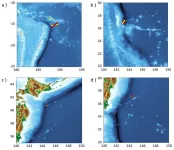
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – Tsunamis are incredibly destructive waves that can destroy coastal infrastructure and cause loss of life. Early warnings for such natural disasters are difficult because the risk of a tsunami is highly dependent on the features of the underwater earthquake that triggers it.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles and Cardiff University in the U.K. developed an early warning system that combines state-of-the-art acoustic technology with artificial intelligence to immediately classify earthquakes and determine potential tsunami ...
Lead vocal tracks in popular music go quiet
2023-04-25
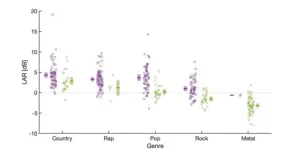
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – A general rule of music production involves mixing various soundtracks so the lead singer’s voice is in the foreground. But it is unclear how such track mixing – and closely related lyric intelligibility – has changed over the years.
Scientists from the University of Oldenburg in Germany carried out an analysis of hundreds of popular song recordings from 1946 to 2020 to determine the lead vocal to accompaniment ratio, or LAR. Their results appear in JASA Express Letters, published on behalf of the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Argonne’s self-driving lab accelerates the discovery process for materials with multiple applicationsAutonomous discovery lab leading the way in transforming scientific research on sustainable and bio-inspired microelectronics