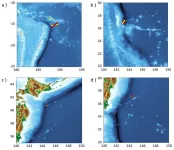
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – Tsunamis are incredibly destructive waves that can destroy coastal infrastructure and cause loss of life. Early warnings for such natural disasters are difficult because the risk of a tsunami is highly dependent on the features of the underwater earthquake that triggers it.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles and Cardiff University in the U.K. developed an early warning system that combines state-of-the-art acoustic technology with artificial intelligence to immediately classify earthquakes and determine potential tsunami risk.
Underwater earthquakes can trigger tsunamis if a large amount of water is displaced, so determining the type of earthquake is critical to assessing the tsunami risk.
“Tectonic events with a strong vertical slip element are more likely to raise or lower the water column compared to horizontal slip elements,” said co-author Bernabe Gomez. “Thus, knowing the slip type at the early stages of the assessment can reduce false alarms and enhance the reliability of the warning systems through independent cross-validation.”
In these cases, time is of the essence, and relying on deep ocean wave buoys to measure water levels often leaves insufficient evacuation time. Instead, the researchers propose measuring the acoustic radiation (sound) produced by the earthquake, which carries information about the tectonic event and travels significantly faster than tsunami waves. Underwater microphones, called hydrophones, record the acoustic waves and monitor tectonic activity in real time.
“Acoustic radiation travels through the water column much faster than tsunami waves. It carries information about the originating source and its pressure field can be recorded at distant locations, even thousands of kilometers away from the source. The derivation of analytical solutions for the pressure field is a key factor in the real-time analysis,” co-author Usama Kadri said.
The computational model triangulates the source of the earthquake from the hydrophones and AI algorithms classify its slip type and magnitude. It then calculates important properties like effective length and width, uplift speed, and duration, which dictate the size of the tsunami.
The authors tested their model with available hydrophone data and found it almost instantaneously and successfully described the earthquake parameters with low computational demand. They are improving the model by factoring in more information to increase the tsunami characterization’s accuracy.
Their work predicting tsunami risk is part of a larger project to enhance hazard warning systems. The tsunami classification is a back-end aspect of a software that can improve the safety of offshore platforms and ships.
###
The article “Numerical validation of an effective slender fault source solution for past tsunami scenarios” is authored by Bernabe Gomez and Usama Kadri. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on April 18, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0144360). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0144360.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
END
Creating a tsunami early warning system using artificial intelligence
Real-time classification of underwater earthquakes based on acoustic signals enables earlier, more reliable disaster preparation
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
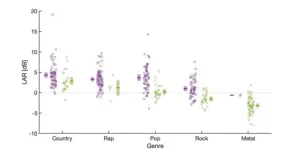
Lead vocal tracks in popular music go quiet
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – A general rule of music production involves mixing various soundtracks so the lead singer’s voice is in the foreground. But it is unclear how such track mixing – and closely related lyric intelligibility – has changed over the years.
Scientists from the University of Oldenburg in Germany carried out an analysis of hundreds of popular song recordings from 1946 to 2020 to determine the lead vocal to accompaniment ratio, or LAR. Their results appear in JASA Express Letters, published on behalf of the ...
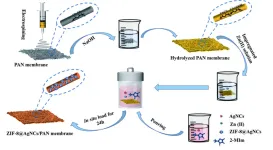
Treating polluted water with nanofiber membranes
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When oil contaminates water, it creates a film that reduces oxygen levels and introduces toxic substances. This can lead to the death of aquatic plants and animals, contaminate soil, and ultimately threaten human health.
Separating oil from polluted water is therefore of great importance. Current methods can be expensive and challenging, and some may introduce further pollutants into the system. For example, membrane materials can act as a barrier to intercept ...
Trends in buprenorphine initiation and retention
2023-04-25
About The Study: During January 2016 through October 2022, the monthly buprenorphine initiation rate in the U.S. increased, then flattened. This flattening occurred prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, suggesting that factors other than the pandemic were involved.
Authors: Kao-Ping Chua, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.1207)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
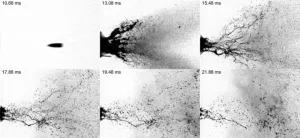
Improving bloodstain pattern analysis with fluid dynamics
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – Often left on the surfaces of a crime scene or on the clothes of an accused criminal, blood back spatter can be used as evidence for forensic scientists to reconstruct what occurred. However, the fluid dynamics at play are complicated, and neglecting the interaction between the blood and the muzzle gases from the firearm could skew the results.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago and Iowa State University modeled the behavior of blood drops during secondary atomization to examine how the phenomenon affects a crime scene.
“Primary atomization of blood is caused by ...
Self-awareness of memory function and clinical progression in cognitively normal older adults
2023-04-25
About The Study: In this study of 436 cognitively normal older adults, unawareness, rather than heightened awareness, of memory decline was strongly associated with future clinical progression, providing further support that discordant self- and informant-reported cognitive decline may provide important information to practitioners.
Authors: Patrizia Vannini, Ph.D., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.9964)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
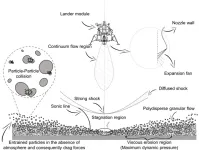
How to land on a planet safely
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When a lander descends toward the moon – or a rocky planet, asteroid, or comet – the exhaust plume of the rocket interacts with the surface, causing erosion and kicking up regolith particles. The resulting blanket of dusty debris can create a dangerous brownout effect, limiting visibility and potentially damaging the spacecraft or nearby equipment.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Chungnam National University, the University of Edinburgh, Gyeongsang National University, and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information ...
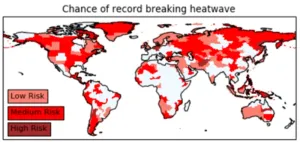
Global research reveals countries where record-breaking heatwaves are likely to cause most harm
2023-04-25
A new study has highlighted under-prepared regions across the world most at risk of the devastating effects of scorching temperatures.
The University of Bristol-led research, published today in Nature Communications, shows that unprecedented heat extremes combined with socioeconomic vulnerability puts certain regions, such as Afghanistan, Papua New Guinea, and Central America, most in peril.
Countries yet to experience the most intense heatwaves are often especially susceptible, as adaptation measures are often only introduced after the event. A high chance of record-breaking ...
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
2023-04-25
Cardiff University media release/Datganiad i’r wasg gan Brifysgol Caerdydd
Under embargo until 16:00 BST/11:00 EST on Tuesday 25 April 2023/O dan embargo tan 16:00 BST/11:00 EST ddydd Mawrth 25 Ebrill 2023
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
Real-time classification of underwater earthquakes enables earlier and more reliable tsunami alerts
An early warning system that quickly classifies submarine earthquakes and determines the risk of tsunami events has been developed by scientists at Cardiff ...
Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine discover how long-lasting memories form in the brain
2023-04-25
April 25, 2023—(BRONX NY)—Helping your mother make pancakes when you were three…riding your bike without training wheels…your first romantic kiss: How do we retain vivid memories of long-ago events? As described in a paper published online on April 25 in Neuron, researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found the explanation.
“The ability to learn new information and store it for long periods is one of the brain’s most remarkable features,” said Robert H. Singer, Ph.D., ...
Researchers find rhythmic brain activity helps to maintain temporary memories
2023-04-25
New research shows that rhythmic brain activity is key to temporarily maintaining important information in memory. Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester published these findings today in Current Biology that found brain rhythms—or patterns of neuronal activity—organize the bursts of activity in the brain that maintain short-term connections.
“The thought has been that the temporary storage of important information is linked to neurons in the brain that just fire away, retaining that information until it is no longer needed. Recent research has shown that it might not be such persistent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] Creating a tsunami early warning system using artificial intelligenceReal-time classification of underwater earthquakes based on acoustic signals enables earlier, more reliable disaster preparation