(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA — MIT engineers have designed a new nanoparticle sensor that could enable early diagnosis of cancer with a simple urine test. The sensors, which can detect many different cancerous proteins, could also be used to distinguish the type of a tumor or how it is responding to treatment.
The nanoparticles are designed so that when they encounter a tumor, they shed short sequences of DNA that are excreted in the urine. Analyzing these DNA “barcodes” can reveal distinguishing features of a particular patient’s tumor. The researchers designed their test so that it can be performed using a strip of paper, similar to an at-home Covid test, which they hope could make it affordable and accessible to as many patients as possible.
“We are trying to innovate in a context of making technology available to low- and middle-resource settings. Putting this diagnostic on paper is part of our goal of democratizing diagnostics and creating inexpensive technologies that can give you a fast answer at the point of care,” says Sangeeta Bhatia, the John and Dorothy Wilson Professor of Health Sciences and Technology and of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT and a member of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research and Institute for Medical Engineering and Science.
In tests in mice, the researchers showed that they could use the sensors to detect the activity of five different enzymes that are expressed in tumors. They also showed that their approach could be scaled up to distinguish at least 46 different DNA barcodes in a single sample, using a microfluidic device to analyze the samples.
Bhatia is the senior author of the paper, which appears today in Nature Nanotechnology. Liangliang Hao, a former MIT research scientist who is now an assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Boston University, is the lead author of the study.
DNA barcodes
For several years, Bhatia’s lab has been developing “synthetic biomarkers” that could be used to diagnose cancer. This work builds on the concept of detecting cancer biomarkers, such as proteins or circulating tumor cells, in a patient’s blood sample. These naturally occurring biomarkers are so rare that it’s nearly impossible to find them, especially at an early stage, but synthetic biomarkers can be used amplify smaller-scale changes that occur within small tumors.
In previous work, Bhatia created nanoparticles that can detect the activity of enzymes called proteases, which help cancer cells to escape their original locations, or settle into new ones, by cutting through proteins of the extracellular matrix. The nanoparticles are coated with peptides that are cleaved by different proteases, and once these peptides are released into the bloodstream, they can then be concentrated and more easily detected in a urine sample.
The original peptide biomarkers were designed to be detected based on small engineered variations in their mass, using a mass spectrometer. This kind of equipment might not be available in low-resource settings, so the researchers set out to develop sensors that could be analyzed more easily and affordably, using DNA barcodes that can be read using CRISPR technology.
For this approach to work, the researchers had to use a chemical modification called phosphorothioate to protect the circulating DNA reporter barcodes from being broken down in the blood. This modification has already been used to improve the stability of modern RNA vaccines, allowing them to survive longer in the body.
Similar to the peptide reporters, each DNA barcode is attached to a nanoparticle by a linker that can be cleaved by a specific protease. If that protease is present, the DNA molecule is released and free to circulate, eventually ending up in the urine. For this study, the researchers used two different types of nanoparticles: one, a particle made from polymers that have been FDA-approved for use in humans, and the other a “nanobody” — an antibody fragment that can be designed to accumulate at a tumor site.
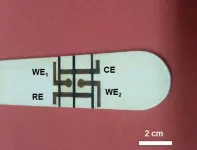
Once the sensors are secreted in the urine, the sample can be analyzed using a paper strip that recognizes a reporter that is activated by a CRISPR enzyme called Cas12a. When a particular DNA barcode is present in the sample, Cas12a amplifies the signal so that it can be seen as a dark strip on a paper test.
The particles can be designed to carry many different DNA barcodes, each of which detects a different type of protease activity, which allows for “multiplexed” sensing. Using a larger number of sensors provides a boost in both sensitivity and specificity, allowing the test to more easily distinguish between tumor types.
Disease signatures
In tests in mice, the researchers showed that a panel of five DNA barcodes could accurately distinguish tumors that first arose in the lungs from tumors formed by colorectal cancer cells that had metastasized to the lungs.
“Our goal here is to build up disease signatures and to see whether we can use these barcoded panels not only read out a disease but also to classify a disease or distinguish different cancer types,” Hao says.
For use in humans, the researchers expect that they may need to use more than five barcodes because there is so much variety between patients’ tumors. To help reach that goal, they worked with researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard led by Harvard University Professor Pardis Sabeti, to create a microfluidic chip that can be used to read up to 46 different DNA barcodes from one sample.
This kind of testing could be used not only for detecting cancer, but also for measuring how well a patient’s tumor responds to treatment and whether it has recurred after treatment. The researchers are now working on further developing the particles with the goal of testing them in humans. Glympse Bio, a company co-founded by Bhatia, has performed phase 1 clinical trials of an earlier version of the urinary diagnostic particles and found them to be safe in patients.
In addition to Bhatia, Hao, and Sabeti, the study’s co-authors include Renee T. Zhao, Nicole L. Welch, Edward Kah Wei Tan, Qian Zhong, Nour Saida Harzallah, Chayanon Ngambenjawong, Henry Ko, and Heather E. Fleming.
###
The research was funded by the Koch Institute Support (core) Grant from the National Cancer Institute, a Core Center Grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, the Marble Center for Cancer Nanomedicine at the Koch Institute, the Koch Institute Frontier Research Program, the Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, and a Pathway to Independence Award from the National Cancer Institute.
END
A simple paper test could offer early cancer diagnosis
The new diagnostic, which is based on analysis of urine samples, could also be designed to reveal whether a tumor has metastasized.
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
BSC develops pioneering artificial intelligence method to fight urban air pollution
2023-04-25
99% of the world's population breathes air that exceeds the limits recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). This scenario is exacerbated in urban areas where more than 50% of the world's population is concentrated. To mitigate the problem of air pollution, considered by the WHO to be the main environmental risk factor for health worldwide, it is crucial to have more reliable and accurate data on the concentration of air pollutants in our cities, especially nitrogen dioxide (NO2) because of its harmful effects on ...
How a horse whisperer can help engineers build better robots
2023-04-25
Humans and horses have enjoyed a strong working relationship for nearly 10,000 years — a partnership that transformed how food was produced, people were transported and even how wars were fought and won. Today, we look to horses for companionship, recreation and as teammates in competitive activities like racing, dressage and showing.
Can these age-old interactions between people and their horses teach us something about building robots designed to improve our lives? Researchers with the University of Florida say yes.
“There are no fundamental guiding principles ...
Say ‘ahhh’: This ecofriendly tongue depressor checks vitals
2023-04-25
Doctors often use tongue depressors when peering in a patient’s mouth and throat. But what if that flat wooden spatula could actively evaluate the patient’s health? That’s the premise of an ecofriendly disposable sensor, reported in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry, that can check levels of glucose and other biomarkers in saliva. Researchers say the easy-to-produce device could someday help doctors assess a range of conditions.
Wood is a renewable, biodegradable, natural material that is widely available at low cost, which makes it attractive for researchers who design electronics and sensors. However, this is challenging because the material isn’t good ...
Biomarker pattern found in kids with COVID 19-linked inflammatory syndrome
2023-04-25
WHAT:
Children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C)—a rare condition linked with the virus that causes COVID-19—have biochemical indicators of cell injury and cell death that are distinct from other children with COVID-19, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. Using high speed, artificial intelligence-controlled molecular sequencing of blood-and-plasma RNA and plasma DNA, researchers found that children with MIS-C have biomarkers indicating damage to multiple organs, the lining of blood vessels and the nervous system. MIS-C usually occurs two to six weeks after ...
Charles Spruck awarded $1.7M to advance “ancient virus” treatment for prostate cancer
2023-04-25
LA JOLLA, CALIF. April 25, 2023 - With the help of a new grant from the U.S. Department of Defense for more than $1.7 million, Associate Professor Charles Spruck, Ph.D., will advance an innovative therapeutic approach for metastatic prostate cancer. Known as viral mimicry, the approach tricks the body into thinking that it has a viral infection, stimulating an immune response that can help the body fight cancer.
“In viral mimicry, the body thinks there’s an infection, which kicks the ...
New motion blur restoration approach for improved weed detection in crop fields
2023-04-25
Effective weed control is crucial in agriculture to ensure high crop productivity. It entails the careful separation of weeds from crops before herbicides are sprayed in the fields. In simple terms, the goal of weed control is to remove the weeds while ensuring that the crop are not harmed. Traditional weed control methods have several drawbacks, such as crop contamination, herbicide waste, and poor accuracy. Therefore, it is essential to develop methods that can precisely locate and identify the boundary between a crop and weed and implement ...
Argonne’s self-driving lab accelerates the discovery process for materials with multiple applications
2023-04-25
Researchers have a new scientific tool called Polybot, combining the power of artificial intelligence with robotics. Potential applications include speeding up the discovery of wearable biomedical devices, materials for better batteries and more.
Today’s wearable technologies like smart glasses and watches are just the start. The next generation of flexible electronics will be more efficient and sustainable, better able to monitor our health and treat certain diseases, and much more. They will be composed of electronic polymer materials — a soft pliable substance that can conduct electricity.
“Just imagine the next generation of polymer ...
Champion for improved perioperative care for older adults: Shelley R. McDonald, DO, PhD, MCG honored as AGS Clinician of the Year
2023-04-25
New York (April 25, 2022) — The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) today announced Shelley R. McDonald, DO, PhD, MCG, as 2023 Clinician of the Year. Dr. McDonald, who is an Associate Professor of Internal Medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, will be honored at the 2023 AGS Annual Scientific Meeting (#AGS23) being held in Long Beach, CA, from May 4-6 (preconference day is May 3).
“Our 2023 Clinician of the year, Dr. Shelley McDonald, is a national champion for improved perioperative care of older adults undergoing surgery,” said ...
RCT-DUPLICATE findings demonstrate capability of real-world evidence studies to reach conclusions similar to randomized clinical trials
2023-04-25
NEW YORK, April 25, 2023 ‒ Aetion®, the global leader in real-world evidence (RWE) technology and analytics, is pleased to announce the culmination of the RCT-DUPLICATE demonstration project, with complete findings published today in The Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). This three-year initiative tested whether researchers asking clinical questions in real-world data (RWD) — data from patients’ day-to-day interactions with the healthcare system — would obtain similar results to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs). In cases where clinical trial designs aligned with real patient care processes, the RWE studies and RCTs came ...
Exposure to cannabinoids in pregnancy increases newborn mortality and respiratory problems
2023-04-25
Consumption of cannabis (marijuana) or derivatives during pregnancy can cause respiratory problems for the baby, such as impaired control of breathing and diminished sensitivity to carbon dioxide, both of which favor sudden infant death syndrome. These are the main findings of a study conducted in Brazil and reported in an article published in the British Journal of Pharmacology.
The authors are researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) and the University of São Paulo (USP). They gave pregnant rats a synthetic compound (WIN 55) that acts on the brain in a similar manner to natural cannabinoids. Harmful effects occurred mainly in male pups.
“Cannabis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
[Press-News.org] A simple paper test could offer early cancer diagnosisThe new diagnostic, which is based on analysis of urine samples, could also be designed to reveal whether a tumor has metastasized.