(Press-News.org)
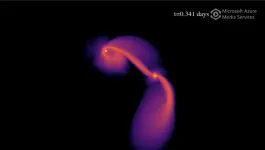
If they exist, intermediate-mass black holes likely devour wayward stars like a messy toddler — taking a few bites and then flinging the remains across the galaxy — a new Northwestern University-led study has found.
In new 3D computer simulations, astrophysicists modeled black holes of varying masses and then hurled stars (about the size of our sun) past them to see what might happen.
When a star approaches an intermediate-mass black hole, it initially gets caught in the black hole’s orbit, the researchers discovered. After that, the black hole begins its lengthy and violent meal. Every time the star makes a lap, the black hole takes a bite — further cannibalizing the star with each passage. Eventually, nothing is left but the star’s misshapen and incredibly dense core.
At that point, the black hole ejects the remains. The star’s remnant flies to safety across the galaxy.
Not only do these new simulations hint at the unknown behaviors of intermediate-mass black holes, they also provide astronomers with new clues to help finally pinpoint these hidden giants within our night sky.
“We obviously cannot observe black holes directly because they don’t emit light,” said Northwestern’s Fulya Kıroğlu, who led the study. “So, instead, we have to look at the interactions between black holes and their environments. We found that stars undergo multiple passages before being ejected. After each passage, they lose more mass, causing a flair of light as its ripped apart. Each flare is brighter than the last, creating a signature that might help astronomers find them.”
Kıroğlu will present this research during the virtual portion of the American Physical Society’s (APS) April meeting. “Tidal disruption events of stars by intermediate-mass black holes” will take place at 1:36 p.m. EDT/12:36 p.m. CDT on Tuesday, April 25, as a part of the session “Medium: Cosmic Rays, AGN & Galaxies.” Complimentary press registration is available for journalists. The Astrophysical Journal has accepted the study for publication.
Kıroğlu is an astrophysics graduate student at Northwestern’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and member of the Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics (CIERA). She is advised by paper co-author Frederic Rasio, the Joseph Cummings Professor of Physics and Astronomy at Weinberg and member of CIERA.
While astrophysicists have proven the existence of lower- and higher-mass block holes, intermediate-mass black holes have remained elusive. Created when supernovae collapse, stellar remnant black holes are about 3 to 10 times the mass of our sun. On the other end of the spectrum, supermassive black holes, which lurk in the centers of galaxies, are millions to billions times the mass of our sun.
Should they exist, intermediate-mass black holes would fit somewhere in the middle — 10 to 10,000 times more massive than stellar remnant black holes but not nearly as massive as supermassive black holes. Although these intermediate-mass black holes theoretically should exist, astrophysicists have yet to find indisputable observational evidence.
“Their presence is still debated,” Kıroğlu said. “Astrophysicists have uncovered evidence that they exist, but that evidence can often be explained by other mechanisms. For example, what appears to be an intermediate-mass black hole might actually be the accumulation of stellar-mass black holes.”
To explore the behavior of these evasive objects, Kıroğlu and her team developed new hydrodynamic simulations. First, they created a model of a star, consisting of many particles. Then, they sent the star toward the black hole and calculated the gravitational force acting on the particles during the star’s approach.
“We can calculate specifically which particle is bound to the star and which particle is disrupted (or no longer bound to the star),” Kıroğlu said.
Through these simulations, Kıroğlu and her team discovered that stars could orbit an intermediate-mass black hole as many as five times before finally being ejected. With each pass around the black hole, the star loses more and more of its mass as its ripped apart. Then, the black hole kicks the leftovers — moving at searing speeds — back out into the galaxy. The repeating pattern would create a stunning light show that should help astronomers recognize — and prove the existence of — intermediate-mass black holes.
“It’s amazing that the star isn’t fully ripped apart,” Kıroğlu said. “Some stars might get lucky and survive the event. The ejection speed is so high that these stars could be identified as hyper-velocity stars, which have been observed at the centers of galaxies.”
Next, Kıroğlu plans to simulate different types of stars, including giant stars and binary stars, to explore their interactions with black holes.
The study, “Partial tidal disruptions of main-sequence stars by intermediate-mass black holes” was supported by the National Science Foundation (grant number AST-2001751) and NASA (grant numbers 80NSSC21K1722, AST-2108624 and 80NSSC22K0722).
END
Dungeness crab fishermen are at high risk for on-the-job injury, but having a metal bar to bang crab pots against as they harvest can help them prevent injury, an Oregon State University study found.
The study sought to determine whether the fishermen-designed “banger bar” actually improves worker safety aboard crab vessels. The metal bar is installed atop the crab-sorting table and makes it easier for fishermen to empty the crab pots they haul up from the ocean floor, but there is no industry standard on whether crabbers install one or how they ...
1. Introduction
While the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is not fully understood, it has been traditionally linked to a reduction in the dopamine available to brain regions involved in motor control (Alexander, 2004, Brooks, 2010, Fahn, 2008, Meder et al., 2019, Obeso et al., 2017, Poewe et al., 2017). It is important to note that much of what is known about the neural bases of motor deficits in PD is based on task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies showing abnormal motor-related blood oxygen ...
Lutz Grossmann is on a scientific mission to create tasty, animal-free protein that has a low carbon footprint and is produced without relying on agricultural land – a usual and progressively stressed source of the global food supply.
“The increasing global population and a changing climate increase the pressure on our food and protein supply coming from these natural habitats,” says Grossmann, an assistant professor of food science at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
“By 2050, we need ...
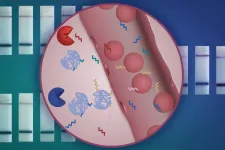
CAMBRIDGE, MA — MIT engineers have designed a new nanoparticle sensor that could enable early diagnosis of cancer with a simple urine test. The sensors, which can detect many different cancerous proteins, could also be used to distinguish the type of a tumor or how it is responding to treatment.
The nanoparticles are designed so that when they encounter a tumor, they shed short sequences of DNA that are excreted in the urine. Analyzing these DNA “barcodes” can reveal distinguishing features of a particular patient’s tumor. The researchers designed their test so that it can be performed using a strip of paper, ...
99% of the world's population breathes air that exceeds the limits recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). This scenario is exacerbated in urban areas where more than 50% of the world's population is concentrated. To mitigate the problem of air pollution, considered by the WHO to be the main environmental risk factor for health worldwide, it is crucial to have more reliable and accurate data on the concentration of air pollutants in our cities, especially nitrogen dioxide (NO2) because of its harmful effects on ...
Humans and horses have enjoyed a strong working relationship for nearly 10,000 years — a partnership that transformed how food was produced, people were transported and even how wars were fought and won. Today, we look to horses for companionship, recreation and as teammates in competitive activities like racing, dressage and showing.
Can these age-old interactions between people and their horses teach us something about building robots designed to improve our lives? Researchers with the University of Florida say yes.
“There are no fundamental guiding principles ...
Doctors often use tongue depressors when peering in a patient’s mouth and throat. But what if that flat wooden spatula could actively evaluate the patient’s health? That’s the premise of an ecofriendly disposable sensor, reported in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry, that can check levels of glucose and other biomarkers in saliva. Researchers say the easy-to-produce device could someday help doctors assess a range of conditions.
Wood is a renewable, biodegradable, natural material that is widely available at low cost, which makes it attractive for researchers who design electronics and sensors. However, this is challenging because the material isn’t good ...
WHAT:
Children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C)—a rare condition linked with the virus that causes COVID-19—have biochemical indicators of cell injury and cell death that are distinct from other children with COVID-19, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. Using high speed, artificial intelligence-controlled molecular sequencing of blood-and-plasma RNA and plasma DNA, researchers found that children with MIS-C have biomarkers indicating damage to multiple organs, the lining of blood vessels and the nervous system. MIS-C usually occurs two to six weeks after ...
LA JOLLA, CALIF. April 25, 2023 - With the help of a new grant from the U.S. Department of Defense for more than $1.7 million, Associate Professor Charles Spruck, Ph.D., will advance an innovative therapeutic approach for metastatic prostate cancer. Known as viral mimicry, the approach tricks the body into thinking that it has a viral infection, stimulating an immune response that can help the body fight cancer.
“In viral mimicry, the body thinks there’s an infection, which kicks the ...
Effective weed control is crucial in agriculture to ensure high crop productivity. It entails the careful separation of weeds from crops before herbicides are sprayed in the fields. In simple terms, the goal of weed control is to remove the weeds while ensuring that the crop are not harmed. Traditional weed control methods have several drawbacks, such as crop contamination, herbicide waste, and poor accuracy. Therefore, it is essential to develop methods that can precisely locate and identify the boundary between a crop and weed and implement ...