(Press-News.org) -- JOINT PRESS RELEASE OF FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JÜLICH AND JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIVERSITY MAINZ --
SynDLP could be a bacterial ancestor of eukaryotic membrane proteins
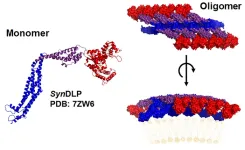
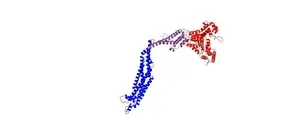
The cells of living organisms are equipped with proteins that are involved in the shaping and remodeling of cellular membranes, thereby performing important tasks. The cell membrane encloses the cell interior, but is constantly remodeled, for example, due to membrane budding, invagination, or fusion processes. This also involves various proteins that were long assumed to be present exclusively or predominantly in higher organisms. In the past 10 to 20 years, however, proteins have been identified or predicted to be present also in simple organisms that do not possess a nucleus. In a research collaboration, a protein involved in membrane remodeling in cyanobacteria has now been described for the first time. The existence of such a bacterial protein was suspected, but proof was still pending. The studied protein is likely a bacterial representative of a similar protein found in higher organisms such as animals and plants.
Membrane proteins also discovered in prokaryotes
Membrane proteins are involved in a variety of membrane remodeling as well as repair processes to cope with membrane damage and thus ensure cell survival. In the past decade, such proteins have also been discovered in prokaryotes, i.e., simple organisms that do not have a cell nucleus. Many of these have similarities to proteins previously thought to be found solely in more complex organisms that contain a cell nucleus, i.e., the eukaryotes, such as animals and plants.
So-called dynamins and dynamin-like proteins were also originally thought to be eukaryotic inventions until a bioinformatics study in 1999 predicted the existence of bacterial dynamin-like proteins or DLPs. These DLPs belong to the dynamin protein superfamily and are involved in various membrane remodeling processes in eukaryotes.
Recently, a specific DLP, namely SynDLP, has been identified in the genome of a cyanobacterium. This protein was studied by research teams from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and Forschungszentrum Jülich with participation from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU). "We previously assumed that we would only find this type of protein in eukaryotic cells," said Professor Dirk Schneider, head of the Membrane Proteins group at JGU. "SynDLP has a structure that we previously thought only exists in higher organisms," added Professor Carsten Sachse, a scientist at Forschungszentrum Jülich and professor at HHU. "The structural properties of SynDLP suggest that it is the closest known bacterial ancestor of eukaryotic dynamin," Sachse described the results. "We assume that this protein was already present in a primordial cell before they further developed into cells with and without a nucleus," added Schneider.
Cyanobacteria use an internal membrane system for photosynthesis
Cyanobacteria are among the oldest organisms on earth. They are also called blue-green bacteria because of their color. Unlike other bacteria, they possess a second internal membrane system in which the light reactions of photosynthesis take place. However, precisely because of the light reaction, the membrane is very vulnerable and is subject to constant repair and remodeling. Therefore, membrane-remodeling proteins are particularly important for the reconstruction or repair of the membrane.
"We do not yet know exactly what function SynDLP has in membrane dynamics," said Professor Dirk Schneider. It does not appear to be vital under laboratory conditions. "However, if it were not essential, it would not have been conserved over billions of years," surmised the chemist from Mainz University. In the future, the scientists want to pursue this question and investigate exactly what function the protein performs in bacterial cells.
Long-term research cooperation bears fruit
Three young scientists played a key role in the eight years of research now published: Dr. Ruven Jilly and Lucas Gewehr from JGU and Dr. Benedikt Junglas from Forschungszentrum Jülich, formerly a doctoral student at the Max Planck Graduate Center with Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (MPGC). Other collaborators are from the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research in Mainz and Aarhus University in Denmark. The work has just been published in Nature Communications.
Publications:
L. Gewehr et al., SynDLP is a dynamin-like protein of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 with eukaryotic features, Nature Communications 14: 2156, 14 April 2023,
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37746-9
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37746-9
C. Siebenaller, D. Schneider, Cyanobacterial membrane dynamics in the light of eukaryotic principles, Bioscience Reports 43: 2, 23 February 2023,
DOI: 10.1042/BSR20221269
https://portlandpress.com/bioscirep/article/43/2/BSR20221269/232406/Cyanobacterial-membrane-dynamics-in-the-light-of
Related links:
https://www.blogs.uni-mainz.de/fb09-schneider/ – Membrane Proteins group of Professor Dirk Schneider at the JGU Department of Chemistry
https://www.mpip-mainz.mpg.de/en/home – Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research
https://www.fz-juelich.de – Forschungszentrum Jülich
http://www.fz-juelich.de/er-c/er-c-3 – Structural Biology research division at the Ernst-Ruska Center for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons at Forschungszentrum Jülich
:
https://press.uni-mainz.de/membrane-proteins-of-bacteria-and-humans-show-surprising-similarities/ – press release "Membrane proteins of bacteria and humans show surprising similarities" (24 June 2021)
https://press.uni-mainz.de/protective-shield-a-membrane-attached-protein-protects-bacteria-and-chloroplasts-from-stress/ – press release "Protective shield: A membrane-attached protein protects bacteria and chloroplasts from stress" (23 Oct. 2020)
https://press.uni-mainz.de/fusion-protein-controls-design-of-photosynthesis-platform/ – press release "Fusion protein controls design of photosynthesis platform" (13 May 2015) END
Relatives discovered: Membrane proteins of cyanobacteria and higher organisms are structurally highly similar
SynDLP could be a bacterial ancestor of eukaryotic membrane proteins
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medium-sized black holes eat stars like messy toddlers
2023-04-25
If they exist, intermediate-mass black holes likely devour wayward stars like a messy toddler — taking a few bites and then flinging the remains across the galaxy — a new Northwestern University-led study has found.
In new 3D computer simulations, astrophysicists modeled black holes of varying masses and then hurled stars (about the size of our sun) past them to see what might happen.
When a star approaches an intermediate-mass black hole, it initially gets caught in the black hole’s orbit, the researchers discovered. After that, the black hole begins its lengthy and violent meal. Every time the star makes a lap, the black hole takes a bite — ...
Fishermen-developed “banger bar” helps reduce risk of injury on crab boats, OSU study finds
2023-04-25
Dungeness crab fishermen are at high risk for on-the-job injury, but having a metal bar to bang crab pots against as they harvest can help them prevent injury, an Oregon State University study found.
The study sought to determine whether the fishermen-designed “banger bar” actually improves worker safety aboard crab vessels. The metal bar is installed atop the crab-sorting table and makes it easier for fishermen to empty the crab pots they haul up from the ocean floor, but there is no industry standard on whether crabbers install one or how they ...
New Parkinson's research could allow doctors to map brain of patients with neurodegenerative disorder
2023-04-25
1. Introduction
While the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is not fully understood, it has been traditionally linked to a reduction in the dopamine available to brain regions involved in motor control (Alexander, 2004, Brooks, 2010, Fahn, 2008, Meder et al., 2019, Obeso et al., 2017, Poewe et al., 2017). It is important to note that much of what is known about the neural bases of motor deficits in PD is based on task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies showing abnormal motor-related blood oxygen ...
Researcher aims to create a sustainable protein source powered by hydrogen
2023-04-25
Lutz Grossmann is on a scientific mission to create tasty, animal-free protein that has a low carbon footprint and is produced without relying on agricultural land – a usual and progressively stressed source of the global food supply.
“The increasing global population and a changing climate increase the pressure on our food and protein supply coming from these natural habitats,” says Grossmann, an assistant professor of food science at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
“By 2050, we need ...
A simple paper test could offer early cancer diagnosis
2023-04-25
CAMBRIDGE, MA — MIT engineers have designed a new nanoparticle sensor that could enable early diagnosis of cancer with a simple urine test. The sensors, which can detect many different cancerous proteins, could also be used to distinguish the type of a tumor or how it is responding to treatment.
The nanoparticles are designed so that when they encounter a tumor, they shed short sequences of DNA that are excreted in the urine. Analyzing these DNA “barcodes” can reveal distinguishing features of a particular patient’s tumor. The researchers designed their test so that it can be performed using a strip of paper, ...
BSC develops pioneering artificial intelligence method to fight urban air pollution
2023-04-25
99% of the world's population breathes air that exceeds the limits recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). This scenario is exacerbated in urban areas where more than 50% of the world's population is concentrated. To mitigate the problem of air pollution, considered by the WHO to be the main environmental risk factor for health worldwide, it is crucial to have more reliable and accurate data on the concentration of air pollutants in our cities, especially nitrogen dioxide (NO2) because of its harmful effects on ...
How a horse whisperer can help engineers build better robots
2023-04-25
Humans and horses have enjoyed a strong working relationship for nearly 10,000 years — a partnership that transformed how food was produced, people were transported and even how wars were fought and won. Today, we look to horses for companionship, recreation and as teammates in competitive activities like racing, dressage and showing.
Can these age-old interactions between people and their horses teach us something about building robots designed to improve our lives? Researchers with the University of Florida say yes.
“There are no fundamental guiding principles ...
Say ‘ahhh’: This ecofriendly tongue depressor checks vitals
2023-04-25
Doctors often use tongue depressors when peering in a patient’s mouth and throat. But what if that flat wooden spatula could actively evaluate the patient’s health? That’s the premise of an ecofriendly disposable sensor, reported in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry, that can check levels of glucose and other biomarkers in saliva. Researchers say the easy-to-produce device could someday help doctors assess a range of conditions.
Wood is a renewable, biodegradable, natural material that is widely available at low cost, which makes it attractive for researchers who design electronics and sensors. However, this is challenging because the material isn’t good ...
Biomarker pattern found in kids with COVID 19-linked inflammatory syndrome
2023-04-25
WHAT:
Children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C)—a rare condition linked with the virus that causes COVID-19—have biochemical indicators of cell injury and cell death that are distinct from other children with COVID-19, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. Using high speed, artificial intelligence-controlled molecular sequencing of blood-and-plasma RNA and plasma DNA, researchers found that children with MIS-C have biomarkers indicating damage to multiple organs, the lining of blood vessels and the nervous system. MIS-C usually occurs two to six weeks after ...
Charles Spruck awarded $1.7M to advance “ancient virus” treatment for prostate cancer
2023-04-25
LA JOLLA, CALIF. April 25, 2023 - With the help of a new grant from the U.S. Department of Defense for more than $1.7 million, Associate Professor Charles Spruck, Ph.D., will advance an innovative therapeutic approach for metastatic prostate cancer. Known as viral mimicry, the approach tricks the body into thinking that it has a viral infection, stimulating an immune response that can help the body fight cancer.
“In viral mimicry, the body thinks there’s an infection, which kicks the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Relatives discovered: Membrane proteins of cyanobacteria and higher organisms are structurally highly similarSynDLP could be a bacterial ancestor of eukaryotic membrane proteins