(Press-News.org) Dr Araujo, from the QUT School of Mathematical Sciences, said the research findings represented a blueprint for adaptation-capable signalling networks across all domains of life and for the design of synthetic biosystems.
“Our study considers a process called robust perfect adaptation (RPA) whereby biological systems, from individual cells to entire organisms, maintain important molecules within narrow concentration ranges despite continually being bombarded with disturbances to the system,” Dr Araujo said.
“Until now, no one had a general way to explain how this vital process was orchestrated at the molecular level through the vast, complex, often highly intricate networks of chemical reactions among different types of molecules, mostly proteins.
“We have now solved this problem, having discovered fundamental molecular-level design principles that organise all forms of biological complexity into robustness-promoting, and ultimately, survival-promoting, chemical reaction structures.”
Dr Araujo said they had found that collections of interacting molecules in living systems cannot simply ‘transmit’ biochemical signals but must actually make ‘computations’ on these signals.
“These complex intermolecular interactions must implement a special type of regulation known as integral control – a design strategy known to engineers for almost a century.
“However, signalling networks in nature are vastly different, having evolved to rely on the physical interactions between discrete molecules. So, nature’s ‘solutions’ operate through remarkable and highly intricate collections of interactions, without engineering’s specially designed, integral-computing components, and often without feedback loops.
“We show that molecular network structures use a form of integral control in which multiple independent integrals, each with a very special and simple structure, can collaborate to confer the capacity for adaptation on specific molecules.
“Using an algebraic algorithm based on this finding, we have been able to demonstrate the existence of embedded integrals in biologically important chemical reaction networks whose ability to exhibit adaptation could never before be explained by any systematic method.”
Professor Liotta said the quest to uncover the fundamental design principles of biological systems throughout nature is considered to be one of the most important and far-reaching grand challenges in the life sciences.
“On the basis of this ground-breaking new research, RPA currently stands alone as a keystone biological response for which there now exists a universal explanatory framework.
“It’s a framework that imposes strict and inviolable design criteria on arbitrarily large and complex networks, and one that now accounts for the subtleties of intricate intermolecular interactions at the network microscale.
“At a practical level, this discovery could provide a completely fresh approach to tackle grand challenges in personalized medicine such as cancer drug resistance, addiction, and autoimmune diseases.”
Universal structures for adaptation in biochemical reaction networks was published in Nature Communications.
END
Maths unlocks molecular interactions that open window to how life evolved
A “window to evolution” has opened after mathematicians uncovered the universal explanatory framework for how molecules interact with each other to adapt to new and variable conditions while maintaining tight control over key survival properties.
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The conservation laws of a dynamical system are no mystery to artificial intelligence
2023-04-27
Osaka, Japan – Many real-world systems, from climate systems to the physical mechanisms of robots, are governed by the invariant quantities that arise from their underlying geometric structures. Modelling these systems using computer simulations is a key tool for understanding them (for weather forecasting, for instance, or developing robot locomotion). It’s often possible to collect data for these systems, but making sense of those data to build a model is a more challenging task.
Artificial intelligence ...
Infectious-diseases response initiative reduced staff burnout and helped prevent HAI increases at VA health care system during covid-19 pandemic
2023-04-27
Arlington, Va., April 27, 2023 – A serious infectious threat response initiative (SITRI) implemented by the Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) team at Veterans Affairs North Texas Health Care System (VANTHCS) positively impacted IPC staff burnout and helped prevent an increase in healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings, published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC), suggest that pre-emptive investment in preparedness initiatives can enable healthcare facilities to retain routine prevention efforts and improve patient safety during infectious disease outbreaks.
“During ...
Former EPA and NIEHS directors urge overhaul of WHO’s draft PFAS drinking water guidance
2023-04-27
The World Health Organization’s draft drinking water guidance for the two most well-studied per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exhibit a “striking and inappropriate disregard of the best available science,” according to former directors of the U.S. EPA’s Office of Science and Technology and the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). In a viewpoint for the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science & Technology, Betsy Southerland and Linda Birnbaum strongly recommend ...
Using microbes to get more out of mining waste
2023-04-27
Researchers have developed a new mining technique which uses microbes to recover metals and store carbon in the waste produced by mining. Adopting this technique of reusing mining waste, called tailings, could transform the mining industry and create a greener and more sustainable future.
Tailings are a by-product of mining. They are the fine-grained waste materials left after extracting the target ore mineral, which are then stacked and stored. This method is called dry-stack tailing.
Over time, mining practices have evolved and become more efficient. But the climate crisis and rising demand for critical minerals require the development of new ore removal and ...
Carnegie Mellon research aims to revive office chatter
2023-04-26
About one-third of our lives are spent at work, and the relationships we build there can have personal and professional benefits. But a majority of workers indicate difficulty connecting with co-workers socially, especially in the new landscape of remote and hybrid work arrangements.
To ease the friction caused by reduced in-person interaction, a team of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University's Human-Computer Interaction Institute created a Slack application that helps to initiate casual conversations and create affinity groups in an online workspace.
"We were freshly out of the pandemic, and we realized that everyone around us was complaining ...
Differential silencing of STAT3 isoforms leads to changes in STAT3 activation
2023-04-26
“Our study emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between STAT3α and STAT3β proteins and their active forms when discussing STAT3-related cancer diagnosis and therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 26, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 24, 2023, entitled, “Differential silencing of STAT3 isoforms leads to changes in STAT3 activation.”
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor involved in ...
Terasaki Institute to celebrate grand opening of Woodland Hills Research Center with ribbon-cutting
2023-04-26
WOODLAND HILLS, Calif. – April 26, 2023 – The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation, a nonprofit dedicated to rapidly translating scientific knowledge into real-world solutions, will celebrate the grand opening of its latest biomedical research center with a ribbon-cutting ceremony on Saturday, April 29.
When: Saturday, April 29 at 11:30 a.m.
Where: 21100[ML1] Erwin St., Woodland Hills, Calif., 91367
What: ...
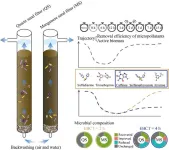
Backwashing affects the removal of micropollutants and the dynamic changes in the microbial community in sand filters
2023-04-26
Sand filters are commonly applied in drinking water treatment and can efficiently remove suspended solids, organic matter, and microorganisms from source water. During the process, particulate matter and microbes can attach to filter sands and develop a thick biofilm in both rapid and slow sand filters. To prevent clogging and restore pollutant removal efficiency, backwashing using air, water, or a combination of both is usually required for sand filters. However, backwashing can induce a loss in biomass, thus decreasing the pollutant ...
Researchers create antimicrobial ‘superfoam’
2023-04-26
A versatile new foam material developed by researchers at the University of Georgia could significantly reduce health care-related infections caused by implanted medical devices—or drastically improve cleanup efforts following environmental disasters like oil spills.
Like a spongy Swiss Army knife, the porous three-dimensional foam is water repellent—meaning it resists blood, microbes and proteins, while also exhibiting antimicrobial and oil-water separation properties. Its versatility, functionality and relatively inexpensive production costs could make it a valuable resource for future clinicians and environmental remediation professionals ...
Integrative neuro-oncology for brain tumor patients
2023-04-26
The University of Cincinnati's Soma Sengupta, MD, PhD, published an article in the Journal of Neuro-Oncology April 25 discussing her journey and approach to practicing integrative neuro-oncology.
Sengupta, associate professor in neurology, director of neuro-oncology clinical trials, associate director of the Brain Tumor Center and a UC Health neuro-oncologist, funded by the Harold C. Schott Endowed Chair in Molecular Therapeutics (Neurosurgery) and the Pam and Tom Mischell Funds, said she personally ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Maths unlocks molecular interactions that open window to how life evolvedA “window to evolution” has opened after mathematicians uncovered the universal explanatory framework for how molecules interact with each other to adapt to new and variable conditions while maintaining tight control over key survival properties.