(Press-News.org) Low-income immigrant children in sanctuary states were nearly 10% more likely to be enrolled in Medicaid in the years following the 2018 announcement of the revised “public charge” rule, according to a new national study. Researchers examined trends in children’s Medicaid enrollment in sanctuary states—states that limit collaboration with federal Immigration and Customs Enforcement personnel. The research will be presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2023 Meeting, held April 27-May 1 in Washington, D.C.
Researchers explored Medicaid enrollment rates among low-income immigrant children following a 2018 federal rule denying immigrants permanent residency based on participation in public programs, including Medicaid for adults but not for children.
Researchers found that Medicaid enrollment among low-income immigrant children in sanctuary states— Calif., Colo., Conn., Ill., N.Y., Ore., R.I., Vt., and Wash.—increased after the 2018 rule update. Medicaid enrollment rates among low-income immigrant children in non-sanctuary states decreased during the same period.
“Federal immigration policies can serve as political determinants of health, denying children in immigrant families access to health insurance and medical care,” said Marine-Ayan Ibrahim Aibo, medical student at Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and presenting author. “States can break barriers to care that federal immigration policies create and ensure every child receives the care they need.”
The study looked at 3,943 immigrant children from the U.S. Census Bureau and U.S. Bureau of Labor and Statistics’ Current Population Survey to compare Medicaid enrollment in sanctuary and non-sanctuary states, adjusting for race, ethnicity, state, year, and Medicaid expansion status.
# # #
EDITOR:
Ms. Ibrahim Aibo will present “Association of State Sanctuary Policies with Medicaid Participation Among Immigrant Children Following the Revised Public Charge Rule” on Monday, May 1 at 9:15 a.m. ET.
Reporters interested in an interview with Ms. Ibrahim Aibo should contact Amber Fraley at amber.fraley@pasmeeting.org.
The PAS Meeting connects thousands of pediatricians and other health care providers worldwide. For more information about the PAS Meeting, please visit www.pas-meeting.org.
About the Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting
The Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) Meeting is the premier North American scholarly child health meeting. The PAS Meeting connects thousands of pediatricians and other health care providers worldwide. The PAS Meeting is produced through a partnership of four pediatric organizations that are leaders in the advancement of pediatric research and child advocacy: American Pediatric Society, Society for Pediatric Research, Academic Pediatric Association and American Academy of Pediatrics. For more information, please visit www.pas-meeting.org. Follow us on Twitter @PASMeeting and like us on Facebook PASMeeting.
Abstract: Association of State Sanctuary Policies with Medicaid Participation Among Immigrant Children Following the Revised Public Charge Rule
Presenting Author: Marine-Ayan Ibrahim Aibo, B.A.
Organization
Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
Topic
Health Equity/Social Determinants of Health
Background
Immigration policies are political determinants of health that can impact children’s access to health-promoting government benefit programs. From 2011-2017, nine US states enacted statewide sanctuary policies designed to limit state collaboration with federal Immigration and Customs Enforcement and protect immigrants’ health and well being. In 2018, the Trump administration announced a plan to revise the federal “public charge” rule to deny legal permanent resident status to immigrants based on their participation in benefit programs, including Medicaid for adults but not children.
Objective
To assess whether state-level sanctuary immigration policies may protect access to health care for immigrant children, we compared Medicaid participation among immigrant children in sanctuary vs. non-sanctuary states before and after the 2018 announcement of the revised public charge rule.
Design/Methods
We used 2015-2021 Current Population Survey nationally representative data to compare Medicaid participation among low-income immigrant children living in sanctuary vs. non-sanctuary states. Immigration status was determined by self report; documentation status was not assessed. We then used difference-indifferences regression modeling to assess the change in Medicaid participation among immigrant children in sanctuary relative to non sanctuary states, after adjusting for race, ethnicity, state, year, and Medicaid expansion status.
Results
Our sample included 3,943 immigrant children with household incomes < 150% of the federal poverty level. Sanctuary and non-sanctuary states had similar rates of child poverty, and sanctuary states had a greater baseline proportion of Latinx residents (Table 1). Although children’s Medicaid participation was not considered in the revised public charge rule, Medicaid participation among immigrant children in non-sanctuary states declined after the rule was announced. In contrast, Medicaid participation among immigrant children in sanctuary states increased during this time period (Figure 2). In adjusted difference-in-differences models, immigrant children in sanctuary states had a 9.8% greater probability of Medicaid participation (95% CI 2.9-16.6%, p=0.005) relative to children in non-sanctuary states, following the public charge rule.
Conclusion(s)
Following the revised public charge rule, low-income immigrant children in states with sanctuary immigration policies were more likely to receive Medicaid than children in non-sanctuary states. Sanctuary policies may protect against the harmful effects of federal legislation on immigrant children.
Tables and Images
Figure 1.png
Table 1.png
Figure 2.png
END
Study: Medicaid enrollment among immigrant children higher in sanctuary states
Findings revealed at the 2023 Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting
2023-04-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Older drivers drinking or using drugs up to four times likelier to be at fault during a car crash
2023-04-28
Substance use among older drivers increases the probability of them being at-fault two to four times during a crash, a new study, analyzing nine years’ worth of US nationwide highway traffic data, shows.
Although older drivers are less likely to report using substances, this research found that out of a sample of 87,060 drivers involved in two moving vehicle crashes, more than one-third were motorists over the age of 70 who tested positive for substances.
Findings are published today in the peer-reviewed journal Traffic Injury Prevention.
“In general older drivers are at an elevated risk for ...
DNA methylation markers for increased risk of schizophrenia identified for first time in newborns
2023-04-27
An international research team led by investigators at Virginia Commonwealth University has identified for the first time markers that may indicate early in life if a person has susceptibility to schizophrenia.
The ability to predict the risk of developing schizophrenia later in life may allow early detection and intervention, which the researchers hope can reduce the impact of the disease on individuals, families and communities. Their results have been published in Molecular Psychiatry.
Schizophrenia is a serious psychiatric disorder that is most often detected in young adulthood. It ...
Geneticists link phenotype of Balto, famed sled dog, to modern breeds
2023-04-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led project has added a new chapter to the story of Balto – the most famous sled dog in history – by using ancient DNA extraction and analysis to reconstruct his phenotype and identify his genetic connections to modern dog breeds.
The research reveals Balto’s lineage was genetically healthier and less inbred than modern breeds, with characteristics adapted to the extreme environment of 1920s Alaska.
The team’s paper, “Comparative Genomics of Balto, a Famous Historic Dog, Captures Lost Diversity of 1920s Sled Dogs,” published April 27 in Science.
Heather Huson, associate professor of animal science ...
Highly dexterous robot hand can operate in the dark -- just like us
2023-04-27
New York, NY—April 27, 2023—Think about what you do with your hands when you’re home at night pushing buttons on your TV’s remote control, or at a restaurant using all kinds of cutlery and glassware. These skills are all based on touch, while you’re watching a TV program or choosing something from the menu. Our hands and fingers are incredibly skilled mechanisms, and highly sensitive to boot.
Robotics researchers have long been trying to create “true” dexterity in robot ...
Texas Tech researchers contribute to groundbreaking mammal research
2023-04-27
Why was Balto, a famous sled dog from the 1920s, able to survive the unforgiving conditions of Alaska? It was one of many findings uncovered through the Zoonomia Project, which involved researchers from Texas Tech University.
More than a dozen researchers from the Department of Biological Sciences were among the major collaborators in the Zoonomia Project who will publish their multi-year comparative genomic analysis of mammals and the influence of genetic change on health and disease in the April 28 issue of Science magazine.
The laboratory of David Ray, professor and associate chair of the department, studies transposable elements ...
Snowballing effects of beech leaf disease hurt helpful root fungi
2023-04-27
The American beech, Fagus grandifolia, is a North American staple and the dominant species in many northeastern forests. In 2012, a new disease was first spotted, infecting trees in northeastern Ohio. The worst afflicted had dark banding on their leaves, which emerged crumpled and leathery in the spring. Not until 2018 would experts discover the nematode pest, Litylenchus crenatae mccannii, overwintering in the buds of infected trees.
As it marches across the continent, researchers are still ...
Higher rates of autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in American children
2023-04-27
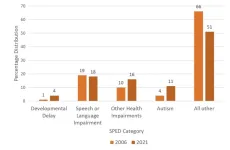
In a recent publication released by PubMed, American scientists led by Dr. Dufault at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, reported alarming increases in the numbers of children requiring special education services. While student enrollment in US schools remained stable from 2006-2021, the percentage of children receiving special education services increased 10.4%. Of the three disability categories under which children with autism may receive services, autism caseload percentages tripled jumping from 4% to 11% while developmental delay caseload ...
Improving geriatric surgical quality is feasible for a wide range of hospitals
2023-04-27
Key takeaways
Feasible for small and large hospitals: Pilot institutions in the study included community hospitals and academic medical centers representing every region of the United States.
Geriatric surgical patients are a growing population: American College of Surgeons standards for geriatric surgery address a growing population that most hospitals serve.
Standards help address barriers to implementation: ACS geriatric surgery standards help hospitals identify and address challenges to providing optimal care, including staffing, manpower, and lack of geriatricians in many hospitals.
CHICAGO: ...
Scripps Research preclinical study finds insomnia drug blocks oxycodone relapse
2023-04-27
LA JOLLA, CA—The insomnia drug suvorexant (Belsomra®) might be an effective treatment for opioid use disorder, according to a preclinical study from Scripps Research.
In the study, published April 27, 2023, in Frontiers in Pharmacology, the Scripps Research scientists found that suvorexant reduced prescription opioid intake and helped protect against relapse in rats modeling opioid use disorder (OUD). If the results translate to humans in clinical trials, the insomnia drug could offer a promising approach for the millions of people who have OUD.
“Our results suggest that repurposing suvorexant could be a good strategy for reducing drug intake and blocking relapse in cases ...
Calling all canines: Help sniff out the dangerous spotted lanternfly
2023-04-27
From New York to North Carolina and as far west as Illinois, the invasive spotted lanternfly is causing chaos in many states where agricultural and forestry industries are essential to the economy. It has been estimated that crops and forest production losses caused by insects and pathogens are close to $40 billion a year.
Spotted laternflies, native to mainland China, prey upon 70-plus host plant species, stealing their nutrients with their piercing snouts, called stylets. They are often characterized as “hitchhikers” for their ability to move ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Study: Medicaid enrollment among immigrant children higher in sanctuary statesFindings revealed at the 2023 Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting