(Press-News.org) A team from the University of Illinois has modeled improving photosynthesis through enzyme modification and simulated soybean growth with realistic climate conditions, determining to what extent the improvements in photosynthesis could result in increased yields.
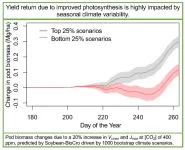
“There’s a complex relationship between photosynthesis improvement and actual yield, having higher photosynthesis doesn’t necessarily mean you have higher yield. The yield return is highly impacted by seasonal climate conditions” said Yufeng He, a postdoctoral researcher at Illinois, who led this work for a research project called Realizing Increased Photosynthetic Efficiency (RIPE). “This study has created a bridge that links the missing part between photosynthesis improvements and higher yields at field scale.”
RIPE, which is led by Illinois, is engineering crops to be more productive by improving photosynthesis, the natural process all plants use to convert sunlight into energy and yields. This RIPE research was supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Foundation for Food & Agriculture Research, and U.K. Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office.
He and his colleagues in the Matthews Research Group used the BioCro modeling framework to simulate soybeans in Illinois fields under normal and elevated CO2 conditions, paying specific attention to two important parameters that affect the plant canopy’s photosynthetic process; Jmax and Vcmax. They wanted to determine the effect of boosting these photosynthetic processes at the canopy level, rather than just at the leaf level, and determine if the effects could lead to higher yields under a range of climate conditions.
The team found that the overall returns in plant photosynthesis and pod biomass (yields) were affected when plants were simulated in a high CO2 environment. They also found that correlations between increased photosynthesis and increased yield were dependent on the climate conditions at different stages of soybean growth. Their findings were recently published in Field Crops Research.
“There has been evidence showing that photosynthesis can be improved by modifying certain enzymes, but most of these studies were either done only looking at the leaf-scale impacts or the impacts from a limited number of field trials and seasonal climate conditions,” said Megan Matthews, Assistant Professor in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Illinois and Principal Investigator on the research. “We studied the impacts of seasonal climate conditions at the field level on the improvements of photosynthesis. Using realistic climate inputs to run our models and show how those improvements would vary with different climates.”
The next steps for the researchers involve adding specific data from African plant cultivars and environmental conditions and incorporating more detailed mechanistic models to apply the findings to crop growth in Sub-Saharan Africa.
END
RIPE researchers model ‘link’ between improved photosynthesis and increased yield
2023-05-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dual-purpose therapeutic targets for aging and glioblastoma identified with PandaOmics
2023-05-02
“[...] AI-powered algorithms, such as PandaOmics, may accelerate subsequent gene target discovery not only for GBM but for a broader range of age-associated diseases.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 2, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “Identification of dual-purpose therapeutic targets implicated in aging and glioblastoma multiforme using PandaOmics - an AI-enabled biological target discovery platform.”
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive and most ...
Flagship report of the North American Commission for Environmental Cooperation, Taking Stock, examines where 5 billion kg of industrial pollutants go every year in North America
2023-05-02
Montreal — The North American Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) today released a new report compiling and analyzing data reported by approximately 24,000 industrial facilities in Canada, Mexico and the United States to their respective national pollutant release and transfer registers. The report reveals important gaps in the reporting and tracking of transfers to disposal across the region due to differing reporting requirements, shared responsibilities across agencies and jurisdictions, and the lack of information about the fate of waste pollutants when they are transferred to third parties (such as waste management service providers) or across national ...
Cedars-Sinai Cancer appoints new biobank director
2023-05-02
Cedars-Sinai Cancer welcomes Karine Sargsyan, MD, formerly director of one of the world’s largest clinical biobanks, as scientific director of its OncoBiobank. Sargsyan is charged with leading biobank development and creating new strategies for the optimal deployment and use of the Cedars-Sinai Cancer Molecular Twin Precision Oncology Platform for both research and clinical practice. She will work collaboratively with Nicholas Tatonetti, PhD, associate director of Computational Oncology, on the ...
Upcycling method turns textile trash to functional coatings
2023-05-02
ITHACA, N.Y. - In an effort to make textiles more sustainable, a new method allows researchers to break old clothing down chemically and reuse polyester compounds to create fire resistant, anti-bacterial or wrinkle-free coatings that could then be applied to clothes and fabrics.
The proof-of-principle study provides hope for unsustainable textile, apparel and footwear industries that together generate 20% of global solid waste. Many so-called recyclers end up illegally dumping textiles as trash in countries in Asia and Africa.
“We think that our clothes are recycled or reprocessed, but most ...
Joyful music could be a game changer for virtual reality headaches
2023-05-02
Joyful music could be a game changer for virtual reality headaches
Listening to music could reduce the dizziness, nausea and headaches virtual reality users might experience after using digital devices, research suggests.
Cybersickness – a type of motion sickness from virtual reality experiences such as computer games – significantly reduces when joyful music is part of the immersive experience, the study found.
The intensity of the nausea-related symptoms of cybersickness was also found to substantially decrease with both joyful and calming music.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh assessed the effects of music ...
Study shows governments escape blame by contracting services such as prisoner transport
2023-05-02
LAWRENCE — Governments and private contractors work together on countless functions, but when something goes wrong, who is to blame?
Zach Mohr, associate professor of public affairs & administration at the University of Kansas, is involved in a series of studies to examine how people determine blame and hold those in power accountable.
While research has shown deaths in prisons have increased in recent years, there is little public data available about how those deaths occur in specific ...
New research reveals that most child victims of gun violence are innocent bystanders
2023-05-02
A University of Missouri School of Medicine researcher examining the circumstances behind pediatric firearm assaults found that most child shooting victims were shot outdoors for unknown reasons and were likely not intentionally targeted.
Firearm injuries surpassed motor vehicle accidents as the leading cause of child deaths in 2020. Assault has become the most common cause of firearm injury among American children and adolescents, surpassing firearm suicide and accidental firearm injuries. However, very little research exists examining the circumstances ...
National trends in mental health–related emergency department visits among youth
2023-05-02
About The Study: Over the last 10 years, the proportion of pediatric emergency department visits for mental health reasons have approximately doubled, including a 5-fold increase in suicide-related visits. These findings underscore an urgent need to improve crisis and emergency mental health service capacity for young people, especially for children experiencing suicidal symptoms.
Authors: Greg Rhee, Ph.D., of the University of Connecticut School of Medicine in Farmington, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
USPSTF recommendation statement on screening for latent tuberculosis infection in adults
2023-05-02
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in populations at increased risk. Populations at increased risk for LTBI based on increased prevalence of active disease and increased risk of exposure include persons who were born in, or are former residents of, countries with high tuberculosis prevalence and persons who live in, or have lived in, high-risk congregate settings (e.g., homeless shelters or correctional facilities). The precise prevalence rate of LTBI in the U.S. is difficult to determine; however, estimated prevalence is about 5.0%, or up to 13 million persons. ...
Classifying cancer cells to predict metastatic potential
2023-05-02
WASHINGTON, May 2, 2023 – Cancer cells that initiate metastasis, or the spread of the disease from its primary location, are different from cancer cells that stay in the original tumor. Distinguishing metastasis-initiating cell types can determine the severity of cancer and help medical practitioners decide on a course of treatment.
In APL Machine Learning, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Texas Tech University developed a deep learning model to classify cancer cells by type. The tool requires only a simple microscope and a ...