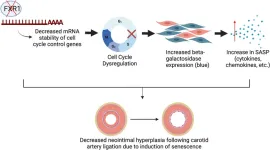
(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, May 2, 2023 – Vascular diseases, including myocardial infarction, stroke, renal failure, and peripheral vascular disease, continue to account for one third of all mortality in the United States, Europe, and the developing world (World Health Organization, 2021). Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) activation plays a crucial role in the development of multiple vascular diseases. In a novel study in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, researchers found that when fragile-X related protein-1 (FXR1) is absent, VSMC proliferate more slowly, become senescent, and scar tissue (neointima) development is reduced. Therefore, drugs targeting FXR1 may treat vascular proliferative diseases.
“Our lab previously reported that expression of FXR1, a muscle-enhanced RNA binding protein that appears to decrease inflammatory transcripts, is increased in injured arteries and in plaque VSMC in human aortas,” explained lead investigator Michael V. Autieri, PhD, Department of Cardiovascular Sciences, Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, PA, USA. “However, the role of FXR1 expression in the vascular response to injury had not yet been studied in a relevant animal model of vascular disease, and so we designed our study to explore this further.”
To extend their understanding of the impact of the absence of FXR1, investigators performed RNA-sequencing on FXR1-depleted human VSMCs. Their results suggest that FXR1 appears to stabilize a group of transcripts involved in control of the cell cycle, most of which are associated with proliferation and cell division. In addition, they noted an increase in beta galactosidase and gamma H2AX, molecules indicative of cell senescence.
Next, to understand how the absence of FXR1 would affect vascular occlusive disease, they developed a mouse model to specifically deplete FXR1 in the smooth muscles upon drug induction. The mice were subjected to carotid ligation, which is a model of vascular stenosis. Drug-induced depletion of FXR1 in smooth muscle cells protected the mice against neointima formation following injury. Injured arteries had a gene expression profile similar to human VSMC following FXR1 knockdown.
“These results are the first to suggest that in addition to destabilization of inflammatory transcripts, FXR1 may stabilize cell cycle related genes in VSMC, and absence of FXR1 leads to induction of a senescent phenotype. This supports the hypothesis that FXR1 may mediate vascular disease by regulating stability of proliferative mRNA in VSMC,” commented Dr. Autieri.
The fact that FXR1 stabilized this group of transcripts, while it normally is regarded as an RNA-binding protein that destabilizes transcripts, was surprising to investigators. Additionally, while they expected to see a difference in the knockout mouse phenotype compared to controls, they did not expect such a dramatic result.
“Because we have seen that in the absence of FXR1, VSMC have significantly reduced proliferation and become senescent, drugs that target FXR1 may have implications for modalities to combat vascular proliferative diseases such as atherosclerosis, restenosis, hypertension, and abdominal aortic aneurysm. Given the global increase in cardiovascular diseases in an aging and increasingly sedentary population, it is critical to do everything we can to investigate potential genes and targets that may be exploited to influence disease pathology,” Dr. Autieri concluded.
END
Study identifies a new potential target for treating vascular disease
Drugs that target fragile-X related protein-1 (FXR1), an mRNA-binding protein, may aid in treating vascular proliferative disease, report investigators in The American Journal of Pathology
2023-05-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Positive long-term outcomes with arthroscopy for young adults with borderline hip dysplasia
2023-05-02
May 2, 2023 – For young adults with borderline hip dysplasia (BHD), primary arthroscopy provides positive long-term outcomes, improving symptoms and function while avoiding the need for hip replacement surgery in most cases, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Ten-year follow-up data provides new evidence on the benefits of arthroscopy for treatment of BHD, according to the case series by Benjamin G. Domb, MD, of the American Hip Institute, Chicago.
New ...
Can ET detect us?
2023-05-02
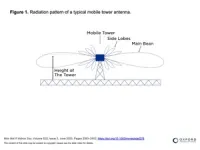
May 2, 2023, Mountain View, CA, Manchester, UK and Mauritius -- What would the Earth look like to an alien civilization located light years away? A team of researchers from Mauritius and Manchester University has used crowd-sourced data to simulate radio leakage from mobile towers and predict what an alien civilization might detect from various nearby stars, including Barnard's star, six light years away from Earth. Ramiro Saide, currently an intern at the SETI Institute's Hat Creek Radio Observatory and M.Phils. student at the University of Mauritius, generated models displaying the radio power that these civilizations would receive as the Earth rotates and the ...
UCSF is first in California to provide drug-gene testing
2023-05-02
Precision Medicine Milestone Will Result in Smarter Prescribing
Beginning May 9, UC San Francisco will be the first hospital in California, and one of only a few nationwide, to offer pharmacogenetic testing. The test will provide critical clues about a patient’s unique genetic makeup, enabling pharmacists to tailor medications and dosages accordingly.
The service will result in smarter prescribing and improved clinical outcomes, said Bani Tamraz, PharmD, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Clinical Pharmacy at the UCSF School of Pharmacy and lead of the pharmacogenomics program. A patient’s blood will be tested for 15 genes ...
A touch-responsive fabric armband – for flexible keyboards, wearable sketchpads
2023-05-02
It's time to roll up your sleeves for the next advance in wearable technology – a fabric armband that’s actually a touch pad. In ACS Nano, researchers say they have devised a way to make playing video games, sketching cartoons and signing documents easier. Their proof-of-concept silk armband turns a person’s forearm into a keyboard or sketchpad. The three-layer, touch-responsive material interprets what a user draws or types and converts it into images on a computer.
Computer trackpads and electronic signature-capture ...
New ACS report finds smoking rates, alcohol use, physical inactivity decreased during COVID-19; worsening trends in obesity, cervical cancer screening
2023-05-02
ATLANTA, May 2, 2023 – In a new report, American Cancer Society (ACS) researchers discovered both favorable and unfavorable changes in major cancer risk factors, preventive behaviors and services, and screenings in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. Between 2019 and 2021, current smoking, physical inactivity, and heavy alcohol consumption declined, and human papillomavirus vaccination and stool testing for colorectal cancer screening uptake increased. In contrast, obesity prevalence increased, while cervical cancer screening declined during the same timeframe. Additionally, disparities by racial/ethnic and socioeconomic status persisted.
The findings were released ...
New AI algorithm boosts COVID-19 mRNA vaccine antibody response by 128 times
2023-05-02
A team of researchers from Baidu Research has developed an AI algorithm that can rapidly design highly stable COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sequences that were previously unattainable. The algorithm, named LinearDesign, represents a major leap in both stability and efficacy for vaccine sequences, achieving a 128-fold increase in the COVID-19 vaccine’s antibody response.
“This research can apply mRNA medicine encoding to a wider range of therapeutic proteins, such as monoclonal antibodies and anti-cancer drugs, promising broad applications and far-reaching impact,” said Dr. He Zhang, Staff Software Engineer ...
RIPE researchers model ‘link’ between improved photosynthesis and increased yield
2023-05-02
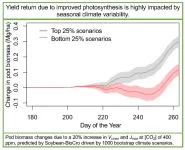
A team from the University of Illinois has modeled improving photosynthesis through enzyme modification and simulated soybean growth with realistic climate conditions, determining to what extent the improvements in photosynthesis could result in increased yields.
“There’s a complex relationship between photosynthesis improvement and actual yield, having higher photosynthesis doesn’t necessarily mean you have higher yield. The yield return is highly impacted by seasonal climate conditions” said Yufeng He, a postdoctoral researcher at Illinois, who led this work for a research project called Realizing Increased ...
Dual-purpose therapeutic targets for aging and glioblastoma identified with PandaOmics
2023-05-02
“[...] AI-powered algorithms, such as PandaOmics, may accelerate subsequent gene target discovery not only for GBM but for a broader range of age-associated diseases.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 2, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “Identification of dual-purpose therapeutic targets implicated in aging and glioblastoma multiforme using PandaOmics - an AI-enabled biological target discovery platform.”
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive and most ...
Flagship report of the North American Commission for Environmental Cooperation, Taking Stock, examines where 5 billion kg of industrial pollutants go every year in North America
2023-05-02
Montreal — The North American Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) today released a new report compiling and analyzing data reported by approximately 24,000 industrial facilities in Canada, Mexico and the United States to their respective national pollutant release and transfer registers. The report reveals important gaps in the reporting and tracking of transfers to disposal across the region due to differing reporting requirements, shared responsibilities across agencies and jurisdictions, and the lack of information about the fate of waste pollutants when they are transferred to third parties (such as waste management service providers) or across national ...
Cedars-Sinai Cancer appoints new biobank director
2023-05-02
Cedars-Sinai Cancer welcomes Karine Sargsyan, MD, formerly director of one of the world’s largest clinical biobanks, as scientific director of its OncoBiobank. Sargsyan is charged with leading biobank development and creating new strategies for the optimal deployment and use of the Cedars-Sinai Cancer Molecular Twin Precision Oncology Platform for both research and clinical practice. She will work collaboratively with Nicholas Tatonetti, PhD, associate director of Computational Oncology, on the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
[Press-News.org] Study identifies a new potential target for treating vascular diseaseDrugs that target fragile-X related protein-1 (FXR1), an mRNA-binding protein, may aid in treating vascular proliferative disease, report investigators in The American Journal of Pathology