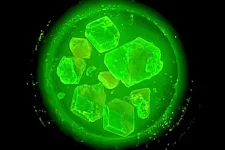
(Press-News.org) For millions of people with seasonal allergies, springtime means runny noses, excessive sneezes and itchy eyes. And, as with many things, climate change appears to be making allergy season even worse. Researchers reporting in ACS Earth and Space Chemistry have shown that common allergen-producing plants ryegrass and ragweed emit more smaller, “subpollen particles” (SPPs) than once thought, yet climate would likely be most affected by their intact pollen grains, which can boost cloud formation.
In addition to annoying sinuses, pollen naturally functions as a way for plants to exchange genetic material and reproduce. When exposed to moisture, these pollen grains can burst into tiny SPPs less than a micron long. Their smaller size allows them to reach the lower respiratory system, where they can last longer and cause more inflammation than their larger counterparts. Both SPPs and whole pollen grains are also thought to act as ice nucleation sites — miniature starting points for clouds. But compared to regular clouds, SPPs and pollen form smaller, more numerous clouds that tend to hold onto their precipitation, helping trap in radiant heat and contributing to climate change. In turn, higher temperatures can extend pollen-release periods, further exacerbating the problem. Previously, Brianna Matthews, Alyssa Alsante and Sarah Brooks studied how oak trees emit SPPs at different humidity levels. But this time, the team wanted to investigate how two other common allergen-producing plants, ragweed and ryegrass, release SPPs under humid conditions, and how those particles could affect ice cloud formation.
The researchers collected samples of ryegrass and ragweed, then placed them into a specialized “pollen chamber.” There, the samples were exposed to different humidity levels and bursts of wind over several hours to simulate real-world conditions.
The group assessed the number of SPPs per pollen grain, as well as the abilities of both to nucleate ice. Surprisingly, the team found that previous experiments on the same types of plants underestimated the amount of SPPs by a factor of 10 to 100. This was likely because the other experiments used a less realistic means of spreading the pollen and generating the SPPs, say the researchers. Ragweed and ryegrass SPPs were very poor ice-nucleating sites, however — barely better than plain water — while whole pollen grains facilitated cloud growth. The researchers say that these updated parameters and numbers of emitted pollen grains and particles could ultimately be used to create more-accurate climate models.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Science Foundation.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Pollen production could impact climate change by helping clouds form
2023-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Plastic can drift far away from its starting point as it sinks into the sea
2023-05-08
Discarded or drifting in the ocean, plastic debris can accumulate on the water’s surface, forming floating islands of garbage. Although it’s harder to spot, researchers suspect a significant amount also sinks. In a new study in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology, one team used computer modeling to study how far bits of lightweight plastic travel when falling into the Mediterranean Sea. Their results suggest these particles can drift farther underwater than previously thought.
From ...
Scintillating science: FSU researchers improve materials for radiation detection and imaging technology
2023-05-08
A team of Florida State University researchers has further developed a new generation of organic-inorganic hybrid materials that can improve image quality in X-ray machines, CT scans and other radiation detection and imaging technologies.
Professor Biwu Ma from the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and his colleagues have developed a new class of materials that can act as highly efficient scintillators, which emit light after being exposed to other forms of high energy radiations, such as X-rays.
The team’s most recent study, published in Advanced Materials, is an improvement upon their previous research to develop better scintillators. The new design concept produces ...
Webb looks for Fomalhaut’s asteroid belt and finds much more
2023-05-08
Astronomers used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to image the warm dust around a nearby young star, Fomalhaut, in order to study the first asteroid belt ever seen outside of our solar system in infrared light. But to their surprise, the dusty structures are much more complex than the asteroid and Kuiper dust belts of our solar system. Overall, there are three nested belts extending out to 14 billion miles (23 billion kilometers) from the star; that’s 150 times the distance of Earth from the Sun. The scale of the outermost belt is roughly twice the scale of our ...
UCI researchers discover new drugs with potential for treating world’s leading causes of blindness in age-related and inherited retinal diseases
2023-05-08
Irvine, CA – May xx, 2023 – In a University of California, Irvine-led study, researchers have discovered small-molecule drugs with potential clinical utility in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy (DR), and retinitis pigmentosa (RP).
The study, titled, “Stress resilience-enhancing drugs preserve tissue structure and function in degenerating retina via phosphodiesterase inhibition,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“In this study, we introduce a new class of therapeutics called ‘Stress ...
First deaf, Black woman receives her PhD in a STEM discipline
2023-05-08
ST. LOUIS, MO - May 8, 2023 – Graduate student Amie Fornah Sankoh recently stood in front of 150 colleagues family and friends at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center to defend her thesis, Investigating the Effects of Salicylic acid on Intercellular Trafficking via Plasmodesmata in Nicotiana benthamiana. Upon her successful defense, Dr. Amie Sankoh became the first Deaf, Black woman to receive a PhD in any STEM discipline.
Completing a PhD is a challenging undertaking for anyone; to do so without easy access to the kinds of verbal communication that hearing people ...
Microbubble macrophages track tumors #ASA184
2023-05-08
CHICAGO, May 8, 2023 – Macrophages, a type of white blood cell, defend the body by engulfing and digesting foreign particles, such as bacteria, viruses, and dead cells. The immune cells also tend to accumulate in solid tumors, so tracking them could enable new ways to detect cancer and the earliest stages of metastasis.
As part of the 184th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, Ashley Alva of the Georgia Institute of Technology will describe how attaching microbubbles to macrophages can create high-resolution and sensitive tracking images useful for disease diagnosis. Her presentation, “Tracking macrophages ...
A cocktail party of 3D-printed robot heads #ASA184
2023-05-08
CHICAGO, May 8, 2023 – Imagine a cocktail party full of 3D-printed, humanoid robots listening and talking to each other. That seemingly sci-fi scene is the goal of the Augmented Listening Laboratory at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. Realistic talking (and listening) heads are crucial for investigating how humans receive sound and developing audio technology.
The team will describe the talking human head simulators in their presentation, “3D-printed acoustic head simulators that talk and move,” on Monday, May 8, at 12:15 p.m. Eastern U.S. in the Northwestern/Ohio State room of the Chicago Marriott Downtown Magnificent Mile Hotel. The talk comes as part of ...
Targeting Mitochondria 2023 will highlight current and future mitochondrial research in October in Berlin
2023-05-08
The World Mitochondria Society is organizing its 14th world conference, Targeting Mitochondria 2023, on October 11-13 at the Steigenberger Hotel Am Kanzleramt, Berlin. Targeting Mitochondria 2023 will address the latest advances and perspectives in mitochondrial research and provide an outlook on future mitochondrial therapies.
Volkmar Weissig, president of the World Mitochondria Society, and Marvin Edeas, president of the scientific committee, said, "This year we will have specific sessions on innovations such as mitochondria in space, exosome-based mitochondrial ...
Uniformity of prey can yield spider-eat-spider world
2023-05-08
A limited menu of prey may weave a tangled food web by emboldening wolf spiders of multiple species to dine on each other and even cannibalize their own, says a study from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Ecologists have long known that predators with otherwise-similar diets can coexist by effectively divvying up the food sources of a community to ease competition and, ideally, leave enough prey for everyone. But analyses of wolf spider species in Nebraska suggest that when the diversity of their mutual prey is lacking, the eight-legged ...
Researchers develop model for how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids
2023-05-08
Researchers at the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute at UCLA and the National Institutes of Health have developed a zebrafish model that provides new insight into how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids, including docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and linolenic acid (ALA). Their findings, published in Nature Communications, have the potential to improve understanding of lipid transport across the blood-brain barrier and of disruptions in this process that can lead to birth defects or neurological conditions. The model may also enable researchers to design drug molecules that are capable of directly ...