(Press-News.org) Scientists have used mitochondrial DNA to trace a female lineage from northern coastal China to the Americas. By integrating contemporary and ancient mitochondrial DNA, the team found evidence of at least two migrations: one during the last ice age, and one during the subsequent melting period. Around the same time as the second migration, another branch of the same lineage migrated to Japan, which could explain Paleolithic archeological similarities between the Americas, China, and Japan. The study appears May 9 in the journal Cell Reports.
“The Asian ancestry of Native Americans is more complicated than previously indicated,” says first author Yu-Chun Li, a molecular anthropologist at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. “In addition to previously described ancestral sources in Siberia, Australo-Melanesia, and Southeast Asia, we show that northern coastal China also contributed to the gene pool of Native Americans.”
Though it was long assumed that Native Americans descended from Siberians who crossed over the Bering Strait’s ephemeral land bridge, more recent genetic, geological, and archeological evidence suggests that multiple waves of humans journeyed to the Americas from various parts of Eurasia.
To shed light on the history of Native Americans in Asia, a team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences followed the trail of an ancestral lineage that might link East Asian Paleolithic-age populations to founding populations in Chile, Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, Ecuador, Mexico, and California. The lineage in question is present in mitochondrial DNA, which can be used to trace kinship through the female line.
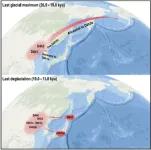
The researchers scoured over 100,000 contemporary and 15,000 ancient DNA samples from across Eurasia to eventually identify 216 contemporary and 39 ancient individuals belonging to the rare lineage. By comparing the accumulated mutations, geographic locations, and carbon-dated age of each of these individuals, the researchers were able to trace the lineage’s branching path. They identified two migration events from northern coastal China to the Americas, and in both cases, they think that the travelers probably set dock in America via the Pacific coast rather than by crossing the inland ice-free corridor (which would not have opened at the time).
The first radiation event occurred between 19,500 and 26,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum, when ice sheet coverage was at its greatest and conditions in northern China were likely inhospitable for humans. The second radiation occurred during the subsequent deglaciation or melting period, between 19,000 and 11,500 years ago. There was a rapid increase in human populations at this time, probably due to the improved climate, which may have fueled expansion into other geographical regions.
The researchers also uncovered an unexpected genetic link between Native Americans and Japanese people. During the deglaciation period, another group branched out from northern coastal China and traveled to Japan. “We were surprised to find that this ancestral source also contributed to the Japanese gene pool, especially the indigenous Ainus,” says Li.
This discovery helps to explain archeological similarities between the Paleolithic peoples of China, Japan, and the Americas. Specifically, the three regions share similarities in how they crafted stemmed projectile points for arrowheads and spears. “This suggests that the Pleistocene connection among the Americas, China, and Japan was not confined to culture but also to genetics,” says senior author Qing-Peng Kong, an evolutionary geneticist at the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Though the study focused on mitochondrial DNA, complementary evidence from Y chromosomal DNA suggests that male ancestors of Native Americans also lived in northern China at around the same time as these female ancestors.
This study adds another piece to the puzzle that is Native American ancestry, but many other elements remain unclear. “The origins of several founder groups are still elusive or controversial,” says Kong. “Next, we plan to collect and investigate more Eurasian lineages to obtain a more complete picture on the origin of Native Americans.”
###
This research was supported by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research, the Strategic Priority Research Program, the Young Scientists in Basic Research, Key Research Program of Frontiers Science, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Digitalization, Development, and Application of Biotic Resource Program, the Italian Ministry of Education University and Research (MIUR), the Department of Biology and Biotechnology at the University of Pavia and Progetti, High-level Talent, Promotion and Training Project of Kunming, Yunling Scholar of the Yunnan Province, Yunnan Ten Thousand Talents Plan, Young & Elite Talents Project, and Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects.
Cell Reports, Li and Gao et al. “Mitogenome evidence shows two radiation events and dispersals of matrilineal ancestry from Northern Coastal China to the Americas and Japan” https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(23)00424-2 DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112413
Cell Reports (@CellReports), published by Cell Press, is a weekly open-access journal that publishes high-quality papers across the entire life sciences spectrum. The journal features reports, articles, and resources that provide new biological insights, are thought-provoking, and/or are examples of cutting-edge research. Visit: http://www.cell.com/cell-reports. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
Evidence of Ice Age human migrations from China to the Americas and Japan
2023-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Trends in deaths from falls among adults age 65 or older
2023-05-09
About The Study: Between 1999 and 2020, deaths coded as being caused by falls among adults age 65 or older in the U.S. increased in number and rates for the overall population and for every population subgroup, although the magnitude of the increase varied. However, the relative ranking of the different groups has not changed over time.
Authors: Alexis R. Santos-Lozada, Ph.D., of Pennsylvania State University in University Park, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.3054)
Editor’s ...
Extracting the best flavor from coffee
2023-05-09
WASHINGTON, May 9, 2023 – Espresso coffee is brewed by first grinding roasted coffee beans into grains. Hot water then forces its way through a bed of coffee grains at high pressure, and the soluble content of the coffee grains dissolves into the water (extraction) to produce espresso.
In 2020, researchers found that more finely ground coffee beans brew a weaker espresso. This counterintuitive experimental result makes sense if, for some reason, regions exist within the coffee bed where less or even no coffee is extracted. This uneven extraction becomes more pronounced when coffee is ground more finely.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, ...
Preserving pine forests by understanding beetle flight
2023-05-09
WASHINGTON, May 9, 2023 – The mountain pine beetle is one of the main causes of tree mortality in the pine forests of North America. For example, the insect has killed thousands of acres of pine forest in British Columbia and Alberta, and as a result, the areas are more vulnerable to wildfire. Increased tree mortality has turned Canada’s forests into a large net source of atmospheric carbon dioxide – emitted from the burned or decaying wood of dead trees – rather than a sink.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Alberta studied the flight performance of the mountain pine beetle from a fluid mechanics and an entomological perspective. ...
US gun violence: half of people from Chicago witness a shooting by age 40, study suggests
2023-05-09
Study following Chicagoans over a 25-year period suggests over half of the city’s Black and Hispanic population, and a quarter of its White population, have seen a shooting by age 40.
Researchers followed over two thousand people, with 50% of all the study’s participants witnessing a shooting.
Average age when first witnessing a shooting was just 14 years old.
Women only slightly less likely than men to witness shootings, despite men being far more likely to get shot.
Such levels of violence exposure may cause chronic stress and knock-on health implications for populations in Chicago and elsewhere.
A ...
Assessment of medical cannabis and health-related quality of life
2023-05-09
About The Study: In this study, patients using medical cannabis reported improvements in health-related quality of life, which were mostly sustained over time. Adverse events were rarely serious but common, highlighting the need for caution with prescribing medical cannabis.
Authors: Thomas R. Arkell, Ph.D., of the Swinburne University of Technology in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Making vaccines longer lasting
2023-05-09
The SARS-Cov-2 pandemic illustrates how variable vaccines can be in their length of efficacy, with regular boosters needed to keep people protected. In comparison, the immunity generated by a single vaccination against the measles virus can last decades.
It has always remained a scientific mystery as to why only some vaccines lead to life-long protection. Now a paper published in the journal, Immunity, led by Prof. David Tarlinton and Dr Marcus Robinson, both from Monash University’s Central Clinical School in Melbourne, Australia, has found that the clue likely lies in the body producing a unique subtype of an immune cell in response to some ...
Long-term study pinpoints who has been shot and witnessed shootings by race, sex, and birth year
2023-05-09
Exposure to gun violence is one of the great traumas of American life, but its harms are not equally distributed. In a first-of-its-kind study published Tuesday in JAMA Network Open, a Harvard sociology professor and his colleagues set out to examine exposure to shootings by race, sex, and birth year in a long-term study that followed respondents from childhood up to age 40.
“The idea here is to take a life-course perspective,” said Robert J. Sampson, the Woodford L. and Ann A. Flowers University Professor. ...
Not all statins are created equal
2023-05-09
We’ve all recently gotten a crash-course in drug repurposing, thanks to near-daily news reports about efforts to identify existing medicines that could help treat COVID-19 in the early phase of the pandemic. A team of scientists at the Wyss Institute at Harvard University jumped into the fray in the spring of 2020, applying novel computational drug repurposing approaches to confront the COVID-19 challenge. This early work led to the surprising prediction that a some, but not all, types of statins (drugs that are widely prescribed to lower cholesterol) might protect patients against SARS-CoV-2 infection. In the flurry of clinical studies being published by other scientists studying ...
Motion capture and 3D scans bring history to life for new Dambusters docudrama
2023-05-09
A new docudrama featuring the attack on the Sorpe Dam, using motion capture technology and 3D scans to create life-like digital representations of RAF 617 Squadron aircrew, is being premiered in Bristol on 13 May 2023 to coincide with the 80th anniversary of the Dambusters raid.
Bristol-based film maker Andrew Panton worked with University of Bath researchers at CAMERA, using the latest digital technology to recreate specific scenes for a film featuring the attack on the Sorpe Dam.
Andrew started working on the documentary in 2017 with the last surviving Dambuster George ...
Exploring the underground connections between trees
2023-05-09
Fungal networks interconnecting trees in a forest is a key factor that determines the nature of forests and their response to climate change. These networks have also been viewed as a means for trees to help their offspring and other tree-friends, according to the increasingly popular “mother-tree hypothesis”. An international group of researchers re-examined the evidence for and against this hypothesis in a new study.
Trees in a forest are interconnected through thread-like structures of symbiotic fungi, called hyphae, which together form an underground network called a mycorrhizal network. While it is well known that ...