(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 9, 2023 – The mountain pine beetle is one of the main causes of tree mortality in the pine forests of North America. For example, the insect has killed thousands of acres of pine forest in British Columbia and Alberta, and as a result, the areas are more vulnerable to wildfire. Increased tree mortality has turned Canada’s forests into a large net source of atmospheric carbon dioxide – emitted from the burned or decaying wood of dead trees – rather than a sink.
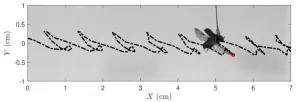
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Alberta studied the flight performance of the mountain pine beetle from a fluid mechanics and an entomological perspective. Understanding these aspects of the insect’s flight could improve estimates of its spread through the environment and preserve pine forests.
To examine insect flight, the team employed a type of model previously used for idealized airfoils. They showed that it can be successfully applied to multiple individual animals across biological sex, insect age, and body size. In doing so, the model can predict how these factors impact flight characteristics.
“We found that there is a dimensionless grouping of velocity and wing beat amplitude that can predict the thrust produced by an insect, and that this grouping can dramatically improve our ability to determine factors that affect flight performance in insects,” said author Zahra Hajati.
After looking at multiple insects, each with its own slightly different wing shape (including some with wing damage), age, and size, the team found differences by group. Female beetles may have greater flight endurance than males, and younger beetles flew with less thrust than other ages.
“This model opens new avenues for entomological investigation, providing a means of dramatically improving statistical confidence levels for insect dispersion studies,” said Hajati.
For the airfoil model to work, the researchers had to modify it to deal with the 3D wing of an insect rather than the classic tear-drop shape of an idealized airfoil. Surprisingly, the primary difference between idealized airfoils and the small, real wings was the relative influence of viscosity, with the insects being more sensitive than the idealized case.
“When we plotted the model against thrust produced by the insects, we were prepared to see a cloud of points roughly arranged into a line, so we were very excited to see such a straight line through our data,” said Hajati “We were surprised at how linearly the forces scaled with wing motion.”
Individual wingbeats are about a hundredth of a second each, and the researchers looked at the forces generated by insects over the course of a few wingbeats. However, in nature, insects can fly for hours during dispersal flights. Going forward, the team plans to relate the wingbeat-to-wingbeat scaling of force generation and energy consumption to how far the insects can disperse over entire flights.
###
The article “Strouhal and Reynolds number scaling of force production in the mountain pine beetle” is authored by Zahra Hajati, Antonia Musso, Zachary Weller, Maya Evenden, and Jaime G. Wong. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on May 9, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0145208). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0145208.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
END
Preserving pine forests by understanding beetle flight
Fluid dynamics models can inform the dispersion of the mountain pine beetle, one of the main causes of tree mortality in pine forests in North America
2023-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US gun violence: half of people from Chicago witness a shooting by age 40, study suggests
2023-05-09
Study following Chicagoans over a 25-year period suggests over half of the city’s Black and Hispanic population, and a quarter of its White population, have seen a shooting by age 40.
Researchers followed over two thousand people, with 50% of all the study’s participants witnessing a shooting.
Average age when first witnessing a shooting was just 14 years old.
Women only slightly less likely than men to witness shootings, despite men being far more likely to get shot.
Such levels of violence exposure may cause chronic stress and knock-on health implications for populations in Chicago and elsewhere.
A ...
Assessment of medical cannabis and health-related quality of life
2023-05-09
About The Study: In this study, patients using medical cannabis reported improvements in health-related quality of life, which were mostly sustained over time. Adverse events were rarely serious but common, highlighting the need for caution with prescribing medical cannabis.
Authors: Thomas R. Arkell, Ph.D., of the Swinburne University of Technology in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Making vaccines longer lasting
2023-05-09
The SARS-Cov-2 pandemic illustrates how variable vaccines can be in their length of efficacy, with regular boosters needed to keep people protected. In comparison, the immunity generated by a single vaccination against the measles virus can last decades.
It has always remained a scientific mystery as to why only some vaccines lead to life-long protection. Now a paper published in the journal, Immunity, led by Prof. David Tarlinton and Dr Marcus Robinson, both from Monash University’s Central Clinical School in Melbourne, Australia, has found that the clue likely lies in the body producing a unique subtype of an immune cell in response to some ...
Long-term study pinpoints who has been shot and witnessed shootings by race, sex, and birth year
2023-05-09
Exposure to gun violence is one of the great traumas of American life, but its harms are not equally distributed. In a first-of-its-kind study published Tuesday in JAMA Network Open, a Harvard sociology professor and his colleagues set out to examine exposure to shootings by race, sex, and birth year in a long-term study that followed respondents from childhood up to age 40.
“The idea here is to take a life-course perspective,” said Robert J. Sampson, the Woodford L. and Ann A. Flowers University Professor. ...
Not all statins are created equal
2023-05-09
We’ve all recently gotten a crash-course in drug repurposing, thanks to near-daily news reports about efforts to identify existing medicines that could help treat COVID-19 in the early phase of the pandemic. A team of scientists at the Wyss Institute at Harvard University jumped into the fray in the spring of 2020, applying novel computational drug repurposing approaches to confront the COVID-19 challenge. This early work led to the surprising prediction that a some, but not all, types of statins (drugs that are widely prescribed to lower cholesterol) might protect patients against SARS-CoV-2 infection. In the flurry of clinical studies being published by other scientists studying ...
Motion capture and 3D scans bring history to life for new Dambusters docudrama
2023-05-09
A new docudrama featuring the attack on the Sorpe Dam, using motion capture technology and 3D scans to create life-like digital representations of RAF 617 Squadron aircrew, is being premiered in Bristol on 13 May 2023 to coincide with the 80th anniversary of the Dambusters raid.
Bristol-based film maker Andrew Panton worked with University of Bath researchers at CAMERA, using the latest digital technology to recreate specific scenes for a film featuring the attack on the Sorpe Dam.
Andrew started working on the documentary in 2017 with the last surviving Dambuster George ...
Exploring the underground connections between trees
2023-05-09
Fungal networks interconnecting trees in a forest is a key factor that determines the nature of forests and their response to climate change. These networks have also been viewed as a means for trees to help their offspring and other tree-friends, according to the increasingly popular “mother-tree hypothesis”. An international group of researchers re-examined the evidence for and against this hypothesis in a new study.
Trees in a forest are interconnected through thread-like structures of symbiotic fungi, called hyphae, which together form an underground network called a mycorrhizal network. While it is well known that ...
New research sheds light on how human vision perceives scale
2023-05-09
Researchers from Aston University and the University of York have discovered new insights into how the human brain makes perceptual judgements of the external world.
The study, published on 8 May in the journal PLOS ONE, explored the computational mechanisms used by the human brain to perceive the size of objects in the world around us.
The research, led by Professor Tim Meese, in the School of Optometry at Aston University and Dr Daniel Baker in the Department of Psychology at University of York, tells us more about how our visual system can exploit ‘defocus blur’ to infer perceptual scale, but that it does ...
Chinese Medical Journal article reviews role of gene involved in brain functions and disorders
2023-05-09
Leucine-rich repeats containing 4 (LRRC4)—a gene abundantly found in the brain and located on human chromosome 7q31–32—plays a pivotal role in memory formation, autism, spinal cord injury, as well as in determining the malignant potential, development, and progression of glioblastoma (GB), an aggressive cancer involving the brain and/or spinal cord. In a review article published (in volume 136 issue 1 on 5 January 2023, and online on 10 February 2023) in the Chinese Medical Journal, researchers shed light on the ...
EuroPCR 2023 – The interventional cardiovascular community is gathering in Paris to learn, share, and shape the future of patient care worldwide
2023-05-09
EuroPCR, the annual world-leading Course in interventional cardiovascular medicine, has been taking place for over 30 years. It is tailored for all those dedicated to the sharing of knowledge and skills, and improvement of patient care worldwide: interventional cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, imaging specialists, radiologists, nurses, allied professionals and other practitioners, as well as researchers, innovators and industry representatives. The 4-day meeting addresses interventions for coronary and peripheral vessels, for the structural heart including valves, for hypertension, heart failure and stroke, while keeping the community up ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
[Press-News.org] Preserving pine forests by understanding beetle flightFluid dynamics models can inform the dispersion of the mountain pine beetle, one of the main causes of tree mortality in pine forests in North America