(Press-News.org) The University of Ottawa’s Interdisciplinary Centre for Black Health survey reveals scope of coronavirus vaccine hesitancy in Black communities in relation to healthcare.
The health care system must play a significant role in combatting COVID-19 mistrust among Black individuals in Canada according to a new University of Ottawa study that found distrust in the healthcare network was so profound that educated individuals were hesitant to receive the vaccine.
Professor Jude Mary Cénat, Associate Professor in the School of Psychology at the Faculty of Social Sciences, is the Chair of the Interdisciplinary Centre for Black Health, which leads research focused on racial disparities in health and social services and led this study.
Background
Datanorth_eastexternal link shows that Black communities were the least vaccinated against COVID-19 yet were the most affected by the global pandemic in terms of infection and mortality in Canada and the West. Black communities saw 2.2 times more deaths from COVID-19 despite having the same access to COVID-19 vaccines.
Findings
Key factors contributing to this mistrust included:
Education: Surprisingly, the level of education was inconsequential in relation to COVID-19 vaccine jabs since even those with professed educated admitted mistrust.
A lack of COVID-19 themed literature geared specifically to Black communities.
Experience of racial discrimination lived inside hospitals and within the healthcare network.
Age: Black individuals between 14-34 were less likely to be vaccinated.
Income level; and
Belief in conspiracy theories.
Of Interest
Black individuals with a familiarity of health resources and literature (health literacy) were more likely to be vaccinated against COVID-19. But these same individuals were less trustful of COVID-19 vaccines and Canada’s health resources if they had experienced systematic racism or discrimination from within the health network.
Research Impact
The link between systematic racism in the healthcare network and lagging COVID-19 trust must be addressed by:
Addressing and finding solutions to combat systematic racism within the healthcare system; and
Creating credible and resourceful healthcare literature that will boost confidence in COVID-19 vaccines in these communities.
Vaccine mistrust among Black individuals in Canada: The major role of health literacy, conspiracy theories, and racial discrimination in the healthcare system, by Jude Mary Cénat, Seyed Mohammad Mahdi Moshirian Farahi, Schwab Mulopo Bakombo, Rose Darly Dalexis, Roland Pongou, Lisa Caulley, Sanni Yaya, Josephine Etowa, Vivek Venkatesh was published in the Journal of Medical Virology on April 24, 2023.
END
Systematic racism in healthcare boosted COVID-19 vaccine mistrust in Black communities: Study
uOttawa’s Interdisciplinary Centre for Black Health survey reveals scope of coronavirus vaccine hesitancy in Black communities in relation to healthcare.
2023-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hey Siri, can you hear me? #ASA184
2023-05-09
CHICAGO, May 9, 2023 – Millions of people now regularly communicate with AI-based devices, such as smartphones, speakers, and cars. Studying these interactions can improve AI’s ability to understand human speech and determine how talking with technology impacts language.
In their talk, “Clear speech in the new digital era: Speaking and listening clearly to voice-AI systems,” Georgia Zellou and Michelle Cohn of the University of California, Davis will describe experiments to investigate how speech and comprehension change when humans communicate ...
Lack of belief in body’s ability to function through pain linked to daily pre-surgery prescribed opioid use among candidates for elective spine surgery
2023-05-09
According to a new Johns Hopkins Medicine study, low pain self-efficacy can predict daily pre-surgery prescribed opioid use among patients seeking elective spine surgery. The study defined pain self-efficacy as the “beliefs held by people with chronic pain that they can carry out certain activities, even when experiencing pain.” Previous studies showed that lower pain self-efficacy is associated with higher pain intensity and greater pain interference in day-to-day life. However, the Johns Hopkins research team believes its study is among the first to investigate ...
Reduced cancer mortality with daily vitamin D intake
2023-05-09
Vitamin D intake could reduce cancer mortality in the population by twelve percent - provided the vitamin is taken daily. This was the result of an evaluation of 14 studies of the highest quality conducted at the German Cancer Research Center with a total of almost 105,000 participants.
Vitamin D deficiency is widespread worldwide and is particularly common among cancer patients. Averaged over the year, the vitamin D blood levels of about 15 percent of German adults are below the threshold for a pronounced vitamin D deficiency*. In contrast, in a study of colorectal ...
Scientists develop AI tool to predict Parkinson’s disease onset
2023-05-09
Scientists from UNSW Sydney with collaborators at Boston University have developed a tool that shows early promise in detecting Parkinson’s disease years before the first symptoms start appearing.
In research published today in the journal ACS Central Science, the researchers described how they used neural networks to analyse biomarkers in patients’ bodily fluids.
The researchers from UNSW School of Chemistry examined blood samples taken from healthy individuals gathered by the Spanish European ...
SwRI selected for Phase A study to develop next-generation NOAA coronagraph
2023-05-09
SAN ANTONIO — May 9, 2023 —NASA has selected Southwest Research Institute for a Phase A study to develop SwRI’s Space Weather Solar Coronagraph (SwSCOR) on behalf of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA’s Space Weather Next Program is charged with providing critical data for its space weather prediction center. SwRI is one of five organizations developing a definition-phase study to produce the next-generation NOAA L1 Series COR instrument to detect and characterize Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
CMEs are huge bursts of coronal plasma threaded with intense magnetic fields ...
Long molecule of RNA essential to our GI tract’s ability to contract and move food along
2023-05-09
AUGUSTA, Ga. (May 9, 2023) – A long molecule of RNA found in abundance in the healthy smooth muscle cells that give our blood vessels strength and flexibility is also essential to the continuous contraction that moves food through our gastrointestinal tract.
Without CARMN, a long, noncoding RNA, which means it doesn’t produce proteins but does help regulate cell activity, the 30-foot-long GI tract doesn’t contract as it should.
That can result in a painful even lethal situation where partially undigested food gets ...
A CRISPR-edited calf shows virus resistance
2023-05-09
A gene-edited calf shows resistance to a common bovine virus. Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) causes gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms as well as reproductive failure in cattle around the world. Vaccines against the virus exist but the virus evolves quickly and vaccines are not always fully protective. Aspen Workman and colleagues used the CRISPR/Cas9 system to swap out just six amino acids in the bovine CD46 receptor in one calf. The calf showed a dramatic reduction in susceptibility to the virus and ...
Potential found to counter depression by restoring key brain rhythm
2023-05-09
Led by researchers from NYU Grossman School of Medicine and University of Szeged in Hungary, a new study in mice and rats found that restoring certain signals in a brain region that processes smells countered depression.
Publishing in the journal Neuron online May 9, the study results revolve around nerve cells (neurons), which “fire” – or emit electrical signals – to transmit information. Researchers in recent years discovered that effective communication between brain regions ...
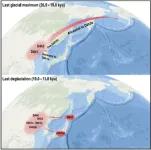
Evidence of Ice Age human migrations from China to the Americas and Japan
2023-05-09
Scientists have used mitochondrial DNA to trace a female lineage from northern coastal China to the Americas. By integrating contemporary and ancient mitochondrial DNA, the team found evidence of at least two migrations: one during the last ice age, and one during the subsequent melting period. Around the same time as the second migration, another branch of the same lineage migrated to Japan, which could explain Paleolithic archeological similarities between the Americas, China, and Japan. The study appears May 9 in the journal Cell Reports.
“The Asian ...
Trends in deaths from falls among adults age 65 or older
2023-05-09
About The Study: Between 1999 and 2020, deaths coded as being caused by falls among adults age 65 or older in the U.S. increased in number and rates for the overall population and for every population subgroup, although the magnitude of the increase varied. However, the relative ranking of the different groups has not changed over time.
Authors: Alexis R. Santos-Lozada, Ph.D., of Pennsylvania State University in University Park, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.3054)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Systematic racism in healthcare boosted COVID-19 vaccine mistrust in Black communities: StudyuOttawa’s Interdisciplinary Centre for Black Health survey reveals scope of coronavirus vaccine hesitancy in Black communities in relation to healthcare.