(Press-News.org) A new drug delivery system delivers an antioxidant directly to mitochondria in the liver, mitigating the effects of oxidative stress.
Mitochondria are microscopic organelles found within cells, and are well-known as the “powerhouse of the cell.” They are by far the largest producer of the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which provides energy to many processes in living cells. The process by which mitochondria synthesize ATP generates a large amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS), chemical groups that are highly reactive.
In a healthy cell, the ROS are controlled by the mitochondria; however, when this balance is lost, the excess ROS damages the mitochondria and subsequently cells and tissues. This phenomenon, known as oxidative stress, can cause premature aging and disease. The ROS that cause oxidative stress can be controlled by antioxidants.
A research team led by Professor Yuma Yamada, Distinguished Professor Hideyoshi Harashima and Assistant Professor Mitsue Hibino at Hokkaido University have developed a system to deliver antioxidants to mitochondria to mitigate the effects of excess ROS. Their findings were published in Scientific Reports.
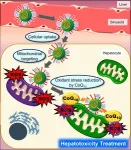
“We previously developed a drug delivery system which we named CoQ10-MITO-Porter,” explained Hibino. “This system consists of the antioxidant molecule Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)—which is also required by mitochondria for ATP production—encapsulated by a lipid nanoparticle that would target mitochondria. In this study, we aimed to test if this system could work in living organisms.”
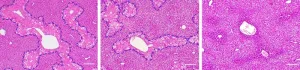
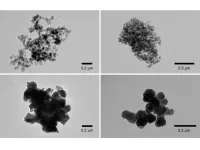
Variations of the formula for the synthesis of CoQ10-MITO-Porter were tested, and their structures were examined with electron microscopy. CoQ10-MITO-Porter was administered to mice models with acetaminophen-induced liver damage. Acetaminophen overdoses cause excess ROS in mitochondria, which in turn damages cells in the liver. CoQ10-MITO-Porter was transported primarily to the liver and measurably reduced the damage caused by ROS. A further discovery was that downsized CoQ10-MITO-Porter particles with more efficient packaging of CoQ10 were more effective at treating liver damage than the original formulation.
“Our study has shown that the MITO-Porter system we developed can be used to deliver CoQ10 to the liver, making it an important therapeutic strategy against conditions that cause oxidative stress,” concluded Yamada. “Our future work will focus on elucidating the mechanism responsible for the therapeutic effect of CoQ10.”
END
Delivery of antioxidants to liver mitochondria
2023-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New breathalyzer for disease sniffs out COVID in real-time, could be used to detect cancer, lung disease
2023-05-10
With each breath, humans exhale more than 1,000 distinct molecules, producing a unique chemical fingerprint or “breathprint” rich with clues about what’s going on inside the body.
For decades, scientists have sought to harness that information, turning to dogs, rats and even bees to literally sniff out cancer, diabetes, tuberculosis and more.
Scientists from CU Boulder and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have made an important leap forward in the quest to diagnose disease using exhaled breath, reporting that a new laser-based breathalyzer powered by artificial intelligence (AI) can detect COVID-19 in real-time with ...
Home measurement of blood oxygen levels by corona patients themselves easily applicable
2023-05-10
May 10 2023, Utrecht (The Netherlands) - When corona patients themselves measure the oxygen level in their blood at home, this is well applicable through the general practice. This was shown in a study conducted by UMC Utrecht during the pandemic. The study showed that patients could easily perform the oxygen measurement themselves at home, they felt safe doing so and the number of GP or hospital visits did not increase. The researchers believe that - by enabling care close to home - patients experience more control and that it contributes to relieving caregivers and keeping ...
Overweight boys more likely to be infertile men
2023-05-10
A new paper in the European Journal of Endocrinology, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that overweight boys tend to have lower testicular volume, putting them at risk for infertility in adulthood.
Infertility weighs on both the psychological health and the economic and social lives of people of childbearing age. Infertility affected 48 million couples in 2010. Although observers often overlook male infertility, researchers believe it is a factor contributing to couple infertility in about half of all cases. Yet ...
First structural analysis of highly reactive anionic Pt(0) complexes
2023-05-10
Anionic M0 complexes (M = group 10 metals) have attracted attention as active species for catalytic reactions; however, their molecular structures have very rarely been determined owing to their extremely high reactivity. Particularly, the structures of Pt0 complexes, which are expected to exhibit a high degree of reactivity, have not been determined, and their syntheses have been almost nonexistent.
Associate Professor Hajime Kameo, and Professor Hiroyuki Matsuzaka from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science and CNRS Senior Researcher Didier Bourissou (Paul Sabatier University - Toulouse III) elucidated the ...
Air pollution worsens movement disorder after stroke
2023-05-10
Air pollution has been shown to have a negative effect on the prognosis of ischemic stroke, or stroke caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, but the exact mechanism is unknown. A team of researchers recently conducted a study to determine whether or not increased inflammation of the brain, also known as neuroinflammation, is the main culprit.
The team published their findings in the February 16, 2023 issue of Particle and Fibre Toxicology.
Mice exposed intranasally to urban aerosols from Beijing, China, for one week demonstrated increased neuroinflammation ...
Most antidepressants prescribed for chronic pain lack reliable evidence of efficacy or safety, scientists warn
2023-05-10
Largest ever investigation into antidepressants used for chronic pain shows insufficient evidence to determine how effective or harmful they may be
Study reviewed commonly prescribed medications including amitriptyline, duloxetine, fluoxetine, citalopram, paroxetine, and sertraline
One third of people globally are living with long-term pain with many prescribed antidepressants to relieve symptoms
Most antidepressants used for chronic pain are being prescribed with “insufficient” evidence of their effectiveness, scientists have warned.
A major investigation into medications used to manage long-term pain found that ...
Dark clouds on the horizon
2023-05-10
Our industrialized society releases many and various pollutants into the world. Combustion in particular produces aerosol mass including black carbon. Although this only accounts for a few percent of aerosol particles, black carbon is especially problematic due to its ability to absorb heat and impede the heat reflection capabilities of surfaces such as snow. So, it’s essential to know how black carbon interacts with sunlight. Researchers have quantified the refractive index of black carbon to the most accurate degree yet which might impact climate models.
There are many factors driving climate change; some are very familiar, such ...
Scientists discover microbes in the Alps and Arctic that can digest plastic at low temperatures
2023-05-10
Finding, cultivating, and bioengineering organisms that can digest plastic not only aids in the removal of pollution, but is now also big business. Several microorganisms that can do this have already been found, but when their enzymes that make this possible are applied at an industrial scale, they typically only work at temperatures above 30°C. The heating required means that industrial applications remain costly to date, and aren’t carbon-neutral. But there is a possible solution to this problem: ...
Salt marshes protect the coast – but not where it is needed most
2023-05-10
Salt marshes provide multiple ecosystem services, one of those is protection of the coast against flooding. This is especially important in low-lying countries like the Netherlands. Scientists from the University of Groningen and the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ), in collaboration with the local water authority, have monitored wave run-up during storms over a three-year period. The results, which were published in the Journal of Applied Ecology on 10 May, help the water authority to quantify the protective effect of salt marshes.
For three years, ecologist Beatriz Marin-Diaz always had one eye on the weather ...
New USC study shows immigrant adults with liver cancer have higher survival rates than those born in the US
2023-05-10
Immigrant adults with liver cancer in the United States have higher survival rates than people with the disease who were born in the U.S., according to new research from the USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer, contributes to more than 27,000 deaths annually in the United States. Immigrants comprise a significant proportion of those diagnosed with HCC in the U.S. Research has shown that birthplace, also referred to as nativity, impacts incidence and risk factors for HCC, but little was known about its influence on survival after diagnosis.
The new study, just published in the Journal of the National ...