(Press-News.org) Purdue April Consumer Food Insights report explores role of dollar stores in food landscape
A market for an expanded grocery selection at dollar stores potentially exists, especially with consumers who live less than 10 minutes away, according to data reported in the April Consumer Food Insights report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conducted and evaluated the survey, which included 1,200 consumers across the U.S.
April’s report assesses differences in food behaviors by food security status rather than demographics. The report includes the first questions center researchers have asked about consumer behavior and food selection at dollar stores.
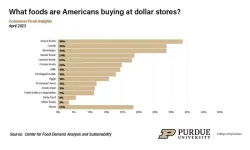
“More than half of Americans have recently shopped at a dollar store,” said Jayson Lusk, the head and Distinguished Professor of Agricultural Economics at Purdue, who leads the center. “When it comes to food, many of these purchases are snack items. If consumers do pick up more food at a dollar store, it makes sense that people typically buy canned or frozen foods since these are the easiest options for dollar stores to stock.”
While only a small percentage of consumers shop for groceries at dollar stores, there could be a market for an expanded food selection since 50% of those surveyed reported that a full-service grocery would be a draw.
“Plus, nearly 60% of consumers say that they live within 10 minutes of a dollar store, which has potential for capitalizing on access issues,” Lusk said.
In the food spending category, the slow easing of food inflation continues. Data from this summer’s reports will provide a helpful picture of how consumers are doing.
“If people go out and spend more at bars and restaurants, as one would expect, then we could say that consumers are feeling fairly confident,” Lusk said. “But if food away from home spending does not increase in our data, especially as food away from home inflation continues to pick up according to official measures, then we might have some questions.”
Lacking pre-January 2022 survey data, the Purdue researchers are unable to compare current responses to times of low inflation. Even so, Lusk said, “It seems that consumers have some degree of elevated inflation baked into their expectations with their 4.3% estimation of future inflation.”
Additional key results include the following:
Total food spending is up 7% from this time last year, while consumers similarly estimate annual food inflation to be about 7%.
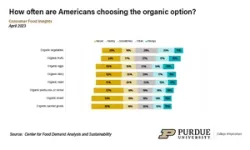
Vegetables and fruits are the most popular organic items, but less than a third of consumers often or always choose organic.
The food behaviors of food-secure and -insecure households differ relatively little on many common shopping choices. Still, it is important to recognize the differences that do exist between the households, said Sam Polzin, a food and agriculture survey scientist for the center and co-author of the report.
“Those facing very low food security are in a more precarious place,” Polzin said. “Over 40% rely on food aid and over 80% report effectively living paycheck to paycheck with regards to food purchasing. They also have a much more negative view toward their own diets, which we might expect would have a cumulative negative effect on overall well-being. They eat at home more often, prefer generic brands, and aren’t buying more expensive products like wild-caught fish or organics as much.”
In some ways, however, Polzin adds, “Food behaviors between food-secure and -insecure households don’t differ as much as we might expect or differ in ways we might not expect.”
For example, people in food-insecure households garden at a higher rate. They are just as likely to buy local foods or check for natural food labels and appear to compost more often.
April’s report also includes a section on how often Americans choose the organic option. These data broadly help show that fruits and vegetables are the most popular organic category.
“Since organics are not purchased that often, we can say that people are likely overstating how often they select these foods,” Polzin noted. “Since organics have one of the largest halos with regards to nutrition, naturalness and the environment, social desirability bias is probably a common factor contributing to this phenomenon.”
Lusk further discusses the report in his blog.
The Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability is part of Purdue’s Next Moves in agriculture and food systems and uses innovative data analysis shared through user-friendly platforms to improve the food system. In addition to the Consumer Food Insights report, the center offers a portfolio of online dashboards.
END
Purdue April Consumer Food Insights report explores role of dollar stores in food landscape
2023-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using reflections to see the world from new points of view
2023-05-10
As a car travels along a narrow city street, reflections off the glossy paint or side mirrors of parked vehicles can help the driver glimpse things that would otherwise be hidden from view, like a child playing on the sidewalk behind the parked cars.
Drawing on this idea, researchers from MIT and Rice University have created a computer vision technique that leverages reflections to image the world. Their method uses reflections to turn glossy objects into “cameras,” enabling a user to see the world as if they were looking through the “lenses” of everyday objects like a ceramic coffee mug or a metallic ...
Stimulating hope: Personalizing treatment options for depression
2023-05-10
Artificial intelligence. Gene editing. mRNA vaccines. It’s safe to say the past few decades have felt like the next big wave of medicine. However, what continues to be needed in virtually every field is a personalized approach to care.
That’s certainly needed when it comes to using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to treat depression, said Medical University of South Carolina Distinguished University Professor Mark George, M.D.
TMS uses a magnet to increase brain activity in ...
Gene p16 drives colorectal cancer emerging as a target for potential therapies
2023-05-10
Colorectal cancer is the fourth most common and second deadliest cancer. How colorectal cancer develops is not well understood, but a team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine reports in the Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research that silencing the gene p16, even though the DNA itself does not change, can drive colorectal cancer progression in animal models. The researchers also revealed a strategy that reduced tumor growth and improved survival in tumor-bearing mice, opening new possibilities for future targeted therapies in patients with gene p16 alterations.
“Years of research have shown ...
New database offers insight into consequences of language loss
2023-05-10
New database offers insight into consequences of language loss
Languages, like animal species, can go extinct. More than half of the world’s approximately 7,000 signed and spoken languages are currently endangered. And without intervention they are likely to become extinct, meaning nobody will speak or sign them any longer.
While language loss is happening across the world, the costs vary strikingly in different places, according to a new study co-authored by Yale linguist Claire Bowern. Regions where all Indigenous language are endangered — including parts of South America and the United States — ...
Bigger isn’t always better: Size of research teams does not equate to better research outcomes, finds new study
2023-05-10
Having a large research team isn’t linked to producing higher quality research, finds a new study from the University of Surrey which analysed data from 1.4 million academic papers.
Professor Sorin Krammer, lead author of the study and Professor of Strategy and International Business at the University of Surrey, said:
“Despite the prevalence of large teams in research, there is still a lack of a good understanding of how their size and diversity affects their performance.”
“Our ...
The acute problem of chronic disease
2023-05-10
In medicine and science, the term “pathogenesis” describes the origin and development of disease. There is not, however, a broadly accepted term to describe the other half of the equation: the process of healing and recovery.
In a new and far-reaching paper, published May 10, 2023 in the journal Mitochondrion, Robert K. Naviaux, MD, PhD, professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Pathology at UC San Diego School of Medicine, proposes both a term and, more importantly, outlines the array of processes and players, beginning with cellular mitochondria, that drive the healing process – and whose dysfunction underlies chronic illnesses from diabetes ...
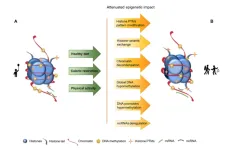
An epigenetic approach to modulating aging with nutrition and exercise
2023-05-10
“In this review, we describe how aging impacts epigenetics and how nutrition and physical exercise can positively impact the aging process, from an epigenetic point of view.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 10, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “How can we modulate aging through nutrition and physical exercise? An epigenetic approach.”
The World Health Organization predicts that by 2050, 2.1 billion people worldwide ...
APL Photonics selects recipient for 2022 Future Luminary Award
2023-05-10
MELVILLE, N.Y., May 10 – The University of Arizona’s Husain Alqattan is the recipient of the APL Photonics 2022 Future Luminary Award for his work in utilizing pulse shaping and waveform synthesis to control electron motion and open the door for ultrafast electronics that process data at unprecedented speeds.
The winning paper, “Attosecond light field synthesis,” was published in the April 2022 issue of APL Photonics. In it, Alqattan and his team used an attosecond light ...
Using AI to predict important measure of heart performance
2023-05-10
Coronary heart disease is the leading cause of adult death worldwide. The coronary angiography procedure provides the clinical standard diagnostic assessment for nearly all related clinical decision-making, from medications to coronary bypass surgery. In many cases, quantifying left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at the time of coronary angiography is critical to optimize clinical decision-making and treatment decisions, particularly when angiography is performed for potentially life-threatening acute coronary syndromes (ACS).
Since the left ventricle is the heart’s pumping center, measuring the ejection fraction in the chamber provides critical information about the percentage ...
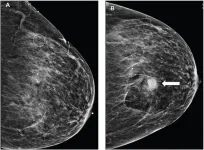
Bleeding after image-guided breast biopsies: Discontinuing vs. maintaining antithrombotic therapy
2023-05-10
Leesburg, VA, May 10, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), frequencies of imaging-apparent and palpable hematoma were not significantly different between patients temporarily discontinuing versus maintaining antithrombotic therapy (AT).
“The findings support safety of continuing AT during breast core-needle biopsy (CNB),” wrote lead researcher Melissa Reichman, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine at New York-Presbyterian ...