Can’t find your phone? There’s a robot for that
Robots can help find objects you’ve lost, thanks to new ‘artificial memory’
2023-05-15
(Press-News.org)
Engineers at the University of Waterloo have discovered a new way to program robots to help people with dementia locate medicine, glasses, phones and other objects they need but have lost.
And while the initial focus is on assisting a specific group of people, the technology could someday be used by anyone who has searched high and low for something they’ve misplaced.
“The long-term impact of this is really exciting,” said Dr. Ali Ayub, a post-doctoral fellow in electrical and computer engineering. “A user can be involved not just with a companion robot but a personalized companion robot that can give them more independence.”
Ayub and three colleagues were struck by the rapidly rising number of people coping with dementia, a condition that restricts brain function, causing confusion, memory loss and disability. Many of these individuals repeatedly forget the location of everyday objects, which diminishes their quality of life and places additional burdens on caregivers.
Engineers believed a companion robot with an episodic memory of its own could be a game-changer in such situations. And they succeeded in using artificial intelligence to create a new kind of artificial memory.
The research team began with a Fetch mobile manipulator robot, which has a camera for perceiving the world around it.
Next, using an object-detection algorithm, they programmed the robot to detect, track and keep a memory log of specific objects in its camera view through stored video. With the robot capable of distinguishing one object from another, it can record the time and date objects enter or leave its view.
Researchers then developed a graphical interface to enable users to choose objects they want to be tracked and, after typing the objects’ names, search for them on a smartphone app or computer. Once that happens, the robot can indicate when and where it last observed the specific object.
Tests have shown the system is highly accurate. And while some individuals with dementia might find the technology daunting, Ayub said caregivers could readily use it.
Moving forward, researchers will conduct user studies with people without disabilities, then people with dementia.
A paper on the project, Where is my phone? Towards developing an episodic memory model for companion robots to track users’ salient objects, was presented at the recent 2023 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-14
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO, Dublin, 17-20 May). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
New research to be presented at this coming week’s European Congress on Obesity in Dublin, Ireland (17-20 May) and published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute shows that both the metabolically healthy and unhealthy ‘forms’ of obesity are associated with an increased risk of various obesity-related cancers, with the relationship stronger in metabolically unhealthy obesity. The study is by Dr Ming Sun, Lund University, Malmö, ...
2023-05-14
The hormone oxytocin is important for social interaction and to control emotions. A deficiency of this hormone has previously been assumed in various diseases such as autism, but has never been proven. Now, for the first time, researchers from the University of Basel and the University Hospital of Basel have succeeded in demonstrating a deficiency of oxytocin in patients with a deficiency of vasopressin caused by a disease of the pituitary gland. This finding could be key to developing new therapeutic approaches.
The hormones oxytocin and vasopressin are produced in the same area of the brain ...
2023-05-14
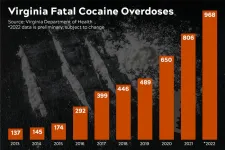
Nearly 2 percent of the U.S. population reported cocaine use in 2020, and the highly addictive substance was involved in nearly one in five overdose deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
In Virginia, the number of cocaine-related overdoses has been increasing since 2013, with 968 fatal overdoses in 2022, according to preliminary data from the Virginia Department of Health, a 20 percent increase over 2021. Of those, four in five included fentanyl — prescription, illicit or analog — a driving force behind the fatalities.
Researchers at the ...
2023-05-13
In a recently published commentary, UK HealthCare physicians call for standard-of-care treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) among patients who are incarcerated.
The viewpoint article by Anna-Maria South, M.D., Laura Fanucchi, M.D., and Michelle Lofwall, M.D., published in JAMA April 24 highlights the barriers to initiating medication for opioid use disorder (MOUD) among people who are incarcerated.
For patients with opioid use disorder, medications such as buprenorphine and methadone are considered by the medical community as standard of care treatments, as they alleviate withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings and pain, ...
2023-05-13
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated fear of childbirth among pregnant people in the U.S., according to a new Dartmouth study.
The researchers were particularly interested in understanding, from a U.S. context, which factors predict childbirth fear and how the pandemic has affected this fear and birth outcomes. The findings are published in Evolution, Medicine, and Public Health.
"Our results showed really high rates of childbirth fear in our sample," says first author Zaneta Thayer '08, an associate professor of anthropology at Dartmouth. "Since there's no pre-pandemic U.S. data, we cannot compare our data to that context but we know that ...
2023-05-13
A team of neuroscientists at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) has identified changes in the activity of brain cells known as pyramidal neurons, which contribute to drug seeking in a preclinical model of opioid use disorder. After access to heroin was stopped, these neurons became more excitable. The activity of these neurons was restored to normal by blocking the enzyme protein kinase A (PKA). Inhibiting this enzyme also reduced opioid-seeking behavior. Jacqueline McGinty, Ph.D., professor of neuroscience, and Saurabh Kokane, Ph.D., a postdoctoral scholar in McGinty’s laboratory, recently published their team’s findings in the Journal of Neuroscience.
The risk ...
2023-05-13
High levels of the stress hormone cortisol during the third trimester of pregnancy may improve speech and language skills in the first 3 years of a child’s life, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. The findings help researchers further understand the role cortisol plays in both fetal and child development.
Language development during early childhood can indicate how well a baby’s nervous system was developed in the womb. Prenatal exposure to cortisol – a steroid hormone that helps the body respond to ...
2023-05-13
Anabolic steroids not only can cause serious side effects during use, such as heart failure and depression, but can continue being harmful years after stopping, according to two studies presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. These studies, supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation, were carried out by researchers from the Copenhagen University Hospital Rigshospitalet who investigated the impact of anabolic steroids in former users.
Anabolic steroids – synthetic hormones ...
2023-05-13
Long COVID risk has been found to increase with low levels of vitamin D, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. The findings suggest that individuals should have their vitamin D levels checked after COVID-19.
Also known as post COVID-19 syndrome, long COVID is a new condition in which the effects of COVID-19 last for more than 12 weeks after contracting the initial infection. Studies have shown that it affects 50-70% of patients previously hospitalised for COVID-19, yet very little is known about the condition. One risk factor for worse outcomes for hospitalised COVID-19 patients, such as intubation and mechanical ventilation ...
2023-05-12
May 12, 2023 — Accelerated schedules for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) can be offered to patients experiencing treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD), a group of clinician–researchers and neuroscientists have concluded. The group cautions that such treatment should be proposed only after detailed discussion with patients about acceleration being an alternate form of rTMS scheduling, with documentation of informed consent.
The recommendations are published in a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Can’t find your phone? There’s a robot for that
Robots can help find objects you’ve lost, thanks to new ‘artificial memory’