(Press-News.org) The prize, now in its 10th year, is given annually to at least six early-career scientists based in the New York City area by The Pershing Square Sohn Cancer Research Alliance. Prizes are awarded to scientists who are pursuing innovative cancer research and taking risks that might preclude them from traditional funding. Winners receive $250,000 a year for up to three years and access to networking opportunities and an annual retreat with past winners.
For Dr. Simon, the prize will allow him to apply his knowledge as a neuroscientist to cancer research. “I'm not a traditional cancer biologist,” said Dr. Simon, who is also a member of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine. “I think this award is an essential bridge for people like me. I don't think I could pursue this project and answer the questions that I’m deeply interested in answering without this sort of commitment.”
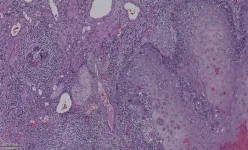
Dr. Simon’s lab at Weill Cornell Medicine traditionally studies the long cable-like fibers called axons that project from nerve cells and connect to other cells of the nervous system, and the mechanisms that control their survival. Axons from the nervous system also enter tumors, however the roles of these axons are unknown. Through a method that provides 3D spatial imaging, called whole mount immunolabeling, his lab is able to get a complete picture of a tumor and its axons in hopes of understanding the role that axons play in the tumor microenvironment, beginning with melanoma.
Using the technique to study skin malignancies seemed like a logical offshoot for the lab. “I realized that we were already studying sensory axons that project to the skin and the skin is the site where melanomas form,” he said. “I thought, ‘we have all of these tools to both visualize axons and to manipulate their function.’”
The award will give Dr. Simon and his lab the boost to keep going with research he otherwise would not be able to pursue by funding postdoctoral salaries and the costs surrounding research on mice. He is particularly excited about his access to The Pershing Square Sohn Cancer Research Alliance network. “One of the nice things about getting the prize is that it's a community,” he said. He welcomes the perspectives of past winners, while also bringing his new perspective to cancer research.
“The ultimate hope,” Dr. Simon said, “is that what we find in melanoma would be applicable to other cancer types.”
END
Dr. David Simon wins Pershing Square Sohn Prize for Young Investigators in Cancer Research Studying Melanoma
2023-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Saturated fatty acids promote immune escape of oral cancers
2023-05-16
A team from the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center and School of Dentistry, led by Yu Leo Lei, D.D.S., Ph.D., have identified a mechanism in mice for how obesity affects some oral cancers’ ability to escape from the immune system.
This study, published in Cell Reports, found that obesity helps to establish a type of tumor microenvironment that promotes tumor progression. How exactly this happens lies in the relationship between the saturated fatty acids, the STING-type-I interferon pathway, and NLRC3.
“We tend to think about the increased risks for gastrointestinal tumors, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and ovarian cancer when it comes to obesity,” ...
When does the gender gap start in the computer science field?
2023-05-16
If you are a third grader, your chances of growing up to be a computer scientist is likely to heavily depend on your gender — a situation Allison Master says is just plain wrong.
How can Master be certain? Because third grade girls are telling her so.
“Our new research addresses a big, longstanding issue in STEM education, that women are highly under-represented in fields like computer science. It’s actually one of the most challenging fields for women’s representation. Only about 20% of people who major in computer science are women,” said Master, assistant professor ...
You’ve got some nerve
2023-05-16
Researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center and the School of Dentistry identified a new metric to articulate the relationship between nerve density and oral cancer. The study, published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, investigated normalized nerve density to translate previous mechanistic studies into a context that could be used in the clinic.
“We are recognizing more and more that there's a very dynamic interaction between nerves and cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment,” said Nisha D’Silva, B.D.S., M.S.D, Ph.D., Donald Kerr Endowed Collegiate ...
National study recommends starting SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination three months after bone marrow transplant
2023-05-16
SEATTLE – (May 16, 2023) – Patients with cancer whose immune systems are being supported or rebuilt by bone marrow transplantation should begin receiving vaccines for protection against SARS-CoV-2 three months post-transplant, according to a large, prospective, observational study led collaboratively by the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research, the Blood & Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center. The research, involving 22 cancer centers and research institutions in the United States and focusing on mRNA-based vaccines, published in The Lancet journal ...
As patients wait for imaging results, WVU research links delays with how online radiologists get paid
2023-05-16
Online workflow systems for off-site radiologists are one reason for health care delays that cost hospitals money and test the patience of patients, according to West Virginia University research.
Bernardo Quiroga, associate professor of supply chain management at the WVU John Chambers College of Business and Economics, and his coauthors analyzed a radiology workflow platform, used by thousands of U.S. hospitals, which allows radiologists working from home to log in, view a pool of tasks such as X-rays or CT and MRI scans that are available for processing, and choose which of those radiological studies to read and report on.
The radiologists’ ...
Are college students with religious tattoos more religious? Yes and no
2023-05-16
Contact: Shelby Cefaratti-Bertin, Baylor University Media & Public Relations, 254-327-8012
Follow us on Twitter: @BaylorUMedi
WACO, Texas (May 15, 2023) – For most of U.S. history, tattoos have been associated with sailors and bikers, but not church-going people. As tattoos have become more popular, with nearly one-third of U.S. adults sporting at least one tattoo, religious-themed tattoos have also increased. A recent study examined the behaviors of college students with tattoos, including religious tattoos.
Jerome R. Koch, Ph.D., professor of sociology at Texas Tech University, and Kevin D. Dougherty, Ph.D., professor of sociology at ...
Neglected 80-year-old antibiotic is effective against multi-drug resistant bacteria
2023-05-16
An old antibiotic may provide much-needed protection against multi-drug resistant bacterial infections, according to a new study publishing May 16th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by James Kirby of Harvard Medical School, US, and colleagues. The finding may offer a new way to fight difficult-to-treat and potentially lethal infections.
Nourseothricin is a natural product made by a soil fungus, which contains multiple forms of a complex molecule called streptothricin. Its discovery in the 1940s generated high hopes ...
A potential new weapon in the war against superbugs
2023-05-16
“The end of modern medicine as we know it.” That’s how the then-director general of the World Health Organization characterized the creeping problem of antimicrobial resistance in 2012. Antimicrobial resistance is the tendency of bacteria, fungus and other disease-causing microbes to evolve strategies to evade the medications humans have discovered and developed to fight them. The evolution of these so-called “super bugs” is an inevitable natural phenomenon, accelerated by misuse of existing drugs and intensified by the lack of new ones in the development ...
Students at the University of Warwick show benefits of social prescribing for dementia
2023-05-16
Students at the University of Warwick are leading social prescribing research for dementia, highlighting the benefits of this innovative approach during Dementia Action Week.
The ground-breaking dementia café project, led by students from Warwick Medical School, is a shining example of the power of social prescribing in dementia care. By regularly connecting people with dementia to community activities, groups, and services, the project aims to meet practical, social, and emotional needs of people living with dementia while improving their overall health and well-being.
Social prescribing ...
Opportunities for improved dengue control in the US territories
2023-05-16
About The Article: This Viewpoint from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention discusses the prevalence of dengue infection in U.S. territories and opportunities to combat it, such as vaccines and novel vector control methods.
Authors: Alfonso C. Hernandez-Romieu, M.D., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in San Juan, Puerto Rico, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.8567)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...