(Press-News.org) Black adults – particularly Black women – with higher levels of education and experiences of discrimination and crime are more likely to own a firearm, according to a study by the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center at Rutgers.
In a new study appearing in the Journal of Clinical Psychology, researchers found that Black adults who endorsed firearm ownership were more likely to grow up in homes with firearms, had previously shot a firearm and planned to acquire a firearm in the coming year.
“The higher rates of firearm ownership among highly educated Black women were somewhat surprising to us,” said Michael Anestis, executive director of the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center and senior author of the study. “This might reflect a broader shift toward women and persons of color purchasing firearms across the United States in recent years, perhaps as a reaction not only to the turmoil of the pandemic era, but also to frequent highly publicized episodes of police brutality against Black men and women and the surge of gun violence witnessed across the U.S. during that time.”
Recent research shows that since 2019 half of all new firearm owners in the United States identify as female.
Risk for injury and death – whether by suicide, unintentional shooting or domestic violence – increases sharply when firearms are kept in and around the home. Recent research has highlighted that Black men and women represent an increasing percentage of the firearm owning community.
Despite this, little research has focused on what distinguishes Black adults who do and don’t own firearms. In the Rutgers study, researchers at the center surveyed two groups of English-speaking adults. The first group included 502 individuals who identified as Black and were recruited from a national sample in mid-2020. The second sample included 1,086 individuals who identified as Black and were recruited from a sample drawn from New Jersey, Mississippi and Minnesota in early 2021. Each participant was asked about their experiences with firearms as well as factors related to their identities. In the second sample, participants were also asked about their experiences with discrimination, crime and suicidal thoughts.
In the second sample, researchers examined how extent adverse life experiences were associated with firearm ownership. Those with more experiences of discrimination, who had encountered more crime, and who felt less safe in their neighborhoods were more likely to endorse firearm ownership.
Black adults who endorsed firearm ownership were also more likely to experience suicide thoughts than Black adult who did not own firearms, according to the study.
Given the increased risk for death by suicide when a firearm is kept in or around the home, this indicates that Black adults at the greatest risk for thinking about suicide also are more likely to have ready access to the most lethal method for suicide. This last finding may help explain the sharply increasing rate of firearm suicide among Black U.S. residents.
“For Black Americans, experiences of racism and systemic inequalities may result in the decision to purchase a firearm to protect themselves and their loved ones,” said Allison Bond, lead author of the study and a doctoral student with the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center. “However, owning a firearm also increases the risk for death by suicide. This is concerning given that Black firearm owners are reporting high rates of suicidal thoughts. Individual and system level prevention and intervention efforts are needed to combat racism, increase secure firearm storage among the Black community and connect those at risk for suicide with evidence-based mental health care.”
END
Discrimination, crime and suicidal thoughts associated with greater odds of firearm ownership among Black adults
Rutgers study highlights that firearm ownership in Black communities may be a reaction to adverse experiences
2023-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Some young cancer survivors face higher risk of premature heart failure
2023-05-16
Mean age at diagnosis of heart failure was 32 years old
First study to estimate risk of heart failure among young adult cancer survivors treated with this category of chemotherapy
Study raises awareness for patients, clinicians to monitor for heart failure symptoms, consider strategies for prevention
CHICAGO --- Imagine surviving cancer only to learn the drug that saved your life has introduced a completely different health risk: heart failure.
A new Northwestern Medicine study has found young adult cancer survivors (between 18 and 39 years old at diagnosis) were at higher risk (2.6 times) of heart failure when treated with anthracyclines, a specific category ...
New research sheds light on how shift work may influence fertility
2023-05-16
Only four weeks of shift work-like patterns in female mice are enough to disrupt their biological clock and reduce fertility, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology. The findings help scientists better understand how circadian disturbances impact female fertility, which could eventually lead to future prevention strategies for women working in non-standard work schedules.
The circadian rhythm is generated by the body’s internal clocks which are synchronised to a 24-hour period, mostly by changes in light across days. These clocks regulate various biological functions and processes, including the sleep-wake cycle, ...
Drs. Dawn Hershman and Primo Lara elected group co-chairs-elect of SWOG Cancer Research Network
2023-05-16
The board of governors of the SWOG Cancer Research Network has elected Primo N. Lara, Jr., MD, and Dawn L. Hershman, MD, MS, as group co-chairs-elect. The two will serve in that capacity until the term of the current group chair, Charles D. Blanke, MD, ends in spring 2025. They will then begin a six-year term as SWOG’s first group co-chairs.
In a joint statement, Hershman and Lara said, “We both understand that the success of SWOG has been fundamentally anchored in collaborative interdisciplinary team science. We are convinced ...
At the foot of the geologically diverse front range
2023-05-16
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America (GSA) is pleased to announce the upcoming 2023 GSA Rocky Mountain Section Meeting to be held from 23–25 May in Fort Collins, Colorado, USA. This highly anticipated event will provide a dynamic platform for scientists, researchers, industry professionals, and students to exchange ideas, present research findings, and foster collaborations. The meeting will feature a wide range of engaging sessions, a plenary lecture on climate intervention, scientific field trips, informative short courses, and impactful mentoring programs ...
Chan Zuckerberg Initiative funds COMBINEDBrain to fast track research for rare neurological disorders
2023-05-16
COMBINEDBrain’s Founder and Director, Dr. Terry Jo Bichell, understands the power of collaboration. In her years as a neuroscientist, advocate, and rare patient parent, she has witnessed the field of neurodevelopment transform from a broad focus on autism or intellectual disability, to an era based on rare genetic disorders. When new disorders are identified, Patient Advocacy Organizations spring up, led by passionate parents with the drive and determination to cure their children. Some of these organizations represent as many as 10,000 patients, some as few as 10. No matter their size, each organization must follow a similar path to ...
Novel ACT-Discover liquid biopsy shows 30% increased sensitivity in detecting tumor DNA in blood
2023-05-16
Liquid biopsy is increasingly stepping up as a non-invasive approach in detecting and tracking circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in blood and providing crucial insights into the dynamics of cancer evolution and intra-tumor heterogeneity as drivers of cancer drug resistance.
One main limitation of liquid biopsy to-date is the low sensitivity of current approaches in tumor types that do not shed enough DNA into the bloodstream, including pancreatic cancer.
Co-led by VHIO’s Rodrigo A. Toledo, a study published in Genome Medicine (1) reports on the development of a novel ctDNA-based approach, Aneuploidy in Circulating Tumor DNA ...
Rutgers researchers find flaws in using source reputation for training automatic misinformation detection algorithms
2023-05-16
Researchers at Rutgers University have found a major flaw in the way that algorithms designed to detect "fake news" evaluate the credibility of online news stories.
Most of these algorithms rely on a credibility score for the "source" of the article, rather than assessing the credibility of each individual article, the researchers said.
"It is not the case that all news articles published by sources labeled 'credible' (e.g., The New York Times) are accurate, nor is it the case that every article published by sources labeled 'noncredible' publications are 'fake news,'" ...
How government guarantees give banking customers peace of mind and keep banks open
2023-05-16
Spooked by volatile reports from the Silicon Valley Bank in early March, many customers panicked and withdrew their money, creating the largest bank failure since the 2007-2008 financial crisis. The problem — investors and customers lost confidence in the bank, proving the perception of a banks’ reliability can significantly impact its success.
Investors tend to respond negatively to volatility in firms’ performance. To mitigate investors’ concerns, when some banks receive extremely high income, they occasionally delay reporting that amount until a later date when the income ...
Automated, accurate reporting for NGS-based clonality testing
2023-05-16
“[...] we have developed a fully automated calling algorithm for determining B and T cell clonality from NGS [next-generation sequencing] data, with greater sensitivity than previously developed models.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 16, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 12, 2023, entitled, “Development and implementation of an automated and highly accurate reporting process for NGS-based clonality testing.”
B and T cells undergo random recombination of the VH/DH/JH portions of the immunoglobulin loci (B cell) and T-cell receptors before becoming ...
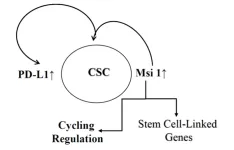
Musashi 1 in breast cancer: Implications for dormancy and survival in bone marrow
2023-05-16
“This study now links Msi 1 to PD-L1.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 16, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 9, entitled, “Increased expression of musashi 1 on breast cancer cells has implication to understand dormancy and survival in bone marrow.”
Breast cancer (BC) stem cells (CSCs) resist treatment and can exist as dormant cells in tissues such as the bone marrow (BM). Years before clinical diagnosis, BC cells (BCCs) could migrate from the primary site where the BM niche ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
[Press-News.org] Discrimination, crime and suicidal thoughts associated with greater odds of firearm ownership among Black adultsRutgers study highlights that firearm ownership in Black communities may be a reaction to adverse experiences