(Press-News.org) A retrospective study of temperatures in the province of Barcelona reveals that low temperatures increase the risk of going on a period of sick leave, due in particular to infectious and respiratory diseases. The study, carried out by researchers from Center for Research in Occupational Health (CISAL) and the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences at UPF (MELIS); the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation and CIBER of Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP), shows that the sectors of the population most affected are women, young people and people who work in the services sector who carry out non-manual tasks which tend to be done in indoor spaces.
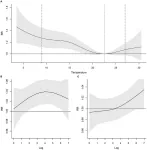
According to the study published in Frontiers in Public Health, the length of sickness absences increases from between two and six days following a period of low temperatures. This rise in sickness absence could be caused by the increase in the circulation and transmission of pathogens such as bronchitis or the flu virus, in indoor spaces, which cause infections of the upper respiratory tract.
"It is important that by monitoring occupational health the elements that cause sickness absence can be identified in order to develop effective measures that go towards improving the health of working people"
Temporary inability to work, commonly called sick leave, is a complex phenomenon which affects the quality of life of working people and the economy, and extends to society as a whole, albeit in different ways. That is why "it is important that by monitoring occupational health the elements that cause sickness absence can be identified in order to develop effective measures that go towards improving the health of working people and their quality of life, and reducing the costs for business people and the social security system", explains Xavier Basagaña, coordinator of the study.
Women stand out among those most affected by this phenomenon. "It shouldn't come as a surprise that women have more sickness absences because they still have more precarious jobs and with worse working conditions than men. Even when this is not the case, women carry more family and care responsibilities, especially if they have children", explains Mireia Utzet, lead author of the study, and Amaya Ayala-García.
In the study, around 100,000 periods of sickness absence and more than 40,000 salaried people were analysed from the Barcelona province between 2012 and 2015. Surprisingly, the study found no relationship between rises in temperature and sickness absence. This lack of a correlation could be due to the nature of the cohort studied, in which a greater number of workers from the third sector were represented, who work in indoor spaces which are often air-conditioned.
This study was initiated by CISAL and CIBERESP researcher Fernando G. Benavides and was based on the cross-referencing of administrative registers from social security data and registers of sickness absence, which allowed highly reliable results to be extracted at low cost.
Reference article:
Utzet M, Ayala-Garcia A, Benavides F. G, Basagaña X. “Extreme temperatures and sickness absence in the Mediterranean province of Barcelona: An occupational health issue”. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1129027. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1129027
END
Low temperatures increase the risk of sickness absence, especially for women, young people and third sector professionals
A study carried out in Barcelona province finds a link between cold weather and sickness absence; this is not however found in periods of high temperatures
2023-05-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newcomers may change ecosystem functions – or not
2023-05-17
In a study tracking climate-induced changes in the distribution of animals and their effects on ecosystem functions, North Carolina State University researchers show that resident species can continue managing some important ecological processes despite the arrival of newcomers that are similar to them, but resident species’ role in ecosystem functioning changes when the newcomers are more different.
The findings could lead to predictive tools for understanding what might happen as climate change forces new species into communities, such as the movement of species from lower to higher latitudes or elevations.
“Species ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researcher contributes to the discovery of an Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone with volcanic activity
2023-05-17
Abu Dhabi, UAE: – A team of scientists led by researchers at the University of Montreal has recently discovered an Earth-sized exoplanet, a world beyond our solar system, that may be carpeted with volcanoes and potentially hospitable to life. Called LP 791-18 d, the planet could undergo volcanic outbursts as often as Jupiter’s moon Io, the most volcanically active body in our solar system. The team includes Mohamad Ali-Dib, a research scientist at the NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) Center for Astro, Particle, and Planetary Physics.
The planet was found and studied using data ...
Automated window shades show potential for significant energy savings, Illinois Tech study finds
2023-05-17
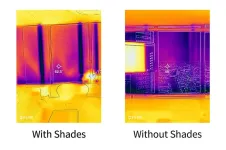
CHICAGO—May 17, 2023—Automated insulating window shades can cut energy consumption by approximately one-quarter and may recoup the cost of installation within three to five years, according to a landmark study conducted by Illinois Institute of Technology researchers at Willis Tower. The study, funded by ComEd, showcases a promising path for sustainability and energy efficiency in architectural design.
Temperature regulation typically accounts for 30–40 percent of the energy used by buildings in climates similar to Chicago. The research team, led by Assistant Professor of Architectural Engineering Mohammad ...
Found: a likely volcano-covered terrestrial world outside the Solar System
2023-05-17
A large international team led by astronomers at the Trottier Institute for Research on Exoplanets at Université de Montréal (UdeM) today announced in the journal Nature the discovery of a new temperate world around a nearby small star.
This planet, named LP 791-18 d, has a radius and a mass consistent with those of Earth. Observations of this exoplanet and another one in the same system indicate that LP 791-18 d is likely covered with volcanoes similar to Jupiter’s moon Io, the most volcanically active body in our Solar System.
“The discovery of this exoplanet is an extraordinary ...
Odd cells found in lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
2023-05-17
A pair of internationally renowned stem cell cloning experts at the University of Houston is reporting their findings of variant cells in the lungs of patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) which likely represent key targets in any future therapy for the condition.
IPF is a progressive, irreversible and fatal lung disease in which the lungs become scarred and breathing becomes difficult. The rapid development and fatal progression of the disease occur by uncertain mechanisms, but the most pervasive school of thought is that IPF arises from recurrent, subclinical lung ...
What did the earliest animals look like?
2023-05-17
For more than a century, biologists have wondered what the earliest animals were like when they first arose in the ancient oceans over half a billion years ago.
Searching among today's most primitive-looking animals for the earliest branch of the animal tree of life, scientists gradually narrowed the possibilities down to two groups: sponges, which spend their entire adult lives in one spot, filtering food from seawater; and comb jellies, voracious predators that oar their way through the world's oceans in search of food.
In a new study published this week in the journal Nature, researchers use a novel approach based on chromosome structure to come up with ...
Researchers pinpoint brain cells that drive appetite in obesity
2023-05-17
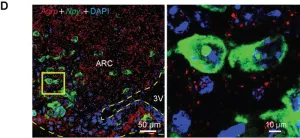
A team at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research has discovered a group of brain cells that boosts appetite when there is a prolonged surplus of energy in the body, such as excess fat accumulation in obesity.
The researchers discovered that these cells not only produced the appetite-stimulating molecule NPY, but they in fact made the brain more sensitive to the molecule, boosting appetite even more.
“These cells kickstart changes in the brain that make it more sensitive to even low levels of NPY when there is a surplus of energy in the body in the form of excess fat – driving appetite during obesity,” explains Professor Herbert Herzog, senior ...
Receipt of medications for chronic disease during the first 2 years of COVID-19
2023-05-17
About The Study: This study of 18.1 million beneficiaries of fee-for service Medicare found that, in contrast to in-person health services, receipt of medications for chronic conditions was relatively stable in the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic overall, across racial and ethnic groups, and for community-dwelling patients with dementia. This finding of stability may hold lessons for other outpatient services during the next pandemic.
Authors: Nancy E. Morden, M.D., M.P.H., of the Geisel ...
Genetic associations between modifiable risk factors and Alzheimer disease
2023-05-17
About The Study: This genetic association study including 39,000 participants with clinically diagnosed Alzheimer disease (AD) and 401,000 control participants without AD found novel genetic associations between high high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol concentrations and high systolic blood pressure with higher risk of AD. These findings may inspire new drug targeting and improved prevention implementation.
Authors: Ruth Frikke-Schmidt, M.D., D.M.Sc., Ph.D., of Copenhagen University Hospital–Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13734)
Editor’s ...
Radio signal reveals supernova origin
2023-05-17
In the latest issue of the journal Nature, astronomers from Stockholm University reveal the origin of a thermonuclear supernova explosion. Strong emission lines of helium and the first detection of such a supernova in radio waves show that the exploding white dwarf star had a helium-rich companion.
Supernovae of Type Ia are important for astronomers since they are used to measure the expansion of the Universe. However, the origin of these explosions has remained an open question. While it is established that the explosion is that of a compact ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Low temperatures increase the risk of sickness absence, especially for women, young people and third sector professionalsA study carried out in Barcelona province finds a link between cold weather and sickness absence; this is not however found in periods of high temperatures