(Press-News.org) About The Study: Among 20 health outcomes that were monitored in near real time in this study including more than 3 million children ages 5 to 17 who received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, a safety signal was identified for only myocarditis or pericarditis. Consistent with other published reports, these results provide additional evidence that COVID-19 vaccines are safe in children.
Authors: Steven A. Anderson, Ph.D., M.P.P., of the Food and Drug Administration in Silver Spring, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.1440)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.1440?guestAccessKey=729f6a2e-2023-46f0-a824-f3998e81ff05&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=052223
END
Safety of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in children ages 5 to 17
JAMA Pediatrics
2023-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
HPV transmission, persistence in pregnant women and neonates
2023-05-22
About The Study: In this study of 1,050 pregnant women and their neonates, vaginal human papillomavirus (HPV) was frequently detected in pregnant women. Perinatal transmission was infrequent, and in this cohort, no infection detected at birth persisted at six months. Although HPV was detected in placentas, it remains difficult to differentiate contamination versus true infection.
Authors: Helen Trottier, M.Sc., Ph.D., of the Universite de Montreal in Montreal, is the corresponding author.
To ...
A giant leap forward in wireless ultrasound monitoring for subjects in motion
2023-05-22
A team of engineers at the University of California San Diego has developed the first fully integrated wearable ultrasound system for deep-tissue monitoring, including for subjects on the go. It facilitates potentially life-saving cardiovascular monitoring and marks a major breakthrough for one of the world’s leading wearable ultrasound labs. The paper, “A fully integrated wearable ultrasound system to monitor deep tissues in moving subjects,” is published in the May 22, 2023 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
“This project gives a complete solution to wearable ultrasound technology—not ...
'Lost' immune cells partly to blame for reduced vaccine response in older people
2023-05-22
Understanding the ways our immune response changes as we age holds the key to designing better vaccines and boosting protection for people most at risk. Research published by Dr Michelle Linterman and her group today in Nature Immunology has explained that the organisation of the germinal centre, which is vital to the generation of longer-lived protection following vaccination, is altered in ageing. By demonstrating that these age-related changes can be reversed in mice, the research sets the foundation for interventions that bolster an effective vaccine response.
After a vaccination ...
Stretching metals at the atomic level allows researchers to create important materials for quantum, electronic, and spintronic applications
2023-05-22
A University of Minnesota Twin Cities-led team has developed a first-of-its-kind, breakthrough method that makes it easier to create high-quality metal oxide thin films out of “stubborn” metals that have historically been difficult to synthesize in an atomically precise manner. This research paves the way for scientists to develop better materials for various next-generation applications including quantum computing, microelectronics, sensors, and energy catalysis.
The researchers’ paper is published in Nature Nanotechnology, ...
AI predicts the function of enzymes
2023-05-22
Enzymes are the molecule factories in biological cells. However, which basic molecular building blocks they use to assemble target molecules is often unknown and difficult to measure. An international team including bioinformaticians from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) has now taken an important step forward in this regard: Their AI method predicts with a high degree of accuracy whether an enzyme can work with a specific substrate. They now present their results in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Enzymes are important biocatalysts in all living cells: They facilitate chemical reactions, through which all molecules ...
Video games and education: five steps for choosing the perfect classroom game
2023-05-22
Minecraft is officially the most played video game in history. Despite been 12 years old, the public does not seem to have lost interest: over 175 million people play Minecraft at least once a month. The number of players of this open-world or sandbox building game, which provides virtually unlimited possibilities for creation, keeps growing, and this is to a great extent thanks to its educational potential. According to Microsoft data, Minecraft Education Edition has over 35 million game licences. And this is just one of the many ways in which it can be ...
Ukraine hospital improving emergency cardiovascular care during national crisis
2023-05-22
The Clinical Hospital of Emergency Services, a municipal hospital serving the community of Dnipro, in Ukraine, is the first in the country to take part in the American College of Cardiology’s Global Quality Solutions program. The hospital joins the program in an effort to improve heart attack care by reducing heart attack related deaths and saving lives in their community.
“When the war started, myself and others on my team decided to stay at work to do our best to help our people, soldiers, neighbors and relatives to survive. But we decided it was not enough to only maintain, but that ...
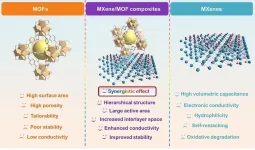
Metal−organic frameworks meet MXene: New opportunities for electrochemical application
2023-05-22
They published their work in Energy Material Advances.
"The investigation of MXene/MOF hybrid materials with high electrochemical performance is important," said paper author Huan Pang, professor with the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University. "Currently, MXene/MOF hybrid materials have received increasing attention in energy-related fields."
Pang explained the motivations for designing MXene/MOF hybrid materials. Firstly, MXenes with numerous negatively charged surface groups can be employed as a valid substrate to support the growth of MOFs, thus not ...
A guide through the genome
2023-05-22
Plants show enormous variety in traits relevant to breeding, such as plant height, yield and resistance to pests. One of the greatest challenges in modern plant research is to identify the differences in genetic information that are responsible for this variation. A research team led by the "Crop Yield" working group at the Institute for Molecular Physiology at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the Carnegie Institution of Science at Stanford has now developed a method to identify precisely these special differences in genetic information. Using the example of maize, they demonstrate the great potential of their method in the journal Genome Biology and present ...
How plants use sugar to produce roots
2023-05-22
Along with sugar reallocation, a basic molecular mechanism within plants controls the formation of new lateral roots. An international team of plant biologists has demonstrated that it is based on the activity of a certain factor, the target of rapamycin (TOR) protein. A better understanding of the processes that regulate root branching at the molecular level could contribute to improving plant growth and therefore crop yields, according to research team leader Prof. Dr Alexis Maizel of the Centre for Organismal Studies at Heidelberg University.
Good root growth ensures that plants can absorb sufficient ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Safety of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in children ages 5 to 17JAMA Pediatrics