GPR141 regulates breast cancer progression via oncogenic mediators and the p-mTOR/p53 axis
2023-05-22
(Press-News.org)
“This research uncovers GPR141 as a stimulator of breast tumorigenesis and metastasis, making it a candidate target for breast cancer therapeutics.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 19, 2023, entitled, “G-protein-coupled receptor 141 mediates breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by regulating oncogenic mediators and the p-mTOR/p53 axis.”
Breast cancer morbidity is surging towards the peak in females across the globe. An inherent property of cancer cells is enhanced cell proliferation rate and migration capability, leading to deregulated cell signaling cascades. G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have recently emerged as a hot-spot target in cancer research.
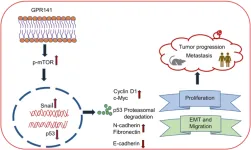
Researchers Monalisa Parija, Amit K. Adhya and Sandip K. Mishra from the Institute of Life Sciences, Regional Centre for Biotechnology and All India Institute of Medical Sciences identified aberrant expression of G-protein-coupled receptor 141 (GPR141) in different breast cancer subtypes that correlate with poor prognosis. However, the molecular mechanism via which GPR141 advances breast cancer remains elusive. Increased GPR141 expression enhances the migratory behavior of breast cancer, driving oncogenic pathways both in vitro and in vivo through activation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), oncogenic mediators and regulation of p-mTOR/p53 signaling.
“Our study unveils a molecular mechanism for p53 downregulation and activation of p-mTOR1 and its substrates in GPR141 overexpressed cells, accelerating breast tumorigenesis.”
In their current study, the researchers found that an E3 ubiquitin ligase, Cullin1, partly mediates p53 degradation via proteasomal pathway. Co-immunoprecipitation results show that the phosphorylated form of 40S ribosome protein S6 (ps6., a p-mTOR1 substrate) forms a complex with Cullin1. These findings suggest an interplay between Cullin1 and p-mTOR1 in GPR141 overexpressed cells that downregulates p53 expression, thus inducing tumor growth.
GPR141 silencing restores p53 expression and attenuates p-mTOR1 signaling events, thereby impeding proliferation and migration in breast cancer cells. Their findings describe the role of GPR141 in breast cancer proliferation, and metastasis, as well as in influencing the tumor microenvironment. Modulating GPR141 expression could pave the way for a better therapeutic approach to regulating breast cancer progression and metastasis.
“In conclusion, our research highlights the gain of function of GPR141 drives breast tumorigenesis by inducing tumor cell properties via the p-mTOR1/p53 axis, altering EMT markers, and enhancing oncogenic mediators.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28433
Correspondence to: Sandip K. Mishra
Email: sandipkmishra@ils.res.in
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptor 141, cell migration, metastasis, p-mTOR, p53
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-22
SAN FRANCISCO, May 22, 2023 – New research, published online today in the American Journal of Psychiatry, provides the most robust and comprehensive evidence to date that children exposed to early psychosocial deprivation benefit substantially from family-based care. Senior author Kathryn L. Humphreys, Ph.D., discussed this work today at a special briefing during the 2023 Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Results of research from the Bucharest Early Intervention Project, the ...
2023-05-22
Baltimore, MD—New research led by Carnegie’s Yixian Zhen and Minjie Hu reveals how coral cells tag friendly algae before ingesting them, initiating a mutually beneficial relationship. This information could guide next-level coral conservation efforts.
Their work is published in Nature Microbiology.
Corals are marine invertebrates that build large exoskeletons from which reefs are constructed. But this architecture is only possible because of a mutually beneficial relationship between the coral and various species of single-celled algae called dinoflagellates ...
2023-05-22
Controlling traumatic situations is synonymous with the daily duties of first responders, yet many mental health programs to combat the increasing stress they encounter are lacking. That’s why West Virginia University researchers are identifying steps policymakers and community members can take to aid front-line workers.
“With elevated risk for suicide and other mental health issues among first responders, we have a significant public health problem,” said Michael Fisher, assistant professor in the WVU School of Public Health ...
2023-05-22
Excess sugar hampers cells that renew the colon’s lining in a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to a new study by University of Pittsburgh scientists.
The findings, published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, could help get to the bottom of why limiting sugary foods can ease symptoms for patients with IBD.
“The prevalence of IBD is rising around the world, and it’s rising the fastest in cultures with industrialized, urban lifestyles, which typically have diets high in sugar,” said senior author Timothy Hand, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at Pitt’s ...
2023-05-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study has identified the bee’s knees of bumble bee dietary options in Ohio and the Upper Midwest.
By viewing almost 23,000 bumble bee-flower interactions over two years, researchers found that these bees don’t always settle for the most abundant flowers in their foraging area – suggesting they have more discerning dietary preferences than one might expect.
Being large, strong and social bees that can fly for long distances, bumble bees are major contributors to pollination, particularly for agriculture – but like other pollinators threatened by habitat ...
2023-05-22
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by joint deterioration. The clinical outcomes of patients with active RA can be improved using anti-rheumatic medications, such as methotrexate (MTX). Many patients rely on MTX to limit the destructive joint damage and functional disability typical of RA. Although the drug is a folic acid antagonist, its precise mechanisms in RA patients are largely unknown.
Previous research suggests that MTX also affects a type of white blood cell called CD4+ T cells. These cells are believed to play a role in the development of RA—specifically, the balance between the activation of interleukin-17-producing helper T ...
2023-05-22
Robert Weigel, Professor, Physics and Astronomy, received funding for: "Infrastructure Development, Maintenance, and Outreach for the Heliophysics Application Programmer's Interface (HAPI)."
Weigel will facilitate HAPI adoption by upcoming missions by providing targeted instrument team support.
He will create additional HAPI server reference implementations.
He will create a meta-server to facilitate an integrated HAPI ecosystem.
He will create higher-level services that build on the uniformity afforded by HAPI ...
2023-05-22
Two hundred and fifty-two million years ago, Earth experienced a mass extinction so devastating that it’s become known as “the Great Dying.” Massive volcanic eruptions triggered catastrophic climate change, killing off nine out of every ten species and eventually setting the stage for the dinosaurs. But the Great Dying was a long goodbye-- the extinction event took place over the course of up to a million years at the end of the Permian period. During that time, the fossil record shows drama and upheaval as species fought to get a foothold in their changing environments. One animal that exemplifies ...
2023-05-22
“We are confident and hope that this can be one of many tools that doctors need to tackle antibiotic resistance, which is a serious and growing problem,” says principal investigator Vicent Pelechano, associate professor at the Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology, Karolinska Institutet.
The method is called 5PSeq, is simple to use, and is based on sequencing the messenger RNA (mRNA) that the bacteria break down as they synthesise proteins. The measurements reveal how the bacteria are affected by different environmental factors, such as antibiotic treatments and other types ...
2023-05-22
Researchers have cloned the wheat rust resistance genes Lr9 and Sr43 and identified that they encode unusual kinase fusion proteins[1][2]. Their research will enable new options for addressing resistance to disease in bread wheat.
Each year about 20 percent of global wheat production is lost to pests and disease, the equivalent of 3,500 grain ships. Breeding resistant cultivars is one of the most economical and environmentally friendly ways to address the problem.
The wild relatives of wheat provide a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] GPR141 regulates breast cancer progression via oncogenic mediators and the p-mTOR/p53 axis