(Press-News.org) About half of cigarette smokers and young adult non-smokers think that nicotine-based electronic cigarettes have the same amount or even more harmful chemicals than regular tobacco-based cigarettes, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in Addiction, measured perceived levels of harmful chemicals in e-cigarettes compared with cigarettes using national samples of more than 1,000 adults ages 18 and older who smoke cigarettes and 1,000-plus adults ages 18 to 29 who are nonsmokers. The study also measured associations with e-cigarette/cigarette relative harm perceptions, e-cigarette use and interest. About 20 percent of all participants believed e-cigarettes contain fewer harmful chemicals than cigarettes, while about 30 percent responded that they did not know how the levels compared.
“Our results were interesting to see given that previous review reports suggest e-cigarettes expose users to fewer types and lower levels of harmful and potentially harmful chemicals than cigarettes,” said Olivia Wackowski of Rutgers Center for Tobacco Studies, an associate professor at the Rutgers School of Public Health and lead researcher of the study. “It was also interesting to find that only about half of adult smokers who thought e-cigarettes have fewer harmful chemicals also thought e-cigarettes are less harmful to health.”
E-cigarette harm perception relative to typical cigarettes is a common question included on major national health and tobacco surveys in the United States. However, surveys of e-cigarettes typically haven’t included a question about the perceived exposure to or level of harmful chemicals in e-cigarettes relative to cigarettes.
According to the study researchers, measuring perceptions of e-cigarette and cigarette chemical exposure is important because e-cigarette communications often directly refer to chemicals in some way, which may impact perceptions about chemicals and harms from using e-cigarettes compared to cigarettes.
The study also found an interest in e-cigarette use was significantly higher among those who perceive them to have fewer harmful chemicals than traditional cigarettes and to be less harmful.
Other authors of the study include Michelle T. Bover Manderski, Stefanie K. Gratale and Caitlin V. Weiger of the Rutgers Center for Tobacco Studies as well as Richard J. O’Connor of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R37CA222002. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
END
Few adult smokers and nonsmokers think e-cigarettes have lower levels of harmful chemicals than cigarettes
Perception is associated with interest and likelihood of using electronic cigarettes
2023-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Capturing transporter structure paves the way for drug development
2023-05-23
(Memphis, Tenn.—May 23, 2023) Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center studied the structure and function of a transporter involved in cancer and immunity. They captured six structures of the transporter, including when it was bound to an inhibitor, providing unprecedented insight into how it works. The findings, published in Cell, have implications for drug development.
Transporters escort substances across the cell membrane so that they can carry out their functions. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is an important signaling molecule that regulates the immune system, blood vessel formation, auditory ...
Did dome-headed dinosaurs sport bristly headgear?
2023-05-23
If you look at enough dinosaur fossils, you'll see that their skulls sport an amazing variety of bony ornaments, ranging from the horns of Triceratops and the mohawk-like crests of hadrosaurs to the bumps and knobs covering the head of Tyrannosaurus rex.
But paleontologists are increasingly finding evidence that dinosaurs had even more elaborate head ornaments not preserved with the fossil skulls — structures made of keratin, the stuff of fingernails, that were likely used as visual signals or semaphores to others of their kind.
A newly described species of dome-headed dinosaur — a pachycephalosaur ...
Lupus Research Alliance and its clinical research affiliate Lupus Therapeutics launch the Lupus Landmark Study to accelerate personalized treatments in lupus
2023-05-23
NEW YORK, NY (May 23) – The Lupus Research Alliance and its clinical research affiliate Lupus Therapeutics today announced the launch of the Lupus Landmark Study, a groundbreaking observational research study to accelerate the development of personalized treatments for people living with lupus. The Lupus Landmark Study, the largest study of its kind in lupus, will prospectively recruit and longitudinally follow 3,500 adults diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The Lupus Landmark Study is a ...
The severity of sleep apnea may be underestimated in Black patients
2023-05-23
Session: C110, Advanced Signal Analysis: New Diagnostics and Physiologic Insights for SDB (sleep-disordered breathing)
Date and Time: 2:15 p.m. ET, Tuesday, May 23, 2023
Location: WEWCC, Room 144 A-C (Street Level)
ATS 2023, Washington, DC – Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) tests may underestimate the severity of OSA in Black patients, according to research published at the ATS 2023 International Conference.
Recent research with ICU patients during the COVID-19 pandemic showed that pulse oximeters—clip-like devices that are attached to a fingertip to measure blood oxygen ...
Strategic city planning can help reduce urban heat island effect
2023-05-23
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The tendency of cities to trap heat — a phenomenon called the “urban heat island,” often referred to as the UHI effect — can lead to dangerous temperatures in the summer months, but new Penn State research suggests that certain urban factors can reduce this effect.
The study found that trees had a cooling effect on outdoor air temperature, mean radiant temperature and predicted mean vote index, a measurement designed to evaluate thermal comfort levels.
Additionally, the researchers determined that higher building-height-to-street-width ratios — when taller ...
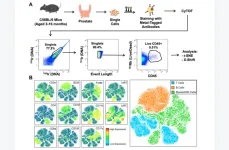
The aging mouse prostate: kinetics of lymphocyte infiltration
2023-05-23
“This dataset presents the most comprehensive profiling of the aging adult mouse prostate immune profile to date.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 23, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 9, entitled, “Highly multiplexed immune profiling throughout adulthood reveals kinetics of lymphocyte infiltration in the aging mouse prostate.”
Aging is a significant risk factor for disease in several tissues, including the prostate. Defining the kinetics ...
Organizations must go beyond medical views on menopause to support women’s professional aspirations - study
2023-05-23
Organisations must enable mid-life women to thrive in the workplace by taking inspiration from societies such as China and Japan to encourage positive conversations around the impact of menopause, a new study reveals.
But as they support older women in pursuing their ambitions and accessing career opportunities, organisations must ensure they do not hinder career progression through overlooked promotions, undervalued work, and lost opportunities.
In Western countries, the menopause is traditionally viewed as a managed medical condition that creates physiological challenges which women must overcome if they are to function as effectively in the workplace ...
Insomnia drug class may not influence death and exacerbation risks among patients with COPD
2023-05-23
Session: C98, Risky Business: Predicting Consequences of OSA
Date and Time: 2:51 p.m. ET, Tuesday, May 23, 2023
Location: Marriott Marquis Washington, Independence Ballroom, Salons E-H (Level M4)
ATS 2023, Washington, DC – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients newly prescribed non-benzodiazepine benzodiazepine receptor agonists (NBZRAs) such as zolpidem (Ambien, Intermezzo and other brands), a class of hypnotic drugs prescribed for insomnia, did not have an increased risk of exacerbations requiring hospitalizations or of death than those prescribed ...
Researchers treat depression by reversing brain signals traveling the wrong way
2023-05-23
Powerful magnetic pulses applied to the scalp to stimulate the brain can bring fast relief to many severely depressed patients for whom standard treatments have failed. Yet it’s been a mystery exactly how transcranial magnetic stimulation, as the treatment is known, changes the brain to dissipate depression. Now, research led by Stanford Medicine scientists has found that the treatment works by reversing the direction of abnormal brain signals.
The findings also suggest that backward streams of neural activity between key areas of the brain could be used as a biomarker to help diagnose depression.
“The leading ...
Strategic habitat restoration can generate a win-win for forests and farmers
2023-05-23
Carefully planned restoration of agricultural coffee landscapes can increase both farmers’ profit and forest cover over a 40-year period, according to a study publishing May 23rd in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Dr. Sofía López-Cubillos at the University of Queensland in Australia, and colleagues.
Restoring patches of natural vegetation in agricultural land presents a trade-off for farmers: while the lost cropland can reduce profitability, increases in ecosystem services like pollination can improve crop yield. To investigate how conservation priorities can be balanced with economic needs, researchers developed a novel planning framework to model the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
[Press-News.org] Few adult smokers and nonsmokers think e-cigarettes have lower levels of harmful chemicals than cigarettesPerception is associated with interest and likelihood of using electronic cigarettes