(Press-News.org) ABSTRACT: 7003
Treatment with luspatercept improved red blood cell counts and erythroid responses compared to treatment with epoetin alfa in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), allowing the majority to no longer require regular blood transfusions. Results from the Phase III COMMANDS trial, led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, were reported at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting.
The study evaluated the efficacy and safety of first-line treatment with luspatercept, which enhances red blood cell maturation, compared with epoetin alfa, a therapy commonly used for low blood cell count, in transfusion-dependent patients with anemia due to very low- to intermediate-risk MDS.
In this interim analysis, 58.5% of patients receiving luspatercept achieved the primary endpoint of independence from red blood cell transfusions compared to 31.2% of patients who received epoetin alfa. Within the first 24 weeks of treatment transfusion, 47.6% of luspatercept patients achieved transfusion independence versus 29.2% of patients receiving epoetin alfa. Additionally, 74.1% of patients who received luspatercept saw hematologic improvement in erythroid responses greater than eight weeks, compared to 51.3% of patients who received epoetin alfa.
“Patients with myelodysplastic syndromes often experience anemia that requires frequent red blood cell transfusions,” said Guillermo Garcia-Manero, M.D., professor of Leukemia and lead investigator of the study. “In this study, we observed a significant improvement in patient red blood cell counts with luspatercept, representing a promising advance to enhance the lives of these patients.”
Myelodysplastic syndromes are a group of diseases in which the bone marrow doesn’t produce enough healthy blood cells, including red blood cells. Patients with MDS often experience symptoms such as anemia, fatigue, shortness of breath and increased vulnerability to infection.
Because of the frequency of anemia, most patients require regular red blood cell transfusions. Some cases of MDS can progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Luspatercept is a novel agent that enables late-stage red blood cell maturation. By targeting the TGF-β signaling pathway, luspatercept helps restore normal red blood cell creation.
The trial enrolled 301 patients at 226 sites. Patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous luspatercept every three weeks or subcutaneous epoetin alfa weekly for 24 weeks. Patient characteristics were balanced across both treatment arms.
Treatment-related adverse events of all grades occurred in 30.3% of patients in the luspatercept group and 17.6% in the epoetin alfa group. Eight patients (4.5%) that received luspatercept discontinued treatment due to treatment-related adverse events. AML progression was reported in four patients receiving luspatercept and five patients receiving epoetin alfa. The safety profile was consistent with previous studies of the drug.
“These results show, for the first time, superior effectiveness of an innovative therapy over epoetin alfa,” Garcia-Manero said. “I am encouraged by these results, as luspatercept represents a transformative therapy that could become a new standard of care for patients with transfusion-dependent myelodysplastic syndromes.”
The patients in this study continue to be followed long term to determine overall survival, time of transfusion independence and frequency of progression to AML.
The study was funded by Bristol Myers Squibb. Garcia-Manero has worked in a consulting/advisory role for and received research support from Bristol Myers Squibb. A full list of co-authors and disclosures can be found here.
END
ASCO: Luspatercept enables majority of patients with MDS to end reliance on blood transfusions
MD Anderson-led COMMANDS trial showed improved red blood cell counts and erythroid responses in transfusion-dependent patients
2023-05-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASCO23: ‘Better sexual health for female patients on endocrine therapy: Strategies across the age spectrum’
2023-05-25
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Strictly EMBARGOED Until May 25, 2023, at 5 P.M. EDT) – Breast cancer treatments that can save a woman’s life can seriously harm her sexual health, says Dr. Kristin E. Rojas, a breast cancer surgeon at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. Although doctors have not historically been prepared to help patients manage these toxic side effects, Rojas is leading efforts to turn the tide.
Rojas, both a fellowship-trained breast surgical oncologist and a gynecologic surgeon, is a national leader in treating sexual dysfunction in female ...
ASCO23: ‘Safety & efficacy of the novel BRAF inhibitor FORE8394 in patients with advanced solid & CNS tumors’
2023-05-25
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL MAY 25, 2023, AT 5 P.M. ET) – An early-phase study led by researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine along with other Cancer Centers, suggests that an experimental therapy may have promising results in treating cancers with BRAF gene alterations – including certain mutations not previously targeted by BRAF inhibitors.
The Phase 1/2a study looking at safety and dosing enrolled 113 patients and targeted a wide range of cancers, including high-grade glioma, low-grade glioma, colorectal cancer, papillary thyroid cancer, melanoma, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights: ASCO 2023 Special Edition
2023-05-25
CHICAGO ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
This special edition features presentations by MD Anderson researchers at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting. In addition to these studies, forthcoming press releases will highlight groundbreaking clinical research, including Phase III trial results evaluating ...
Penn Medicine at the 2023 ASCO Annual Meeting
2023-05-25
CHICAGO – Researchers from the Abramson Cancer Center and Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania will present data on the latest advances in clinical cancer research at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting from June 2-6 in Chicago, Illinois. Follow us on Twitter @PennMDForum and @PennCancer for updates.
Expert Interviews
Experts from the Perelman School of Medicine are available to comment on a wide range of topics in cancer science and medicine during the meeting on site and by video call, telephone, or email. To arrange interviews, please contact Meagan Raeke at Meagan.Raeke@pennmedicine.upenn.edu ...
Internal job candidates have a leg up
2023-05-25
AUSTIN, Texas – Internal job candidates have an advantage over external candidates, because they tend to work harder shortly before a hiring decision, according to new research from The University of Texas at Austin. This is true even when an internal candidate’s skills are inferior.
Eric Chan, assistant professor of accounting at the McCombs School of Business, found that when a new job is on the line, employees will exert more effort to increase their chances of promotion — especially right before the decision. And managers are more likely ...
C. difficile, emerging pathogens, genomics, and antimicrobial resistance
2023-05-25
A new study published in the peer-reviewed OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology identified genes for virulence and antimicrobial resistance in two bacteria that co-occur with C. difficile, suggesting these pathogens as emerging potential threats in planetary health. Click here to read the article now.
Thokur Sreepathy Murali, PhD, Ankit Singh Tanwar, Padival Shruptha and colleagues from Manipal Academy of Higher Education, India, and co-author Angela Brand, MD, PhD, MPH from Maastricht University, The Netherlands, performed comparative genome analyses of three Clostridia species, ...
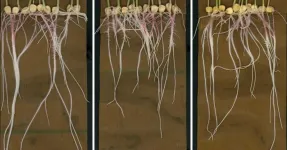
Groundbreaking images of root chemicals offer new insights on plant growth
2023-05-25
On a sunny springtime stroll through a park, it’s easy to ignore the parts of plants that are hidden from view. Plant biologists see things differently. They look below the surface where plant roots are organized in elaborate systems that are critical to the organism’s development. Intricately organized tree root systems, for example, can span as far underground as the tree grows high above the soil.
Applying an advanced imaging technology to plant roots, researchers at the University of California San Diego and Stanford University ...
LJI-led team wins top Nucleate honors for virus vaccine development proposal
2023-05-25
LA JOLLA, CA—A San Diego team, led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI), has won the top prizes in the Nucleate Activator competition. Out of 1,000 initial competitors, the LJI team advanced to the final four teams and swept all the prizes they entered for. Their winning research proposal outlines how scientists could stop dengue virus and Zika virus by developing sophisticated vaccines that activate both B cells and T cells.
Nucleate is a student-led, non-profit organization dedicated to empowering early-stage, ...
Hydrogen battery: Storing hydrogen in coal may help power clean energy economy
2023-05-25
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The quest to develop hydrogen as a clean energy source that could curb our dependence on fossil fuels may lead to an unexpected place — coal. A team of Penn State scientists found that coal may represent a potential way to store hydrogen gas, much like batteries store energy for future use, addressing a major hurdle in developing a clean energy supply chain.
“We found that coal can be this geological hydrogen battery,” said Shimin Liu, associate professor of energy and mineral engineering at Penn State. “You could inject and store the hydrogen energy and have it there when you need to use it.”
Hydrogen ...
Artificial muscle fibers could serve as cell scaffolds
2023-05-25
In two new studies, North Carolina State University researchers designed and tested a series of textile fibers that can change shape and generate force like a muscle. In the first study, the researchers focused on the materials’ influence on artificial muscles’ strength and contraction length. The findings could help researchers tailor the fibers for different applications.
In the second, proof-of-concept study, the researchers tested their fibers as scaffolds for live cells. Their findings suggest the fibers – known as “fiber robots” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] ASCO: Luspatercept enables majority of patients with MDS to end reliance on blood transfusionsMD Anderson-led COMMANDS trial showed improved red blood cell counts and erythroid responses in transfusion-dependent patients