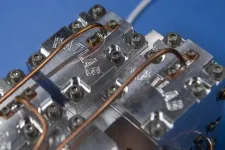
(Press-News.org) The U.S. Army has awarded more than $5.7 million for two projects led by Michael Hatridge, associate professor of physics and astronomy in the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences. Both projects bring together a diverse group of researchers to overcome roadblocks in the field of quantum computing.
A four-year, $2.67 million grant is aimed at the next generation of modular quantum computing systems. Hatridge and co-principal investigators Robert Schoelkopf of Yale University have each developed unique methods to link qubits over long ranges.
With the help of Alex Jones, professor in the Swanson School of Engineering and co-principal investigator on the grant, they hope to bring these methods together, operating in tandem, to develop a new kind of quantum computing system. Jones will explore the best ways to leverage the unique properties of each method using the modular quantum computing system developed in Hatridge’s and Schoelkopf’s labs.
Once complete, the team will have developed new hardware approaches to designing superconducting quantum computers with powerful processors that bring the field a step closer to error-detected operations, or the ability to solve problems consistently and accurately.
The Army has also awarded Hatridge’s amplifier a four-year, $3.03 million grant for projects related to both the physics and the fabrication of parametric amplifiers, or “paramps,” which are necessary components of the processors that lie at the heart of quantum computing. The project’s principal investigators include David Pekker, assistant professor of physics in Pitt’s Dietrich School; José Aumentado, a physicist at the National Institute of Standards and Technology; and Hakan Türeci, an engineering professor at Princeton University.
Building paramps that satisfy the needs of these high-tech processors has been a challenge: They need large, instantaneous bandwidths and the ability to process multiple and large signals. Paramps also require must add minimal noise to amplified signals, currently Hatridge’s team’s amplifiers are within a factor of two of the ultimate limit allowed by quantum mechanics.
In the next four years, Hatridge and his team will work to better understand how the rules of physics limit paramps’ performance. The team also aims to develop and produce practical devices to move the field toward the next generation of processors.
END
Army funds two quantum-related projects at Pitt
The two grants for research led by Michael Hatridge total $5.7M
2023-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Emergence of solvated dielectrons observed for the first time
2023-05-26
Solvated dielectrons are the subject of many hypotheses among scientists, but have never been directly observed. They are described as a pair of electrons that is dissolved in liquids such as water or liquid ammonia. To make space for the electrons a cavity forms in the liquid, which the two electrons occupy. An international research team around Dr. Sebastian Hartweg, initially at Synchrotron SOLEIL (France), now at the Institute of Physics at the University of Freiburg and Prof. Dr. Ruth Signorell from ETH Zurich, including scientists ...
Networks in the dog brain
2023-05-26
A study on canine brain networks reveals that during mammalian brain evolution, the role of the cingulate cortex, a bilateral structure located deep in the cerebral cortex, was partly taken over by the lateral frontal lobes, which control problem-solving, task-switching, and goal-directed behavior. The study relies on a new canine resting state fMRI brain atlas, which can aid in the analysis of diseases characterized by dysfunctional integration and communication among brain areas.
Researchers interested in how dogs think can not only deduce it from their behavior, but they can also investigate their brain activity using fMRI (functional ...
Fractons as information storage: Not yet quite tangible, but close
2023-05-26
Excitations in solids can also be represented mathematically as quasiparticles; for example, lattice vibrations that increase with temperature can be well described as phonons. Mathematically, also quasiparticles can be described that have never been observed in a material before. If such "theoretical" quasiparticles have interesting talents, then it is worth taking a closer look. Take fractons, for example.
Perfect storage of information
Fractons are fractions of spin excitations and are not allowed to possess kinetic energy. As a consequence, they are completely stationary and immobile. This makes fractons new candidates for perfectly secure information storage. Especially since ...
Defence lawyers face challenges accessing and reviewing digital evidence, study shows
2023-05-26
Defence lawyers face numerous challenges accessing and reviewing evidence from phones and computers, a new study shows.
Solicitors and barristers have reported their use of digital evidence can be restricted by limited or late access, large volumes of material, and tight turnaround times to secure legal aid funding and choose and instruct independent experts.
The research calls for more clarity and transparency around the collection and analysis of digital evidence and the streamlining of the format and presentation of information.
The current volume and diversity of digital evidence available escalates tensions, delays access to digital ...
Barren habitat for sows leaves imprint on piglets’ brains
2023-05-26
In a new study, researchers from Uppsala University in Sweden, together with colleagues from the University of São Paulo, Brazil, have investigated the impact that a barren living environment for sows leaves on the next generation. The pigs in the study were bred in Brazil and kept according to breeding standards in that country. The sows’ uncomfortable and unstimulating environment brought with it several different types of changes in the epigenome of their offspring.
In many parts of the world, sows are kept confined in concrete stalls while they are pregnant. This is a bad environment for the pigs, both in terms ...
Quantum sensor for a future navigation system tested aboard Royal Navy ship
2023-05-26
A prototype quantum sensor with potential applications in GPS-free navigation, developed at Imperial College London, has been tested in collaboration with the Royal Navy.
The test marks an important step in bringing new quantum technologies out of the lab and into real-world settings.
Many navigation systems today rely on global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), such as GPS, which uses signals from satellites orbiting the Earth. However, GPS navigation is not always accessible, obstacles like tall buildings can easily block the satellite signals, and they are also susceptible ...
Hydrogen sulfide in cancer treatment
2023-05-26
Hydrogen sulfide is usually a highly toxic gas. However, with careful preparation, it can be used to support photothermal therapy (PTT) in treating cancer, as a team of researchers reporting in the journal Angewandte Chemie has recently discovered. As the team reports, an adjuvant releasing hydrogen sulfide causes tumor cells to lose their natural heat protection and thus to become significantly more sensitive to PTT.
Breathing in gaseous hydrogen sulfide usually causes us to suffocate, because the gas suppresses the respiratory chain in the mitochondria, ...
First death in the UK associated with Xylazine
2023-05-26
The death of a 43-year-old male is the first in the UK to be associated with Xylazine and marks the entry of the drug into the UK drug supply.
New research published in the Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine from King’s College London details the death of the man in May 2022 from the effects of Xylazine alongside heroin, fentanyl and cocaine.
Xylazine is a non-opioid sedative, painkiller and muscle relaxant used in veterinary medicine as a tranquiliser for large animals. The drug – known ...
Developing a blueprint for mobile data visualisation
2023-05-26
By Jovina Ang
SMU Office of Research – It is predicted that by 2025, almost three quarters of the internet users in the world will be mobile-only users.
While mobile devices provide ready access to data, there are limitations to how the data can be optimally presented due to the small form factor and limited screen size.
For example, it is a lot easier to show 10,000 data points on a desktop compared to a smartphone, which typically has a screen size of 2.82 inches (71.5 mm) ...
Optimising outcomes for older adults
2023-05-26
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research – The contribution of team members on a research project can get taken for granted, with storied senior leaders gaining most of the attention.
A recent exception is Micah Tan, an associate researcher at the Centre for Research on Successful Ageing (ROSA) at Singapore Management University (SMU). For his collaborative work at ROSA, Tan was recognised with an inaugural 2022 Research Staff Excellence Award.
“Winning the award has given me a strong sense of fulfilment and has inspired me to want to do more, both for the SMU community but also more generally in terms of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
[Press-News.org] Army funds two quantum-related projects at PittThe two grants for research led by Michael Hatridge total $5.7M