(Press-News.org)
A spacecraft can estimate the attitude state by comparing external measurements from attitude sensors with reference information. CubeSats tend to use 4-quadrant analog solar sensors which have the advantages of extremely low power consumption, minimal volume, low complexity, low cost, and high reliability as attitude sensors, considering the limitation of satellite volume and payload. The performance of the sensor can be importantly improved by the calibration procedure and compensation model. However, the various error sources affecting the calibration of the 4-quadrant sun sensor lead to a complicated process of compensation model establishment. Deep learning, which is widely used in the aerospace field in recent years, is able to approximate any continuous function on a bounded closed set, providing new ideas for solving the traditional problem. In a research paper recently published in Space: Science & Technology, authors from Northwestern Polytechnical University, German Aerospace Center, and Dalian University of Technology together propose a method to calibrate sun sensors by deep learning, which not only is able to integrate the influence of various errors but also avoids the need of analyzing and modeling every single error.
Authors first explains the calibration process of sun sensor based on cubic surface fitting. The calibration and testing platform of the sun sensor includes a solar simulation light source, high-precision 2axis turntable, and servo controller. The outputs of the sun sensor are the incidence λ and azimuth υ, whose theoretical values are obtained from the angle of the turntable and actual values are measured by the sun sensor. There are large errors between the theoretical and actual values, up to 3° (see Fig. 6). By substituting the theoretical and actual values into the 3-order surface fitting formula, the cubic surface fitting model are obtained. The output value of the analog sun sensor is corrected by the cubic surface fitting model and the error is effectively reduced (see Fig. 7). However, there’re larger errors close to the edge of FOV (field of view) of the sun sensor.
Then, authors introduce the learning and training of the deep neural network model which approximates the actual error model and is used for error correction. In the calibration experiment of the analog sun sensor, the deep feedforward neural network is selected to fit the error model, where ReLU (linear rectification function) is selected as the activation function, a full connection as the connection mode between 2 adjacent layers, and the mean square error (MSE) as the loss function. The neural network is trained through gradient descent algorithm and the backpropagation algorithm.
Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified using experimental data. In the calibration experiment of an analog sun sensor, the training of the network model is divided into two stages: the dataset is generated by the cubic surface fitting model in the initial training stage while the deep network model adopts the measured data for learning in the final training stage. Besides, learning data are normalized to the magnitude between 0 and 1 via the max–min method. After network learning in the initial stage, the error between the output of the network model and the estimated value of the cubic surface fitting model is concentrated within 0.02°, indicating that the deep network model at this time can better map the cubic surface fitting model. In the final training stage of the feedforward neural network model, the calibration error of the incident angle can reach 0.1° (1σ) and 0.25° (3σ), which greatly improves the calibration effect of the cubic surface fitting model. These results shows that the method can effectively eliminate deterministic errors, including spot distortion and assembly errors.
Article Title: Deep Neural Network-Based 4-Quadrant Analog Sun Sensor Calibration
Journal: Space: Science & Technology
Authors: Qinbo Sun, Jose Luis Redondo Gutierrez, Xiaozhou Yu*
Affiliations: Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China.
Article Link: https://spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/space.0024
END
Being obese significantly increases the chances of also developing mental disorders. This applies to all age groups, with women at higher risk than men for most diseases, as a recent study of the Complexity Science Hub and the Medical University of Vienna shows. The results were published in the specialist journal "Translational Psychiatry".
“We analyzed a population-wide national registry of inpatient hospitalizations in Austria from 1997 to 2014 in order to determine the ...
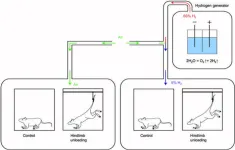
Astronauts are affected by various physical and chemical factors during spaceflight, resulting in a series of pathological and physiological changes. Many studies have shown that spaceflight causes oxidative stress and induces brain disorder in astronauts, negatively affecting neuronal function and brain structure. However, the underlying mechanisms and the countermeasures need to be further explored. Moreover, it is observed that hydrogen has preventative and curative effects on ischemia–reperfusion ...
A team of researchers have confirmed that 107-million-year-old pterosaur bones discovered more than 30 years ago are the oldest of their kind ever found in Australia, providing a rare glimpse into the life of these powerful, flying reptiles that lived among the dinosaurs.
Published in the journal Historical Biology and completed in collaboration with Museums Victoria, the research analysed a partial pelvis bone and a small wing bone discovered by a team led by Museums Victoria Research Institute’s Senior Curator of Vertebrate Palaeontology Dr Tom Rich and Professor Pat Vickers-Rich at Dinosaur Cove in Victoria, Australia in the late 1980s.
The team found the bones belonged ...
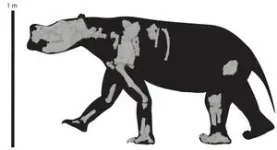
One of Australia’s first long-distance walkers has been described after Flinders University palaeontologists used advanced 3D scans and other technology to take a new look at the partial remains of a 3.5 million year old marsupial from central Australia.
They have named a new genus of diprotodontid Ambulator, meaning walker or wanderer, because the locomotory adaptations of the legs and feet of this quarter-tonne animal would have made it well suited to roam long distances in search of food and ...
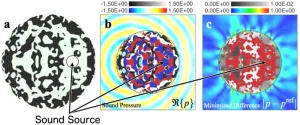
The field of transformation optics has flourished over the past decade, allowing scientists to design metamaterial-based structures that shape and guide the flow of light. One of the most dazzling inventions potentially unlocked by transformation optics is the invisibility cloak — a theoretical fabric that bends incoming light away from the wearer, rendering them invisible. Interestingly, such illusions are not restricted to the manipulations of light alone.
Many of the techniques used in transformation optics have been applied to sound waves, giving rise to the parallel field of transformation acoustics. In fact, researchers ...
When people communicate, speakers and listeners use information shared by both the parties, which is referred to as ‘context.’ It is believed that there are cultural differences in the degree of reliance on this context, with Westerners having a low-context culture, i.e., they speak more directly, and Easterners having a high-context culture, i.e., they are subtle and speak less directly.
Although Chinese are assumed to be in a high-context culture, Yamashina (2018) found that Chinese people are viewed as more direct speakers i.e., low-context cultural communicators ...
Scientists at the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH) are trialling an innovative approach to mitigating climate change and boosting crop yield in mid-Wales. Adding crushed rock dust to farmland has the potential to remove and lock up large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
In the first trial of Enhanced Rock Weathering on upland grasslands in the world, UKCEH scientists have applied 56 tonnes of finely ground basalt rock from quarries to three hectares of farmland in Plynlimon, Powys, this month and are repeating this at the same time next year.
The basalt rock dust particles, which are less than 2mm in size, absorb and store carbon at faster rates ...
A new study from the University of Bergen reveals that including offspring birthweight information from women’s subsequent births, is helpful in identifying a woman's long-term risk of dying from cardiovascular causes.
Knowledge of the association between offspring birthweight and long-term maternal cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality is often based on first-born infants without considering women’s consecutive births.
“These possible relations are also less closely studied among women with term deliveries”, ...
CHICAGO—Researchers will delve into the latest research in diabetes, obesity, reproductive health and other aspects of endocrinology during the Endocrine Society’s ENDO 2023 news conferences June 15-18.
The Society also will share its Hormones and Aging Scientific Statement publicly for the first time during a news conference on Friday, June 16. Reporters will have an opportunity to hear from members of the writing group that drafted the statement on the research landscape.
Other press conferences will feature select abstracts that are being presented at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting. The event is being held at McCormick Place in Chicago, Ill. ...
An artificial intelligence computer program that processes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can accurately identify changes in brain structure that result from repeated head injury, a new study in student athletes shows. These variations have not been captured by other traditional medical images such as computerized tomography (CT) scans. The new technology, researchers say, may help design new diagnostic tools to better understand subtle brain injuries that accumulate over time.
Experts have long known about potential risks of concussion among young athletes, particularly for those who play high-contact sports such as football, hockey, and soccer. Evidence is now mounting ...