(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this study that included 1,979 women indicate that healthy sleep measured prior to SARS-CoV-2 infection, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, may be protective against post–COVID-19 condition (PCC), also known as long COVID. Future research should investigate whether interventions on sleep health may prevent PCC or improve PCC symptoms.
Authors: Siwen Wang, M.D., of the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.15885)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.15885?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=053023
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Sleep health before SARS-CoV-2 infection and risk of long COVID
JAMA Network Open
2023-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Association between heart attack and cognition
2023-05-30
About The Study: In this study of 30,465 adults without myocardial infarction (MI; heart attack), stroke, or dementia, overall, incident MI was not associated with an acute decrease in global cognition, memory, or executive function at the time of the event compared with no MI. The rate of decline in global cognition, memory, and executive function was significantly faster over the years for adults with an MI event compared with those without an MI. These findings suggest that prevention of MI ...
Volunteering, health, and well-being of children and adolescents
2023-05-30
About The Study: Using survey data from across the United States, researchers found that volunteering was associated with higher odds of excellent or very good health and flourishing in children and adolescents, and with lower odds of anxiety in adolescents and behavioral problems in children and adolescents.
Authors: Kevin Lanza, Ph.D., of the Michael & Susan Dell Center for Healthy Living in Austin, Texas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.15980)
Editor’s ...
Use of metabolic and bariatric surgery among youth
2023-05-30
About The Study: Use of and access to metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) have increased among U.S. youth and among most racial and ethnic groups. Compared with 2015-2019, MBS use in youths increased significantly in 2020-2021 during the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic. In contrast, MBS rates in adults decreased in 2020.
Authors: Sarah E. Messiah, Ph.D., of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston School of Public Health—Dallas Campus, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.0803)
Editor’s ...
Racial, ethnic, and language disparities in identifying and mitigating central line–associated bloodstream infections
2023-05-30
About The Study: The results of this study of 8,269 pediatric patients show disparities in central line–associated bloodstream infection rates for Black patients and patients who speak a language other than English that persisted after adjusting for known risk factors, suggesting that systemic racism and bias may play a role in inequitable hospital care for hospital-acquired infections. Stratifying outcomes to assess for disparities prior to quality improvement efforts may inform targeted interventions to improve ...
Philosophy aligns with economics on how to value future generations in climate policy
2023-05-30
A survey of philosophers finds they broadly agree with economists on the best way of valuing the environment of the future in policy decisions made now – although for different reasons.
In a new study published in Nature Climate Change, environmental economists including the University of Exeter’s Professor Ben Groom found consensus between the two academic disciplines over an aspect of climate policy known as the ‘social discount rate’, with philosophers offering support for a rate of 2% - a value predominantly backed by economists, and which is in line with UN climate ...
Researchers proposed a deep neural network-based 4-quadrant analog sun sensor calibration
2023-05-30
A spacecraft can estimate the attitude state by comparing external measurements from attitude sensors with reference information. CubeSats tend to use 4-quadrant analog solar sensors which have the advantages of extremely low power consumption, minimal volume, low complexity, low cost, and high reliability as attitude sensors, considering the limitation of satellite volume and payload. The performance of the sensor can be importantly improved by the calibration procedure and compensation model. However, the various error sources affecting the calibration of the 4-quadrant sun sensor lead to a complicated ...
Obesity increases risk of mental disorders throughout life
2023-05-30
Being obese significantly increases the chances of also developing mental disorders. This applies to all age groups, with women at higher risk than men for most diseases, as a recent study of the Complexity Science Hub and the Medical University of Vienna shows. The results were published in the specialist journal "Translational Psychiatry".
“We analyzed a population-wide national registry of inpatient hospitalizations in Austria from 1997 to 2014 in order to determine the ...
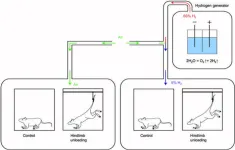
Researchers confirm the protective effect of hydrogen inhalation on declining brain function under hindlimb unloading conditions and disclose the underlying mechanism
2023-05-30
Astronauts are affected by various physical and chemical factors during spaceflight, resulting in a series of pathological and physiological changes. Many studies have shown that spaceflight causes oxidative stress and induces brain disorder in astronauts, negatively affecting neuronal function and brain structure. However, the underlying mechanisms and the countermeasures need to be further explored. Moreover, it is observed that hydrogen has preventative and curative effects on ischemia–reperfusion ...
Study finds 107-million-year-old pterosaur bones are oldest in Australia
2023-05-30
A team of researchers have confirmed that 107-million-year-old pterosaur bones discovered more than 30 years ago are the oldest of their kind ever found in Australia, providing a rare glimpse into the life of these powerful, flying reptiles that lived among the dinosaurs.
Published in the journal Historical Biology and completed in collaboration with Museums Victoria, the research analysed a partial pelvis bone and a small wing bone discovered by a team led by Museums Victoria Research Institute’s Senior Curator of Vertebrate Palaeontology Dr Tom Rich and Professor Pat Vickers-Rich at Dinosaur Cove in Victoria, Australia in the late 1980s.
The team found the bones belonged ...
Quarter-ton marsupial roamed long distances across Australia’s arid interior
2023-05-30
One of Australia’s first long-distance walkers has been described after Flinders University palaeontologists used advanced 3D scans and other technology to take a new look at the partial remains of a 3.5 million year old marsupial from central Australia.
They have named a new genus of diprotodontid Ambulator, meaning walker or wanderer, because the locomotory adaptations of the legs and feet of this quarter-tonne animal would have made it well suited to roam long distances in search of food and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
[Press-News.org] Sleep health before SARS-CoV-2 infection and risk of long COVIDJAMA Network Open