(Press-News.org) Two Southwest Research Institute scientists were part of a James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) team that observed a towering plume of water vapor more than 6,000 miles long — roughly the distance from the U.S. to Japan — spewing from the surface of Saturn’s moon, Enceladus. In light of this NASA JWST Cycle 1 discovery, SwRI’s Dr. Christopher Glein also received a Cycle 2 allocation to study the plume as well as key chemical compounds on the surface, to better understand the potential habitability of this ocean world.
During its 13-year reconnaissance of the Saturn system, the Cassini spacecraft discovered that Enceladus has a subsurface ocean of liquid water, and Cassini analyzed samples as plumes of ice grains and water vapor erupted into space from cracks in the moon’s icy surface.
“Enceladus is one of the most dynamic objects in the solar system and is a prime target in humanity’s search for life beyond Earth,” said Glein, a leading expert in extraterrestrial oceanography. He is a co-author of a paper recently accepted by Nature Astronomy. “In the years since NASA’s Cassini spacecraft first looked at Enceladus, we never cease to be amazed by what we find is happening on this extraordinary moon.”
Once again, the latest observations made with Webb’s Near InfraRed Spectrograph have yielded remarkable results.
“When I was looking at the data, at first, I was thinking I had to be wrong, it was just so shocking to map a plume more than 20 times the diameter of the moon,” said Geronimo Villanueva of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and lead author of the recent paper. “The plume extends far beyond what we could have imagined.”
Webb’s sensitivity reveals a new story about Enceladus and how it feeds the water supply for the entire system of Saturn and its rings. As Enceladus whips around the gas giant in just 33 hours, the moon spews water, leaving a halo, almost like a donut, in its wake. The plume is not only huge, but the water spreads across Saturn’s dense E-ring. JWST data indicate that roughly 30 percent of the water stays in the moon’s wake, while the other 70 percent escapes to supply the rest of the Saturnian system.
“The Webb observations, for the first time, are visually illustrating how the moon's water vapor plumes are playing a role in the formation of the torus,” said SwRI’s Dr. Silvia Protopapa, an expert in the compositional analysis of icy bodies in the solar system who was also on the Cycle 1 team. “This serves as a stunning testament to Webb's extraordinary abilities. I'm thrilled to be part of the Cycle 2 team as we initiate our search for new indications of habitability and plume activity on Enceladus.”
Spurred by the incredible findings from Webb’s first fleeting glimpse of Enceladus, Glein is leading the same team that will observe Enceladus again with JWST in the next year.
“We will search for specific indicators of habitability, such as organic signatures and hydrogen peroxide,” Glein said. “Hydrogen peroxide is particularly interesting because it can provide much more potent sources of metabolic energy than what we previously identified. Cassini didn't give us a clear answer on the availability of such strong oxidants on Enceladus.”
The new observations will provide the best remote opportunity to search for habitability indicators on the surface, by boosting the signal-to-noise ratio by up to a factor of 10 compared with Cycle 1. Understanding the time variability of plume outgassing is also important to plan for future planetary science missions that target the plume.
“Webb can serve as a bridge between Cassini and the proposed search-for-life mission, Orbilander,” Glein said. “After Cycle 2, we will have a better idea if ocean samples are widely distributed over Enceladus’s surface, as opposed to just near the south pole. These next observations could help us determine if Orbilander can access ocean samples near the equator, which may help us get back to Enceladus sooner.”
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world's premier space science observatory. Webb will solve mysteries in our solar system, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency). The team’s results were accepted for publication on May 17, 2023, in Nature Astronomy, and a pre-print pdf is available at https://psg.gsfc.nasa.gov/apps/Enceladus_JWST.pdf.
END
Webb Telescope finds towering plume of water escaping from Saturn moon
SwRI scientist awarded JWST Cycle 2 observations of Enceladus
2023-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ghahari studying correlated and topological phases in Graphene Van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures
2023-05-30
Fereshte Ghahari Kermani, Assistant Professor, Physics and Astronomy, received funding for the project: "Local Probe of Correlated and topological phases in graphene Van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures."
These heterostructures are constructed by different two-dimensional (2D) monolayers vertically stacked and weakly coupled by van der Waals interactions. Such interactions take place when adjacent atoms come close enough that their outer electron clouds barely touch. This action induces charge fluctuations that result in nonspecific, nondirectional attraction.
For this project, Ghahari will ...
A telescope’s last view
2023-05-30
More than 5,000 planets are confirmed to exist beyond our solar system. Over half were discovered by NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope, a resilient observatory that far outlasted its original planned mission. Over nine and a half years, the spacecraft trailed the Earth, scanning the skies for periodic dips in starlight that could signal the presence of a planet crossing in front of its star.
In its last days, the telescope kept recording the brightness of stars as it was running out of fuel. On Oct. 30, 2018, its fuel tanks depleted, the ...
An algorithm for sharper protein films
2023-05-30
Proteins are biological molecules that perform almost all biochemical tasks in all forms of life. In doing so, the tiny structures perform ultra-fast movements. In order to investigate these dynamic processes more precisely than before, researchers have developed a new algorithm that can be used to evaluate measurements at X-ray free-electron lasers such as the SwissFEL more efficiently. They have now presented it in the journal Structural Dynamics.
Sometimes, when using the navigation system while travelling by car, the device will locate you off the road for a short time. This is due to the inaccuracy ...
4,000-year-old plague DNA found – the oldest cases to date in Britain
2023-05-30
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified three 4,000-year-old British cases of Yersinia pestis, the bacteria causing the plague – the oldest evidence of the plague in Britain to date, reported in a paper published today in Nature Communications.
Working with the University of Oxford, the Levens Local History Group and the Wells and Mendip Museum, the team identified two cases of Yersinia pestis in human remains found in a mass burial in Charterhouse Warren in Somerset and one in a ring cairn monument in Levens in Cumbria.
They took small skeletal samples from 34 individuals across the ...
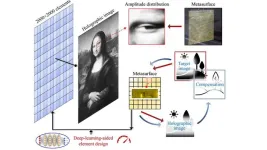
The making of a Mona Lisa hologram
2023-05-30
WASHINGTON, May 30, 2023 – Holograms are often displayed in science fiction as colorful, life-sized projections. But what seems like the technology of the future is actually the technology of the present, and now it has been used to recreate the Mona Lisa.
In Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Tianjin University, the Beijing Institute of Technology, Rowan University, the University of Missouri, Qingdao University, Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, and Beijing Jiaotong University developed an acoustic metasurface-based holography technique that uses a deep learning algorithm to generate and iteratively ...
How insects track odors by navigating microscale winds
2023-05-30
WASHINGTON, May 30, 2023 -- How do flying insects like important pollinators locate odor sources in the great outdoors, despite encountering highly variable wind conditions? They use odor plumes — which travel like smoke and form when the wind blows odor molecules from their source — to track down sources such as flowers or pheromones.
But wind tunnels are typically unable to replicate realistic outdoor wind conditions. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, University of Nevada at Reno researchers decided to explore microscale wind conditions in various outdoor environments to better understand what flying insects might experience while tracking odor plumes.
Authors ...
Sleep health before SARS-CoV-2 infection and risk of long COVID
2023-05-30
About The Study: The findings of this study that included 1,979 women indicate that healthy sleep measured prior to SARS-CoV-2 infection, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, may be protective against post–COVID-19 condition (PCC), also known as long COVID. Future research should investigate whether interventions on sleep health may prevent PCC or improve PCC symptoms.
Authors: Siwen Wang, M.D., of the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Association between heart attack and cognition
2023-05-30
About The Study: In this study of 30,465 adults without myocardial infarction (MI; heart attack), stroke, or dementia, overall, incident MI was not associated with an acute decrease in global cognition, memory, or executive function at the time of the event compared with no MI. The rate of decline in global cognition, memory, and executive function was significantly faster over the years for adults with an MI event compared with those without an MI. These findings suggest that prevention of MI ...
Volunteering, health, and well-being of children and adolescents
2023-05-30
About The Study: Using survey data from across the United States, researchers found that volunteering was associated with higher odds of excellent or very good health and flourishing in children and adolescents, and with lower odds of anxiety in adolescents and behavioral problems in children and adolescents.
Authors: Kevin Lanza, Ph.D., of the Michael & Susan Dell Center for Healthy Living in Austin, Texas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.15980)
Editor’s ...
Use of metabolic and bariatric surgery among youth
2023-05-30
About The Study: Use of and access to metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) have increased among U.S. youth and among most racial and ethnic groups. Compared with 2015-2019, MBS use in youths increased significantly in 2020-2021 during the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic. In contrast, MBS rates in adults decreased in 2020.
Authors: Sarah E. Messiah, Ph.D., of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston School of Public Health—Dallas Campus, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.0803)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
[Press-News.org] Webb Telescope finds towering plume of water escaping from Saturn moonSwRI scientist awarded JWST Cycle 2 observations of Enceladus