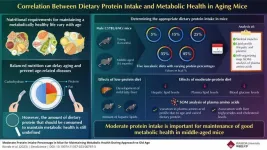
As the proverb “You are what you eat” goes, the type of food we consume influences our health and longevity all through our lives. In fact, there is a direct association between age-related nutritional requirements and metabolic health. Optimal nutrition according to age can help maintain metabolic health, thereby improving the health span (period of life without diseases) and lifespan of an individual. Different nutritional interventions involving varied calorie and protein intake have been known to improve the health and lifespan of rodents and primates. Furthermore, recent studies have also reported the association of dietary macronutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, fats) with cardio-metabolic health and aging in mice. However, the amount of protein that must be consumed to maintain metabolic health is not known.
In a new study published in GeroScience on April 28, 2023, a team of researchers led by Assistant Professor Yoshitaka Kondo from Waseda University, Japan, investigated the amount of dietary protein needed to improve metabolic health in mice approaching old age. The team, which also included Dr. Takuya Chiba, Faculty of Human Sciences, Waseda University, Dr. Akihito Ishigami, Molecular Regulation of Aging, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Geriatrics and Gerontology, Dr. Hitoshi Aoki, Research and Development Division, Nichirei Foods Inc, and Dr. Shin-Ichiro Takahashi, Department of Animal Sciences and Applied Biological Chemistry, Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences, University of Tokyo. They recruited young (6 months old) and middle-aged (16 months old) male C57BL/6NCr mice who were fed isocaloric diets with varying protein content (5 to 45 %) for two months. After two months, the effect of varying protein diets was assessed based on measurements of skeletal muscle weight, liver and plasma lipid profiles, and self‑organizing map (SOM) cluster analysis of plasma amino acid profiles.
When asked about the motivation behind their study, Kondo explains, “The optimal balance of macronutrients for ideal health outcomes may vary across different life stages. Previous studies show the possibility of minimizing age-specific mortality throughout life by changing the ratio of dietary protein to carbohydrates during approach to old age in mice. However, the amount of protein that should be consumed to maintain metabolic health while approaching old age is still unclear.”
The team observed that the consumption of a low-protein diet led to the development of mild fatty liver, with increased levels of hepatic lipids in middle-aged mice as compared to young mice. In contrast, a moderate-protein diet led to reduced blood glucose concentrations and lipid levels in both liver and plasma. These findings indicate that a moderate-protein diet (25% and 35%) kept both young and middle-aged mice metabolically healthier.
On examining the effect of varying protein diets on plasma amino acid concentrations in mice of both age groups, the researchers observed that the plasma concentration of individual amino acids varied with age and varying dietary protein content. This was further validated using SOM analysis of the plasma amino acids. Furthermore, the plasma amino acid profiles revealed using SOM analysis showed the correlation between different protein intake and the varying amounts of hepatic triglycerides and cholesterol levels.
Discussing the impact of their study on public health, Kondo remarks, “Protein requirements change through the course of life, being higher in younger reproductive mice, reducing through middle age, and rising again in older mice as protein efficiency declines. The same pattern is likely to be observed in humans. Therefore, it could be assumed that increasing daily protein intake in meals could promote metabolic health of people. Moreover, ideal dietary macronutrient balance at each life stage could also extend health span.”
In conclusion, a balanced diet with moderate amounts of protein could be the key to a long and healthy life.
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-023-00797-3
Authors:
Yoshitaka Kondo1,5, Hitoshi Aoki2, Masato Masuda3, Hiroki Nishi3, Yoshihiro Noda4, Fumihiko Hakuno3, Shin‑Ichiro Takahashi3, Takuya Chiba5, Akihito Ishigami1
Affiliations:
1 Molecular Regulation of Aging, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology, Japan
2 Research and Development Division, Nichirei Foods Inc, Japan
3 Department of Animal Sciences and Applied Biological Chemistry, University of Tokyo, Japan
4 Department of Animal Facility, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology, Japan
5 Biomedical Gerontology Laboratory, Faculty of Human Sciences, Waseda University, Japan
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. The University has produced many changemakers in its history, including nine prime ministers and many leaders in business, science and technology, literature, sports, and film. Waseda has strong collaborations with overseas research institutions and is committed to advancing cutting-edge research and developing leaders who can contribute to the resolution of complex, global social issues. The University has set a target of achieving a zero-carbon campus by 2032, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015.
To learn more about Waseda University, visit https://www.waseda.jp/top/en
About Professor Yoshitaka Kondo from Waseda University
Dr. Yoshitaka Kondo is an assistant professor at the Faculty of Human Sciences, School of Human Sciences, Waseda University. His research focuses on nutrition, functional foods, calorie restriction, aging, lifespan, and healthy longevity. In particular, he explores the areas of metabolism and endocrinology, functional biochemistry, nutrition and health science, food sciences, pharmaceutical hygiene, biochemistry, and experimental pathology. Assistant Prof. Kondo has published many research papers in reputable journals, with a significant presence in the global research community. He is a member of multiple professional research bodies and has been recognized for his scientific contributions through multiple awards from various research forums.
Funding information
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 22K05482 (Kondo Y), 19H04043 (Ishigami A), 22H03547 (Ishigami A), and the Core-to-Core Program A.A. Advanced Research Networks JPHSCCA2021007 from JSPS and R&D matching funds on the field for Knowledge Integration and Innovation from Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution, NARO, Moonshot Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Research and Development Program from BRAIN, ID#20350956 (Takahashi S-I).
END