(Press-News.org)
Thursday 1st June: Dr Philip Cardiff, Associate Professor at University College Dublin's School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, has received a European Research Council (ERC) Consolidator grant of €2 million for his 5-year project XenoSim. With the support of this award, Dr Cardiff will develop advanced computational techniques that can provide unprecedented insights into the cutting-edge realm of pig-to-human heart transplants
ERC Consolidator Grants are awarded to help excellent scientists, who have 7-12 years’ experience after their PhDs, to pursue their most promising ideas. Worth €657 million in total, the grants will create around 1950 jobs for postdoctoral fellows, PhD students, and other staff at host institutions around Europe
President of the ERC Professor Maria Leptin said: “ERC Consolidator grants support researchers at a crucial time of their careers, strengthening their independence, reinforcing their teams and helping them establish themselves as leaders in their fields. And this backing above all gives them a chance to pursue their scientific dreams.”
A funded investigator in the national Advanced Manufacturing Centre I-Form and Director of the Bekaert University Technology Centre at University College Dublin, Dr Cardiff said: “We stand on the threshold of a groundbreaking medical era where pig-to-human heart transplants are becoming a reality. From an engineering standpoint, pig hearts share similarities with their human counterparts in terms of ‘pump design’; however, their distinct size, shape, and functional characteristics introduce important differences that can impact their performance within the human body.”
“With the support of this ERC Consolidator grant, we aim to unlock invaluable insights into these differences by developing advanced biomechanical computational models. This pioneering research promises to offer not only unprecedented insights into the cutting-edge realm of cardiac xenotransplantation but also to establish pioneering computational techniques with significant implications for a wide range of scientific disciplines.”
The Project
Xenotransplantation has long been a dream for clinicians and now, due to rapid progress in gene editing, is becoming a reality. To overcome immediate rejection, barriers of immunity and infection have to be overcome, but achieving long-term success requires a deep understanding of the physiological and mechanical challenges introduced by the anatomically dissimilar xenotransplants.
‘XenoSim: Providing Computational Insights into Cardiac Xenotransplantation’, aims to address these challenges by providing fundamental clinical insights into the nascent field of cardiac xenotransplantation through the development and application of novel high-resolution, higher-order, multiphysics simulation methods. Tremendous progress has been made in biomedical imaging, nonetheless, a multitude of physical phenomena relevant to xenotransplantation are not available for experimental observation.
In-silico studies are uniquely placed to provide insights into the haemodynamic disruption caused by replacing a human heart with an anatomically dissimilar one. XenoSim is targeting the establishment of the first family of porcine cardiac xenotransplant models that can provide clinically significant insights into the haemodynamic compatibility of porcine donor hearts, the impact of surgical approach, and the consequence of pathologies.
To provide these novel insights requires new coupled simulation approaches. Accordingly, the project aims to create a new class of monolithic finite volume fluid-electrosolid interaction methods, which can provide predictions in clinically relevant timescales through the exploitation of hybrid CPU-GPU systems. XenoSim will establish the new field of computational cardiac xenotransplantation. Furthermore, the novel numerical methods established by XENOSIM are expected to impact a broad range of fields well beyond the project end.
The XenoSim team will employ three Postdoctoral researchers, three PhD students and one Research Assistant.
Learn more about the ERC Consolidator grants and recipients here.
END
Brussels, 1 June 2023 – Today, the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) is excited to share the publication of the first consensus paper by the SISAQOL-IMI Consortium1. The paper provides an overview of the stakeholders’ views on the need for SISAQOL-IMI and the agreed priority set of patient-reported outcome (PRO) objectives that the Consortium will produce international consensus-based recommendations on.
The Setting International Standards in Analysing ...
New Curtin University research has identified the most carbon-rich soils in Australia are in areas that are most threatened by human activities and climate change, including Eucalypt and mangrove forests, and woodland and grassland areas that cover large parts of the country’s interior.
Lead researcher Dr Lewis Walden from Curtin’s Soil & Landscape Science in the School of Molecular and Life Sciences said the findings highlighted the need to protect key terrestrial and coastal marine ecosystems, which play an important contributing role in national strategies to mitigate climate change.
“Using multiscale machine ...
For Embargoed Release: June 1, 2023 at 9:00 am Eastern Time USA
Media Contacts: Kathy Fackelmann, kfackelmann@gwu.edu
WASHINGTON (June 1, 2023)—While ingestible video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, the capsules have been limited by the fact that they could not be controlled by physicians. They moved passively, driven only by gravity and the natural movement of the body. Now, according to a first-of-its-kind research study at George Washington University, physicians can remotely drive a miniature video ...
PHILADELPHIA, UNITED STATES & HANOI, VIETNAM [June 1, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—a not-for-profit alliance of leading cancer centers in the United States—today announced the signing of a Memo of Understanding (MOU) with Vietnam National Cancer Hospital (“K Hospital”) and the Vietnam Cancer Association to work together to improve standards for cancer care throughout the country. Five delegates from NCCN visited Hanoi May 24-26 to sign the MOU and pilot the creation of NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Vietnam.
“We are honored to collaborate with in-country experts to develop and validate Vietnamese harmonizations ...
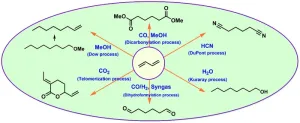
The use of 1,3-butadiene as a cheap and abundant raw material for new applications has attracted more interest in recent decades, specifically in the chemical industry. The review covers several important homogeneously catalyzed processes and technologies that are currently used or have the potential to produce fine and bulk chemicals from 1,3-butadiene. This article focuses specifically on the application of homogeneous catalysts and presents representative examples for the readers. For example, palladium-catalyzed telomerization of 1,3-butadiene offers versatile platform chemicals for ...
PULLMAN, Wash. — Tick season is here, along with the increased danger of Lyme disease, and it turns out the tiny arachnids are even tougher than scientists previously thought.
A recent study in Ecological Monographs shows blacklegged ticks (Ixodes scapularis) are actually really good at surviving extreme cold and heat in nature. Previous lab research suggests that even short periods of especially warm or cold conditions should easily kill ticks, but the Washington State University-led analysis reveals this is only the case for larval ticks in the environment. Instead, ...
The coexistence of wildlife and agricultural practices has long posed challenges for wildlife conservation, especially when conflicts arise. Livestock predation is a prime example of such conflicts, requiring effective management strategies that minimize human-wildlife conflict while preserving valuable agricultural resources. A new study published in PeerJ Life & Environment, titled "Integrating Robotics into Wildlife Conservation: Testing Improvements to Predator Deterrents through Movement," explores the integration of robotics and agricultural ...
EMBARGOED by Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, until June 1, 2023, 7 a.m., ET.
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
(Boston)—Alzheimer disease (AD), the most common neurodegenerative disorder in the world, affects individuals of all races and ethnicities; however, most genetic research for AD has been performed on individuals of European ancestry (EA) with a limited number of large-scale genetic studies in other populations.
For many centuries, Ashkenazi Jews lived in communities in Eastern Europe and were genetically isolated from their non-Jewish neighbors. As a result, ...
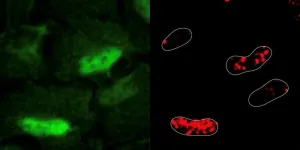
In crisis, the nucleus calls antioxidant enzymes to the rescue. The nucleus being metabolically active is a profound paradigm shift with implications for cancer research.
Summary points
The human nucleus is metabolically active, according to the findings of a new study in Molecular Systems Biology by researchers at the CRG in Barcelona and CeMM/Medical University of Vienna,
In a state of crisis, such as widespread DNA damage, the nucleus protects itself by appropriates mitochondrial machinery to carry out urgent repairs that threaten the genome’s integrity
The ...
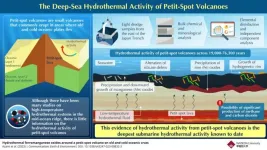
Underwater volcanism on the Earth's crust are active contributors of many different elements to the oceanic environment. Hence, they play an important role in biogeochemical and chemosynthetic cycles of the ocean. Although there have been many studies on high-temperature hydrothermal systems in the mid-ocean ridge—a series of underwater volcanoes that trace the edges of the different oceanic plates—there is little information on low-temperature hydrothermal systems in other volcanoes, such as "petit-spot" volcanoes.
Petit-spot volcanoes are small volcanoes ...