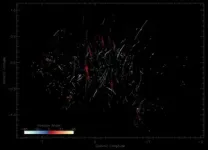
(Press-News.org) New radio telescope images reveal hundreds of filaments along the galactic plane, each measuring 5 to 10 light-years in length
These structures likely originated a few million years ago when outflow from our supermassive black hole interacted with surrounding materials
Researcher: ‘I was actually stunned when I saw these’
EVANSTON, Ill. — An international team of astrophysicists has discovered something wholly new, hidden in the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
In the early 1980s, Northwestern University’s Farhad Yusef-Zadeh discovered gigantic, one-dimensional filaments dangling vertically near Sagittarius A*, our galaxy’s central supermassive black hole. Now, Yusef-Zadeh and his collaborators have discovered a new population of filaments — but these threads are much shorter and lie horizontally or radially, spreading out like spokes on a wheel from the black hole.
Although the two populations of filaments share several similarities, Yusef-Zadeh assumes they have different origins. While the vertical filaments sweep through the galaxy, towering up to 150 light-years high, the horizontal filaments look more like the dots and dashes of Morse code, punctuating only one side of Sagittarius A*.
The study will be published on Friday (June 2) in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
“It was a surprise to suddenly find a new population of structures that seem to be pointing in the direction of the black hole,” Yusef-Zadeh said. “I was actually stunned when I saw these. We had to do a lot of work to establish that we weren’t fooling ourselves. And we found that these filaments are not random but appear to be tied to the outflow of our black hole. By studying them, we could learn more about the black hole’s spin and accretion disk orientation. It is satisfying when one finds order in a middle of a chaotic field of the nucleus of our galaxy.”
An expert in radio astronomy, Yusef-Zadeh is a professor of physics and astronomy at Northwestern’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and member of CIERA.
Decades in the making
The new discovery may come as a surprise, but Yusef-Zadeh is no stranger to uncovering mysteries at the center of our galaxy, located 25,000 light-years from Earth. The latest study builds on four decades of his research. After first discovering the vertical filaments in 1984 with Mark Morris and Don Chance, Yusef-Zadeh along with Ian Heywood and their collaborators later uncovered two gigantic radio-emitting bubbles near Sagittarius A*. Then, in a series of publications in 2022, Yusef-Zadeh (in collaborations with Heywood, Richard Arent and Mark Wardle) revealed nearly 1,000 vertical filaments, which appeared in pairs and clusters, often stacked equally spaced or side by side like strings on a harp.
Yusef-Zadeh credits the flood of new discoveries to enhanced radio astronomy technology, particularly the South African Radio Astronomy Observatory’s (SARAO) MeerKAT telescope. To pinpoint the filaments, Yusef-Zadeh’s team used a technique to remove the background and smooth the noise from MeerKAT images in order to isolate the filaments from surrounding structures.
“The new MeerKAT observations have been a game changer,” he said. “The advancement of technology and dedicated observing time have given us new information. It’s really a technical achievement from radio astronomers.”
Horizontal vs. vertical
After studying the vertical filaments for decades, Yusef-Zadeh was shocked to uncover their horizontal counterparts, which he estimates are about 6 million years old. “We have always been thinking about vertical filaments and their origin,” he said. “I’m used to them being vertical. I never considered there might be others along the plane.”
While both populations comprise one-dimensional filaments that can be viewed with radio waves and appear to be tied to activities in the galactic center, the similarities end there.
The vertical filaments are perpendicular to the galactic plane; the horizontal filaments are parallel to the plane but point radially toward the center of the galaxy where the black hole lies. The vertical filaments are magnetic and relativistic; the horizontal filaments appear to emit thermal radiation. The vertical filaments encompass particles moving at speeds near the speed of light; the horizontal filaments appear to accelerate thermal material in a molecular cloud. There are several hundred vertical filaments and just a few hundred horizontal filaments. And the vertical filaments, which measure up to 150 light-years high, far surpass the size of the horizontal filaments, which measure just 5 to 10 light-years in length. The vertical filaments also adorn space around the nucleus of the galaxy; the horizontal filaments appear to spread out to only one side, pointing toward the black hole.
“One of the most important implications of radial outflow that we have detected is the orientation of the accretion disk and the jet-driven outflow from Sagittarius A* along the galactic plane,” Yusef-Zadeh said.
‘Our work is never complete’
The new discovery is filled with unknowns, and Yusef-Zadeh’s work to unravel its mysteries has just begun. For now, he can only consider a plausible explanation about the new population’s mechanisms and origins.
“We think they must have originated with some kind of outflow from an activity that happened a few million years ago,” Yusef-Zadeh said. “It seems to be the result of an interaction of that outflowing material with objects near it. Our work is never complete. We always need to make new observations and continually challenge our ideas and tighten up our analysis.”
The study, “The population of the galactic center filaments: Position angle distribution reveal a degree-scale collimated outflow from Sgr A* along the galactic plane,” was supported by NASA (award number 80GSFC21M0002). The SARAO is a facility of the National Research Foundation, an agency of the Department of Science and Innovation.
END
A study involving UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers found when ribociclib, a targeted therapy drug, is added to hormone therapy there are a significant invasive disease-free survival benefit in patients with early hormone-receptor (HR) positive/HER2 negative breast cancer.
Researchers found that patients who took the combination therapy had substantially longer invasive disease-free survival compared to those who were treated with the hormone therapy alone, regardless of whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The addition of the targeted therapy reduced the risk of recurrence by 25%.
The results were shared today during the American Society of Clinical ...
The world is getting hotter, causing shifts in seasonal patterns and increasing the amount of extreme weather such as severe droughts and heat waves, which can affect crop yields and food supplies. A recent study led by a researcher at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University found that the likelihood of extreme temperatures that could affect crop yields has increased significantly in wheat-producing regions of the U.S. and China.
The findings predict heat waves that happened approximately ...
New theoretical research by Michael Wondrak, Walter van Suijlekom and Heino Falcke of Radboud University has shown that Stephen Hawking was right about black holes, although not completely. Due to Hawking radiation, black holes will eventually evaporate, but the event horizon is not as crucial as had been believed. Gravity and the curvature of spacetime cause this radiation too. This means that all large objects in the universe, like the remnants of stars, will eventually evaporate.
Using a clever combination of quantum physics and Einstein’s theory of gravity, Stephen Hawking argued that the spontaneous creation and annihilation ...
Human activity has degraded ecosystems and damaged biodiversity around the world, but ecosystem restoration offers hope for the future. Scientists studying the restoration of underwater seaweed forests which provide other species with food and shelter have found that 10 years of restoration efforts have helped a damaged forest regrow to richness and strength comparable to forests that have never been disturbed.
“Macroalgal forests are found along over one-third of the world’s coastlines and underpin ...
Green hydrogen, which produces hydrogen without the use of fossil fuels or the emission of carbon dioxide, has become increasingly important in recent years as part of efforts to realize a decarbonized economy. However, due to the high production cost of water electrolysis devices that produce green hydrogen, the economic feasibility of green hydrogen has not been very high. However, the development of a technology that drastically reduces the amount of rare metals such as iridium and platinum used in polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis devices is opening the way to lower production costs.
A research team led by Dr. Hyun S. Park and Sung Jong ...
Sarcomas
Dr. Jonathan C. Trent, a medical oncologist specializing in Sarcoma and Connective Tissue Medical Oncology at Sylvester, is available to discuss a wide range of issues related to Sarcoma research and experimental therapeutics. He and collaborators are involved in multiple ASCO23 presentations, including:
Multi-omic characterization of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) in a large real-world patient cohort.
Outcomes in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor who did not have ...
Adolescents who show signs of alcohol dependence are more likely to develop depression by their mid-20s, according to a new study led by UCL (University College London) and University of Bristol researchers.
Drinking large amounts of alcohol regularly, but with no signs of dependency, did not predict depression risk, according to the findings published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Co-lead author Dr Gemma Lewis (UCL Psychiatry) said: “By using a large, longitudinal dataset, we have found evidence that problematic drinking patterns in late adolescence may increase the risk of developing ...
The UK’s growing mismatch between the fish we catch and the fish we want to eat has clear implications for our future food security, according to new research.
Led by the University of Essex and the Centre for Environment Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (Cefas), the study, published in the international peer-reviewed journal Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, for the first time offers a comprehensive, long-term analysis of how major policy changes in the past 120 years have influenced patterns in UK seafood production, trade and consumption.
It shows that even if we changed our fish-eating habits away from choosing flaky white fish such as cod ...
A new study of 3,745 families from across the UK demonstrates a “sizeable” gap in the financial knowledge of children depending on which socio-economic group they come from.
The research highlights significant inequalities in young people’s financial capabilities, with the results pointing toward disadvantaged children not developing key financial skills.
In findings published in the peer-reviewed British Journal of Educational Studies, an expert team from UCL are calling for a greater emphasis on developing financial skills amongst children starting at primary school, particularly aimed towards those from disadvantaged social backgrounds, with “a particular need ...
DOWNLOADABLE B-ROLL/VIDEO
MIAMI, FLORIDA (June 1, 2023) – Historically, surgery was the first line of treatment for patients with thyroid cancer. Now, as targeted therapies and other new medications emerge, surgery for certain patients may become more of a secondary option if those treatments fail. This new context could potentially change how some procedures are conducted.
Otolaryngologist and head and neck surgeon Dr. Zoukaa Sargi, will join a June 2 panel discussion on thyroid cancer care ...