(Press-News.org) Contrary to expectations, the risk for relapses, overdoses and deaths related to substance use disorder didn’t increase after a large-scale prison release in New Jersey, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in JAMA Health Forum, examined whether post-release overdose deaths and drug-related hospital and emergency department visits increased after more than 2,000 individuals were released from prison in late 2020 as the result of a pandemic-era policy.
“Risk of relapse and adverse health events is high following prison release, with risk of fatal overdose as much as 129 times greater in the two weeks post-release than in the general population,” said Peter Treitler, a research project manager at the Center for Health Services Research at the Rutgers Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research (IFH) and lead author of the study.
In November 2020, New Jersey enacted the Public Health Emergency Credit Act to reduce COVID-19 transmission among people in state prisons. The legislation resulted in the release of more than 2,000 individuals in one day. The large-scale release posed concerns regarding the capacity of reentry services and a potential increased risk for relapse or drug overdose for individuals with substance use disorders, according to researchers.
The researchers analyzed prison releases among incarcerated individuals with substance use disorders in New Jersey from 2019 to 2020 and examined hospital and death records within 45 days after their release from prison. They found the risk of overdose or death in individuals with substance use disorder after the mass prison release in 2020 didn’t increase compared with earlier periods of time.
“New Jersey has robust reentry supports for incarcerated people with substance use disorder, which may have lowered post-release risks,” said Treitler. “N.J.’s decarceration experience may provide a model for future policy reform as correctional systems seek to reduce incarceration without increasing health risk.”
Researchers said next steps for further study include assessing outcomes after longer periods of time and examining additional health-related outcomes, such as primary care utilization and adherence to medication treatment for those released on medications for opioid use disorder.
Coauthors of the study include Molly Nowels and Stephen Crystal of IFH; Rusty Reeves and Lisa DeBilio of Rutgers University Correctional Health Care; and Kenneth Feder and Brendan Saloner of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Study funding was provided by Bloomberg Philanthropies, the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
END
Reentry services may help stabilize substance use risks after mass prison release
After the release of more than 2,000 individuals in late 2020, reentry services helped with substance use disorder, Rutgers researchers say
2023-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Memory killer cells can improve survival for melanoma patients
2023-06-02
Our skin contains specialised long-lived killer cells that protect against intruders. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have now identified how these cells are formed, and shown that high levels of memory killer cells in cancer tissue correlate with a better survival rate in people with melanoma. The study is published in the journal Immunity.
Certain immune T cells called tissue-resident memory cells are formed locally in the skin and other tissue, and protect against infections that they have encountered before. Some of ...
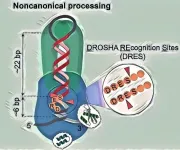
HKUST researchers unveil long-sought noncanonical cleavage mechanism in miRNA biogenesis
2023-06-02
To discover and thoroughly demonstrate the newly identified noncanonical cleavage mechanism, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) research team, led by Prof. Tuan Anh Nguyen, Assistant Professor of the Division of Life Science, used several sophisticated techniques, such as miRNA sequencing, pri-miRNA structure analysis, and high-throughput pri-miRNA cleavage assays for approximately 260,000 pri-miRNA sequences. In contrast to the canonical mechanism, the noncanonical mechanism does not rely on several essential protein and RNA elements ...
Immune system discovery could benefit spinal cord injuries
2023-06-02
New research suggests that the immune system’s ability to respond to spinal cord injuries diminishes with age – and identifies potential avenues to improve that response and help patients heal.
The new findings offer important insights into how the immune system responds to spinal-cord injuries, and why that response becomes blunted with the passing years. Further, it reveals an important role for the membranes surrounding the spinal cord in mounting the immune response to spinal-cord injury. With this information, doctors one day may be able to bolster the body’s natural immune response to improve patient outcomes, particularly among older adults.
“Recently, ...
UTHSC researchers’ work on human pangenome aids understanding of common chromosomal abnormality
2023-06-02
Researchers from the University of Tennessee Health Science Center have made a foundational discovery about chromosome biology through their work on the first-ever human pangenome reference.
Published recently by the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium in the journal Nature, the draft pangenome uses complete genome assemblies to provide a diverse look at the genetic makeup of humans. Researchers in the UTHSC Department of Genetics, Genomics and Informatics created the technical tools to build the pangenome, and then used the tools to understand variation in parts of the genome that could not be seen before.
The pangenome ...
Mysterious dashes revealed in Milky Way’s center
2023-06-02
New radio telescope images reveal hundreds of filaments along the galactic plane, each measuring 5 to 10 light-years in length
These structures likely originated a few million years ago when outflow from our supermassive black hole interacted with surrounding materials
Researcher: ‘I was actually stunned when I saw these’
EVANSTON, Ill. — An international team of astrophysicists has discovered something wholly new, hidden in the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
In the early 1980s, Northwestern University’s Farhad Yusef-Zadeh discovered gigantic, one-dimensional filaments dangling vertically near Sagittarius A*, our ...
ASCO: Adding ribociclib to hormone therapy improves outcomes in patients with early breast cancer
2023-06-02
A study involving UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers found when ribociclib, a targeted therapy drug, is added to hormone therapy there are a significant invasive disease-free survival benefit in patients with early hormone-receptor (HR) positive/HER2 negative breast cancer.
Researchers found that patients who took the combination therapy had substantially longer invasive disease-free survival compared to those who were treated with the hormone therapy alone, regardless of whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The addition of the targeted therapy reduced the risk of recurrence by 25%.
The results were shared today during the American Society of Clinical ...
New research suggests wheat crops may be threatened by unprecedented heat and drought
2023-06-02
The world is getting hotter, causing shifts in seasonal patterns and increasing the amount of extreme weather such as severe droughts and heat waves, which can affect crop yields and food supplies. A recent study led by a researcher at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University found that the likelihood of extreme temperatures that could affect crop yields has increased significantly in wheat-producing regions of the U.S. and China.
The findings predict heat waves that happened approximately ...
Eventually everything will evaporate, not only black holes
2023-06-02
New theoretical research by Michael Wondrak, Walter van Suijlekom and Heino Falcke of Radboud University has shown that Stephen Hawking was right about black holes, although not completely. Due to Hawking radiation, black holes will eventually evaporate, but the event horizon is not as crucial as had been believed. Gravity and the curvature of spacetime cause this radiation too. This means that all large objects in the universe, like the remnants of stars, will eventually evaporate.
Using a clever combination of quantum physics and Einstein’s theory of gravity, Stephen Hawking argued that the spontaneous creation and annihilation ...
Underwater forest's recovery offers hope for marine restoration across the globe
2023-06-02
Human activity has degraded ecosystems and damaged biodiversity around the world, but ecosystem restoration offers hope for the future. Scientists studying the restoration of underwater seaweed forests which provide other species with food and shelter have found that 10 years of restoration efforts have helped a damaged forest regrow to richness and strength comparable to forests that have never been disturbed.
“Macroalgal forests are found along over one-third of the world’s coastlines and underpin ...
Developing technologies to reduce the cost of green hydrogen production
2023-06-02
Green hydrogen, which produces hydrogen without the use of fossil fuels or the emission of carbon dioxide, has become increasingly important in recent years as part of efforts to realize a decarbonized economy. However, due to the high production cost of water electrolysis devices that produce green hydrogen, the economic feasibility of green hydrogen has not been very high. However, the development of a technology that drastically reduces the amount of rare metals such as iridium and platinum used in polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis devices is opening the way to lower production costs.
A research team led by Dr. Hyun S. Park and Sung Jong ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
[Press-News.org] Reentry services may help stabilize substance use risks after mass prison releaseAfter the release of more than 2,000 individuals in late 2020, reentry services helped with substance use disorder, Rutgers researchers say