(Press-News.org) McKinney, TX., June 5, 2023 - The Cure Mito Foundation, a parent-led organization dedicated to advancing research and treatments for Leigh syndrome, has launched the first-of-its-kind online resource about Leigh syndrome, the most common type of pediatric mitochondrial disease.
The free resource, “About Leigh Syndrome” (https://www.aboutleighsyndrome.com), serves as a central place where patients, caregivers and doctors can find information on Leigh syndrome, including its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and more. Translation to multiple languages is available to ensure accessibility for the international community. The site also highlights important initiatives for the entire community, such as Leigh syndrome global patient registry (https://www.curemito.org/leighsyndromeregistry).
The goal and vision behind the project was to create a website that provides accurate and reliable medical content, along with an appealing layout, colorful design, user-friendly features, engaging graphics, and pictures of families and children. It's dedicated to being a platform where individuals can find support, resources, and feel seen (not just as patients, but as people).
The Cure Mito Foundation invited the community to join the effort, which created collaborative work and input from patient families and professionals across multiple specialties.
Dr. Ibrahim Elsharkawi, MD, current metabolism fellow at Harvard Medical School and incoming Assistant Professor at Mt. Sinai, who donated many hours to help review and edit medical information presented in the new resource, said: "I did a dedicated mitochondrial medicine fellowship after my pediatric genetics training in order to learn how to provide a holistic, comprehensive approach to treating patients and helping families touched by mitochondrial disease. It is deeply meaningful to me”, Elsharkawi continued, “to have been able to partner with families and science experts to play a small role in shaping this resource, which will hopefully provide families and patients with information that empowers them when they receive this life altering diagnosis, when things may seem overwhelming and confusing."
Leigh syndrome is a rare and progressive genetic disorder primarily affecting the central nervous system, causing developmental regression and neurological symptoms. While information about Leigh syndrome exists, it is often difficult to find and not presented in a patient-friendly or easily understandable format, making the situation hard for families seeking help, especially when newly diagnosed or shortly after.
Kasey Woleben, Cure Mito co-founder and a mom to Will, who has Leigh syndrome, said: “When my son was diagnosed with Leigh syndrome 9 years ago, I would have loved a resource like this solely dedicated to the disease. Our family didn't have much hope - now we do. We hope that this resource will continue to grow and help many families facing this disease. Having a united Leigh syndrome community is so important for the advancement of research and hopefully a treatment for our children and the future children. We are beyond grateful to all who believe in our vision, partner with us, and support and encourage us on this journey. Together we will change the world. ”
Updates on this and other projects will be shared at the virtual annual Leigh syndrome symposium in September. Please find more information and register at: https://www.curemito.org/conference
About The Cure Mito Foundation:
Cure Mito Foundation is a parent-led 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization founded in 2018 as a Cure SURF1 Foundation by a group of families determined to fight for their children’s lives. In 2021, after successfully blazing the trail for SURF1 gene therapy at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, the mission of the organization expanded and the name was amended. Cure Mito’s mission is to unite the global Leigh syndrome community to accelerate patient-centered research, treatments, and cures. For more information please visit curemito.org, and follow us on LinkedIn | Twitter | Facebook | Instagram.
END
Cure Mito Foundation launches resource on Leigh syndrome
New site, aboutleighsyndrome.com, focuses on most common type of pediatric mitochondrial disease.
2023-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tools to assess crime risk for young cohorts are likely to fail over time if they ignore social change
2023-06-05
Risk assessment instruments (RAIs) are widely used to inform high-stakes decision making in the criminal justice system and other areas, such as health care and child welfare. These tools typically assume a relation between predictors and outcomes that does not vary with time. But because societies change, this assumption may not hold in all settings, generating what a new study calls cohort bias—a bias resulting from cohort-wide influences not experienced by past or future cohorts.
The study, by researchers ...
Direct air capture technology licensed to Knoxville-based Holocene
2023-06-05
An innovative and sustainable chemistry developed at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory for capturing carbon dioxide from air has been licensed to Holocene, a Knoxville-based startup focused on designing and building plants that remove carbon dioxide from atmospheric air.
“ORNL is tackling climate change by developing numerous technologies that reduce or eliminate emissions,” said Susan Hubbard, ORNL deputy for science and technology. “But with billions ...
Fetal exposure to PCBs affects hearing health later in life
2023-06-05
Music, mice, and microscopic imaging combine to provide new insight into the effects of environmental chemicals on hearing loss.
Researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology found that early exposure to an environmental chemical called polychlorinated biphenyls, or PCBs, made it more difficult for mice to recover from sound-related trauma sustained later in life.
Their paper appears in the Journal of Neuroscience.
PCBs are carcinogenic compounds formerly used in industrial and consumer products. Although they were banned in the United States in 1979 and haven’t seen industrial use in decades, their highly ...
Quantum computers are better at guessing, new study demonstrates
2023-06-05
Daniel Lidar, the Viterbi Professor of Engineering at USC and Director of the USC Center for Quantum Information Science & Technology, and first author Dr. Bibek Pokharel, a Research Scientist at IBM Quantum, achieved this quantum speedup advantage in the context of a “bitstring guessing game.” They managed strings up to 26 bits long, significantly larger than previously possible, by effectively suppressing errors typically seen at this scale. (A bit is a binary number that is either zero or one).
Quantum computers promise to solve certain problems with an advantage that increases as the ...
New discoveries about where atherosclerotic plaques rupture can lead to preventive treatments
2023-06-05
A common cause of myocardial infarction and stroke is the rupture of atherosclerotic plaques. The exact location of plaque ruptures has previously been unknown, but now researchers at Lund University have mapped this. The research team has also identified an enzyme, a marker, that they hope will help predict who is at risk of having a myocardial infarction or a stroke due to a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque.
In atherosclerosis , fat is accumulated in the artery walls creating atherosclerotic ...
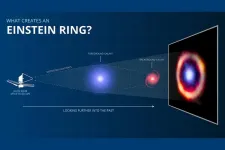
Webb Space Telescope detects universe’s most distant complex organic molecules
2023-06-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers have detected complex organic molecules in a galaxy more than 12 billion light-years away from Earth – the most distant galaxy in which these molecules are now known to exist. Thanks to the capabilities of the recently launched James Webb Space Telescope and careful analyses from the research team, a new study lends critical insight into the complex chemical interactions that occur in the first galaxies in the early universe.
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign astronomy and physics professor Joaquin Vieira and graduate student Kedar Phadke collaborated with researchers at Texas A&M ...
Zoonoses: Welcome to Professor Fernando Rosado Spilki, the new Executive Editor-in-Chief
2023-06-05
As the Co-Editors-in-Chief of Zoonoses, Dr. Lynn Soong (University of Texas Medical Branch, TX, USA) and Dr. Xiaoping Dong (Chinese Center for Disease Control & Prevention, Beijing, China) extend a warm welcome to Dr. Fernando Rosado Spilki, new Executive Editor-in-Chief (Vector Biology/Epidemiology) of Zoonoses.
Dr. Spilki is currently a Professor in the Institute of Health Sciences at Feevale University, Novo Hamburgo, Brazil. He received B.S. in Veterinary Medicine (2001), M.S. in Veterinary Sciences/Animal Virology (2004) both from the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, and his Ph.D. in Genetics & Molecular ...
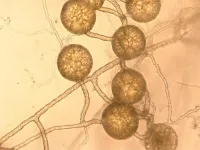
Fungi stores a third of carbon from fossil fuel emissions and could be essential to reaching net zero, new study reveals
2023-06-05
Fungi stores a third of carbon from fossil fuel emissions and could be essential to reaching net zero, new study reveals
Mycorrhizal fungi are responsible for holding up to 36 per cent of yearly global fossil fuel emissions below ground - more than China emits each year
The fungi make up a vast underground network all over the planet underneath grasslands and forests, as well as roads, gardens, and houses on every continent on Earth
It is not only crucial to storing carbon and keeping the planet cooler, but are also essential to global biodiversity
Researchers ...
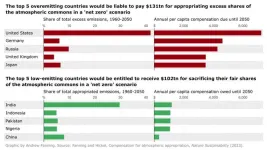
Climate justice: Global North owes $170 trillion for excessive CO2 emissions, says study
2023-06-05
Industrialised nations responsible for excessive levels of carbon dioxide emissions could be liable to pay a total of $170 trillion in compensation or reparations by 2050 to ensure climate change targets are met, say researchers.
This money, which amounts to nearly $6 trillion per year or about 7% of annual global Gross Domestic Product (GDP), would be distributed as compensation to low-emitting countries that must decarbonise their economies far more rapidly than would otherwise be required.
Financial redress for the losses and damages that climate-vulnerable countries face due to the excessive CO2 emissions of others is seen as an increasingly important ...
BRIDGEcereal: Self-teaching web app improves speed, accuracy of classifying DNA variations among cereal varieties
2023-06-05
Kim Kaplan
301-588-5314
Kim.Kaplan@usda.gov
BRIDGEcereal: Self-Teaching Web App Improves Speed, Accuracy of Classifying DNA Variations Among Cereal Varieties
PULLMAN, WA, June 5, 2023—Agricultural Research Service and Washington State University scientists have developed an innovative web app called BRIDGEcereal [https://bridgecereal.scinet.usda.gov/] that can quickly and accurately analyze the vast amount of genomic data now available for cereal crops and organize the material into intuitive charts that identify patterns locating genes of interest.
With the rapid advancements in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Cure Mito Foundation launches resource on Leigh syndromeNew site, aboutleighsyndrome.com, focuses on most common type of pediatric mitochondrial disease.