(Press-News.org) Daniel Lidar, the Viterbi Professor of Engineering at USC and Director of the USC Center for Quantum Information Science & Technology, and first author Dr. Bibek Pokharel, a Research Scientist at IBM Quantum, achieved this quantum speedup advantage in the context of a “bitstring guessing game.” They managed strings up to 26 bits long, significantly larger than previously possible, by effectively suppressing errors typically seen at this scale. (A bit is a binary number that is either zero or one).
Quantum computers promise to solve certain problems with an advantage that increases as the problems increase in complexity. However, they are also highly prone to errors, or noise. The challenge, says Lidar, is “to obtain an advantage in the real world where today’s quantum computers are still ‘noisy.’” This noise-prone condition of current quantum computing is termed the "NISQ" (Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum) era, a term adapted from the RISC architecture used to describe classical computing devices. Thus, any present demonstration of quantum speed advantage necessitates noise reduction.
The more unknown variables a problem has, the harder it usually is for a computer to solve. Scholars can evaluate a computer's performance by playing a type of game with it to see how quickly an algorithm can guess hidden information. For instance, imagine a version of the TV game Jeopardy, where contestants take turns guessing a secret word of known length, one whole word at a time. The host reveals only one correct letter for each guessed word before changing the secret word randomly.
In their study, the researchers replaced words with bitstrings. A classical computer would, on average, require approximately 33 million guesses to correctly identify a 26-bit string. In contrast, a perfectly functioning quantum computer, presenting guesses in quantum superposition, could identify the correct answer in just one guess. This efficiency comes from running a quantum algorithm developed more than 25 years ago by computer scientists Ethan Bernstein and Umesh Vazirani. However, noise can significantly hamper this exponential quantum advantage.
Lidar and Pokharel achieved their quantum speedup by adapting a noise suppression technique called dynamical decoupling. They spent a year experimenting, with Pokharel working as a doctoral candidate under Lidar at USC. Initially, applying dynamical decoupling seemed to degrade performance. However, after numerous refinements, the quantum algorithm functioned as intended. The time to solve problems then grew more slowly than with any classical computer, with the quantum advantage becoming increasingly evident as the problems became more complex.
Lidar notes that “currently, classical computers can still solve the problem faster in absolute terms.” In other words, the reported advantage is measured in terms of the time-scaling it takes to find the solution, not the absolute time. This means that for sufficiently long bitstrings, the quantum solution will eventually be quicker.
The study conclusively demonstrates that with proper error control, quantum computers can execute complete algorithms with better scaling of the time it takes to find the solution than conventional computers, even in the NISQ era.
END
Quantum computers are better at guessing, new study demonstrates
USC researchers leverage techniques to manage error accumulation, demonstrating the potential of quantum computing in the error-prone NISQ era
2023-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New discoveries about where atherosclerotic plaques rupture can lead to preventive treatments
2023-06-05
A common cause of myocardial infarction and stroke is the rupture of atherosclerotic plaques. The exact location of plaque ruptures has previously been unknown, but now researchers at Lund University have mapped this. The research team has also identified an enzyme, a marker, that they hope will help predict who is at risk of having a myocardial infarction or a stroke due to a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque.
In atherosclerosis , fat is accumulated in the artery walls creating atherosclerotic ...
Webb Space Telescope detects universe’s most distant complex organic molecules
2023-06-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers have detected complex organic molecules in a galaxy more than 12 billion light-years away from Earth – the most distant galaxy in which these molecules are now known to exist. Thanks to the capabilities of the recently launched James Webb Space Telescope and careful analyses from the research team, a new study lends critical insight into the complex chemical interactions that occur in the first galaxies in the early universe.
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign astronomy and physics professor Joaquin Vieira and graduate student Kedar Phadke collaborated with researchers at Texas A&M ...
Zoonoses: Welcome to Professor Fernando Rosado Spilki, the new Executive Editor-in-Chief
2023-06-05
As the Co-Editors-in-Chief of Zoonoses, Dr. Lynn Soong (University of Texas Medical Branch, TX, USA) and Dr. Xiaoping Dong (Chinese Center for Disease Control & Prevention, Beijing, China) extend a warm welcome to Dr. Fernando Rosado Spilki, new Executive Editor-in-Chief (Vector Biology/Epidemiology) of Zoonoses.
Dr. Spilki is currently a Professor in the Institute of Health Sciences at Feevale University, Novo Hamburgo, Brazil. He received B.S. in Veterinary Medicine (2001), M.S. in Veterinary Sciences/Animal Virology (2004) both from the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, and his Ph.D. in Genetics & Molecular ...
Fungi stores a third of carbon from fossil fuel emissions and could be essential to reaching net zero, new study reveals
2023-06-05
Fungi stores a third of carbon from fossil fuel emissions and could be essential to reaching net zero, new study reveals
Mycorrhizal fungi are responsible for holding up to 36 per cent of yearly global fossil fuel emissions below ground - more than China emits each year
The fungi make up a vast underground network all over the planet underneath grasslands and forests, as well as roads, gardens, and houses on every continent on Earth
It is not only crucial to storing carbon and keeping the planet cooler, but are also essential to global biodiversity
Researchers ...
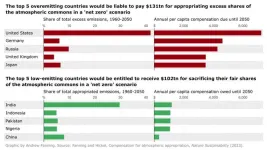
Climate justice: Global North owes $170 trillion for excessive CO2 emissions, says study
2023-06-05
Industrialised nations responsible for excessive levels of carbon dioxide emissions could be liable to pay a total of $170 trillion in compensation or reparations by 2050 to ensure climate change targets are met, say researchers.
This money, which amounts to nearly $6 trillion per year or about 7% of annual global Gross Domestic Product (GDP), would be distributed as compensation to low-emitting countries that must decarbonise their economies far more rapidly than would otherwise be required.
Financial redress for the losses and damages that climate-vulnerable countries face due to the excessive CO2 emissions of others is seen as an increasingly important ...
BRIDGEcereal: Self-teaching web app improves speed, accuracy of classifying DNA variations among cereal varieties
2023-06-05
Kim Kaplan
301-588-5314
Kim.Kaplan@usda.gov
BRIDGEcereal: Self-Teaching Web App Improves Speed, Accuracy of Classifying DNA Variations Among Cereal Varieties
PULLMAN, WA, June 5, 2023—Agricultural Research Service and Washington State University scientists have developed an innovative web app called BRIDGEcereal [https://bridgecereal.scinet.usda.gov/] that can quickly and accurately analyze the vast amount of genomic data now available for cereal crops and organize the material into intuitive charts that identify patterns locating genes of interest.
With the rapid advancements in ...
Availability of LGBTQ mental health services for youth
2023-06-05
About The Study: This survey study found that 28% of youth-serving U.S. mental health facilities offered LGBTQ-specific mental health services in 2020. Although some states had relatively high levels of LGBTQ service availability as a percentage of facilities, many of these states had few facilities available to children per capita. Public mental health facilities were less likely to offer LGBTQ-specific mental health services, a concern given that the cost of care is a barrier to services. The findings suggest a need to expand availability of LGBTQ services ...
Can exercise help counteract genetic risk of disease?
2023-06-05
New research has revealed being active could lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, even in people with a high genetic risk of developing the medical condition.
The University of Sydney-led study found higher levels of total physical activity, especially moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity, had a strong association with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The findings were published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
The researchers say the study demonstrates higher levels of physical activity should be promoted as a major strategy for type 2 diabetes ...
DNA sequencing in newborns reveals years of actionable findings for infants and families
2023-06-05
Researchers who lead the world’s first comprehensive sequencing program for newborn infants have published the next chapter in the ongoing study of the BabySeq Project, with new findings on infants and families who have been followed for 3-5 years. In a study published today in the American Journal of Human Genetics, researchers from Mass General Brigham and Boston Children’s Hospital reported that over 10 percent of the first 159 infants to undergo screening through DNA sequencing were discovered ...
Tirzepatide has unique activity to stimulate insulin secretion
2023-06-05
DURHAM, N.C. – Tirzepatide, a drug approved for diabetes and on the fast track for approval as a weight loss therapy, works through a unique ability to activate two different mechanisms the body uses to control insulin secretion and energy balance, Duke Health researchers report.
The finding, reported June 5 in the journal Nature Metabolism, is the first study to use cells from human donors to demonstrate how tirzepatide stimulates insulin secretion, an important action utilized by this drug to lower blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes.
“Understanding the potential of drugs ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Quantum computers are better at guessing, new study demonstratesUSC researchers leverage techniques to manage error accumulation, demonstrating the potential of quantum computing in the error-prone NISQ era